Luxury car cybersecurity risks 2025? Yeah, it’s a bigger deal than you think. These aren’t your grandpa’s gas guzzlers; today’s luxury rides are basically rolling computers, packed with internet connectivity, sophisticated infotainment systems, and enough data to make your head spin. This means hackers aren’t just after your wallet – they could be after your car, your data, or even your life.
We’re diving deep into the vulnerabilities, the potential attacks, and what the future holds for keeping these high-tech machines safe.
From remote hacking attempts to sneaky insider threats, the risks are diverse and evolving rapidly. We’ll explore the weak points in communication protocols, the dangers of over-the-air updates, and the sensitive personal data these cars collect. Think stolen identities, remote vehicle control, and even the potential for physical harm. We’ll also examine the legal landscape, the latest security tech, and what luxury car manufacturers are doing (or should be doing) to protect their customers.
Connectivity Vulnerabilities in Luxury Cars (2025)
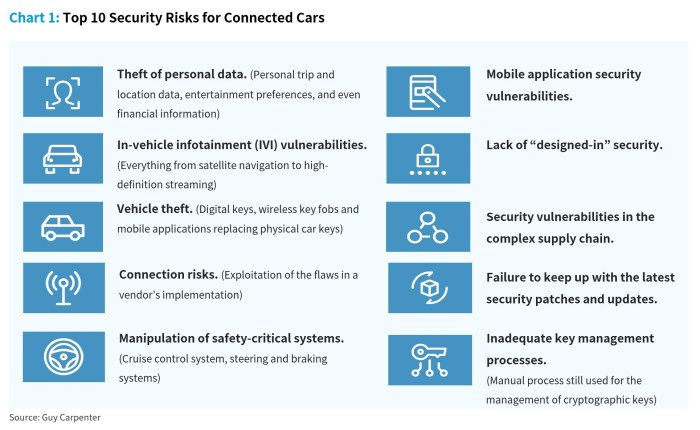
Luxury cars in 2025 will be incredibly connected, relying heavily on networks for everything from entertainment to crucial safety features. This increased connectivity, however, introduces a significant expansion of potential attack surfaces, making cybersecurity a paramount concern. The sophisticated technology designed for convenience and performance also creates opportunities for malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities.
Network Communication Protocols and Security Weaknesses
Modern luxury vehicles utilize a variety of network communication protocols, including CAN (Controller Area Network), LIN (Local Interconnect Network), FlexRay, and Ethernet. These protocols, while efficient for data transfer within the vehicle, often lack robust security features. For example, CAN, a legacy bus system, was not originally designed with security in mind, making it susceptible to manipulation and eavesdropping.
While newer protocols like Ethernet offer more advanced security options, their implementation varies widely across manufacturers, leading to inconsistencies in security levels. This heterogeneity makes it difficult to establish a uniform security standard across the industry. Furthermore, the reliance on wireless communication protocols like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi for infotainment and other features introduces further vulnerabilities. These wireless protocols are often subject to well-known attacks such as man-in-the-middle attacks and denial-of-service attacks.
Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates and Security Risks
OTA updates are a crucial aspect of maintaining the software in modern luxury vehicles. They allow manufacturers to quickly deploy security patches and add new features. However, the very process of OTA updates presents security challenges. If the update mechanism itself is vulnerable, attackers could potentially inject malicious code into the update package, compromising the vehicle’s systems. A compromised update process could lead to a range of issues, from minor malfunctions to complete control of the vehicle.
Ensuring the authenticity and integrity of OTA updates is therefore critical. This requires robust digital signature verification and secure update protocols to prevent unauthorized modifications.
Infotainment System and External Network Vulnerabilities
The infotainment system, often connected to external networks via cellular or Wi-Fi, acts as a gateway to the vehicle’s internal network. A compromised infotainment system can provide attackers with a foothold to access other vehicle systems. For example, malicious apps downloaded from unsecured app stores could potentially exploit vulnerabilities in the infotainment system’s operating system, gaining access to sensitive data or even controlling vehicle functions.
Furthermore, the use of public Wi-Fi networks increases the risk of man-in-the-middle attacks and data breaches. This necessitates the implementation of strong authentication and encryption protocols to protect the communication between the infotainment system and external networks. Regular security updates for the infotainment system’s software are also crucial to mitigate known vulnerabilities.
Cybersecurity Feature Comparison Across Luxury Car Brands
| Brand | Feature | Strength | Weakness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mercedes-Benz | Integrated firewall and intrusion detection system | Provides strong protection against network-based attacks. | Reliance on proprietary systems may limit interoperability and independent security audits. |
| BMW | Regular OTA security updates and strong encryption protocols | Keeps the vehicle software up-to-date and secure. | The effectiveness depends on timely update adoption by the user and the overall security of the OTA update mechanism. |
| Audi | Multi-layered security architecture with access control features | Provides granular control over access to various vehicle systems. | Complexity of the architecture could potentially introduce new vulnerabilities. |
Data Privacy and Security in Luxury Vehicles (2025)
Luxury cars in 2025 will be significantly more connected than their predecessors, integrating advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), infotainment features, and telematics. This increased connectivity, while offering enhanced convenience and performance, also dramatically expands the surface area for potential data breaches and privacy violations. The sheer volume and sensitivity of the data collected pose significant challenges for manufacturers and users alike.
Luxury vehicle systems collect a wide array of sensitive personal data, including precise location data (GPS coordinates, travel patterns), biometric information (fingerprint scans, facial recognition data used for driver identification and personalization), driver behavior data (speed, acceleration, braking habits), communication data (phone calls, text messages, emails accessed through the vehicle’s infotainment system), and potentially even health data (if the car integrates health monitoring features).
A data breach could expose this information to malicious actors, leading to identity theft, stalking, insurance fraud, blackmail, and other serious consequences. The potential for misuse is amplified by the increasing reliance on cloud-based services for data storage and processing.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks Governing Data Privacy in Connected Vehicles (2025)
By 2025, we can expect a more robust and complex legal landscape surrounding data privacy in connected vehicles. Existing regulations like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) will likely be further refined and expanded to specifically address the unique challenges posed by connected car technologies. New regulations might focus on data minimization, purpose limitation, data security standards, and user consent mechanisms.
International harmonization of data privacy laws related to connected cars will remain a significant hurdle, creating complexities for global manufacturers. Expect to see increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies and potentially significant fines for companies failing to comply with these evolving regulations. The automotive industry will likely see the emergence of industry-specific standards and certifications related to data privacy and security, aiming to provide consumers with greater transparency and trust.
Data Encryption and Anonymization Techniques in Luxury Cars
Protecting sensitive data within luxury vehicles will rely heavily on advanced encryption techniques. Data at rest and in transit should be encrypted using robust algorithms to prevent unauthorized access. This includes encryption of data stored on the vehicle’s onboard systems, as well as data transmitted wirelessly to cloud servers or other connected devices. Data anonymization techniques, such as differential privacy and data masking, will play a crucial role in reducing the risk of re-identification of individuals from aggregated data sets.
However, the effectiveness of these techniques will depend on their proper implementation and ongoing monitoring for vulnerabilities. The use of blockchain technology to enhance data security and transparency is also a possibility, though challenges related to scalability and performance will need to be addressed.
Examples of Privacy Violations Resulting from Compromised In-Car Data Systems
Imagine a scenario where a hacker gains access to a luxury vehicle’s data system through a vulnerability in its infotainment system. They could potentially track the vehicle’s location in real-time, potentially leading to stalking or even theft. Access to biometric data could facilitate identity theft, enabling the hacker to impersonate the vehicle’s owner to access financial accounts or other sensitive information.
Compromised driver behavior data could be used to manipulate insurance claims or even target the driver with personalized phishing attacks. A breach exposing communication data could lead to privacy violations related to personal conversations, business dealings, or sensitive medical information if such data is transmitted through the vehicle’s systems. The consequences of such breaches could range from financial losses and reputational damage to significant emotional distress and legal repercussions for both the vehicle owner and the manufacturer.
External Attack Vectors Targeting Luxury Cars (2025)
Luxury vehicles, with their increasing reliance on sophisticated technology and connectivity, represent a growing target for malicious actors. The interconnected nature of modern cars, from their infotainment systems to advanced driver-assistance features, creates numerous vulnerabilities that can be exploited for various nefarious purposes, ranging from data theft to physical harm. Understanding these potential attack vectors is crucial for developing effective security measures.The rise of sophisticated cyberattacks targeting luxury vehicles is a significant concern.
These attacks leverage vulnerabilities in both the vehicle’s internal systems and its external communications to compromise functionality and safety. The increasing connectivity of these vehicles through V2X technology, while offering benefits like improved traffic flow and safety features, also introduces new avenues for exploitation.
Remote Attacks on Luxury Vehicle Systems
Remote attacks, such as hacking and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, can severely compromise a luxury vehicle’s functionality and safety. Hackers could remotely gain control of critical systems, like braking, steering, or acceleration, potentially causing accidents. A DoS attack could disable crucial safety features, leaving the vehicle vulnerable. For instance, a sophisticated attack could exploit a vulnerability in the car’s telematics unit to gain remote access and manipulate engine control modules.
Imagine a scenario where a hacker remotely disables the anti-lock braking system (ABS) during an emergency stop, leading to a potentially catastrophic accident.
Exploiting Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication Vulnerabilities
V2X communication, while designed to enhance safety and efficiency, presents significant security risks if not properly secured. Malicious actors could intercept or manipulate V2X messages to disrupt traffic flow, cause accidents, or even target specific vehicles. For example, a compromised V2X system could send false information about traffic conditions, causing drivers to make unsafe maneuvers. Another scenario could involve a hacker injecting false emergency signals, potentially leading to widespread traffic congestion and panic.
Luxury car cybersecurity is a huge deal in 2025, with hackers potentially targeting everything from braking systems to infotainment. To get a sense of the advanced safety features automakers are implementing to counter these threats, check out this Volvo EX90 safety features review 2025 ; it highlights how manufacturers are trying to stay ahead of the curve. Ultimately, though, the race to secure these increasingly connected vehicles is far from over.
Robust encryption and authentication protocols are essential to mitigate these risks.
Impact of Sophisticated Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks targeting luxury car owners are a significant threat. These attacks could trick owners into revealing sensitive information, such as vehicle identification numbers (VINs), passwords, or access credentials, granting attackers remote access to vehicle systems. A sophisticated phishing campaign could mimic official communications from the car manufacturer or a trusted service provider, making it difficult for unsuspecting owners to identify the scam.
Luxury car cybersecurity risks in 2025 are a serious concern, potentially impacting everything from navigation systems to braking. Think about it – if hackers can remotely control a car’s functions, even something as seemingly simple as finding the right child safety seat installation might be compromised. For example, checking compatibility for a Range Rover Velar, like you would with this guide Child safety seats in Range Rover Velar , could be sabotaged by a malicious actor.
This highlights how far-reaching these cybersecurity threats really are.
Once access is gained, attackers could unlock the vehicle, track its location, or even steal personal data stored within the car’s systems.
Categorization of Potential Attack Vectors by Impact
The following list categorizes potential attack vectors based on their potential impact:
- Data Theft: This includes stealing personal information, navigation data, driving habits, and financial information stored within the vehicle’s systems. This data could be used for identity theft, targeted advertising, or even blackmail.
- System Control: This involves gaining unauthorized control over vehicle systems, such as braking, steering, acceleration, or infotainment functions. This can lead to accidents, vehicle theft, or even ransom demands.
- Physical Harm: This encompasses attacks that directly endanger the occupants’ physical safety, such as remotely disabling safety features or manipulating vehicle controls to cause accidents. This represents the most severe type of attack.
Internal Threats and Insider Risks in Luxury Car Cybersecurity (2025)
The increasing sophistication of luxury car technology, coupled with the interconnected nature of modern vehicles, presents a significant vulnerability to internal threats. Employees with access to sensitive design data, manufacturing processes, or software development, along with compromised supply chains, pose a considerable risk to the cybersecurity of these vehicles. Understanding these internal threats is crucial for mitigating potential damage and maintaining the integrity of luxury car brands.
Internal threats represent a particularly insidious risk because they often leverage existing access and knowledge to bypass traditional security measures. Unlike external attacks that must overcome perimeter defenses, malicious insiders can exploit vulnerabilities from within the system. This makes detecting and preventing these attacks more challenging, demanding a multi-layered security approach encompassing employee vetting, secure software development practices, and robust supply chain management.
Employee Malfeasance and Data Breaches
Employees with access to luxury car design blueprints, manufacturing processes, or software code represent a significant security risk. A disgruntled employee, for instance, could steal intellectual property, sabotage production lines through malware injection into control systems, or introduce vulnerabilities into the vehicle’s software. This could lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and potential legal ramifications for the manufacturer.
The risk is amplified in the context of autonomous driving systems, where compromised software could have severe safety implications. Consider a scenario where a software engineer introduces a backdoor into the autonomous driving software, allowing remote control of a vehicle, potentially causing accidents or enabling theft. The consequences could include significant financial losses from lawsuits, recall costs, and irreparable damage to brand reputation.
Compromised Supply Chain Components
The complex global supply chains involved in luxury car manufacturing create opportunities for malicious actors to introduce compromised components. A seemingly innocuous part, such as a sensor or control unit, could contain malware or hardware backdoors introduced during the manufacturing process. This could allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to the vehicle’s systems, potentially enabling theft, data exfiltration, or even remote control.
Imagine a scenario where a compromised GPS module is installed in several high-end vehicles. This compromised component could subtly transmit location data to malicious actors, potentially leading to vehicle theft or targeted attacks on high-profile owners. The impact could include substantial financial losses due to theft and insurance claims, as well as damage to the brand’s reputation due to compromised customer privacy.
Exploitation of Software Vulnerabilities by Malicious Insiders, Luxury car cybersecurity risks 2025
Malicious insiders with knowledge of the vehicle’s software architecture could exploit vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access or control. This could involve using known vulnerabilities to gain root access, modifying software to introduce backdoors, or even disabling critical safety features. For example, a software developer could introduce a vulnerability that allows remote unlocking of vehicles, potentially leading to widespread theft.
This scenario could result in substantial financial losses due to vehicle theft and insurance claims, alongside damage to brand reputation and potential legal liabilities.
Hypothetical Insider Threat Scenario: The Case of Project Nightingale
Imagine a senior software engineer, “Alex,” working on Project Nightingale, the autonomous driving system for a new luxury SUV. Alex feels overlooked for a promotion and harbors resentment towards the company. Alex leverages their intimate knowledge of the system’s architecture to introduce a backdoor into the software during a late-night coding session. This backdoor allows Alex to remotely control certain vehicle functions, such as braking and steering.
Alex initially uses the backdoor to subtly test their access, but later, driven by anger, remotely disables the autonomous driving system in a test vehicle during a high-profile demonstration, causing a minor accident and significant reputational damage to the company. The consequences include public scrutiny, financial losses from the incident and subsequent investigation, a damaged brand image, and potential legal action.
Mitigation Strategies and Future Trends in Luxury Car Cybersecurity (2025)

The escalating sophistication of cyberattacks targeting luxury vehicles necessitates a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity. By 2025, manufacturers will need to move beyond reactive measures and embrace proactive strategies that leverage advanced technologies and robust security protocols to protect both the vehicle and its occupants. This section explores the key mitigation strategies and future trends shaping the landscape of luxury car cybersecurity.
Hardware-Based Security Solutions
Hardware-based security offers a robust foundation for protecting luxury car systems. This approach focuses on incorporating secure hardware components directly into the vehicle’s architecture, making it more difficult for attackers to compromise the system. Examples include secure microcontrollers with tamper-resistant features, hardware security modules (HSMs) for cryptographic operations, and physically unclonable functions (PUFs) for device authentication. These components can provide strong protection against various attacks, including unauthorized access, data breaches, and firmware manipulation.
The use of hardware root of trust ensures that the system’s integrity is verified at the lowest level, enhancing overall security. For instance, a tamper-evident casing on a critical ECU could visually alert mechanics or technicians to potential tampering.
Software-Based Security Solutions
Software-based solutions complement hardware security by providing an additional layer of defense. These solutions include robust encryption algorithms to protect sensitive data transmitted wirelessly, secure coding practices to minimize vulnerabilities in the vehicle’s software, and intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) to monitor network traffic and identify malicious activity. Regular software updates and patches are crucial to address newly discovered vulnerabilities and enhance the system’s resilience against attacks.
For example, over-the-air (OTA) updates allow for quick deployment of security patches, minimizing the window of vulnerability. Furthermore, the implementation of secure boot processes ensures that only authorized software can be loaded onto the vehicle’s systems.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming cybersecurity by enabling proactive threat detection and response. ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from various vehicle sensors and networks to identify patterns indicative of malicious activity. This allows for the early detection of anomalies and potential attacks, enabling timely mitigation efforts. AI-powered systems can also learn and adapt to evolving attack techniques, improving their effectiveness over time.
For instance, an AI system might detect unusual driving patterns or communication anomalies that could signal a hijacking attempt, alerting the driver and potentially disabling certain vehicle functions.
Proactive Cybersecurity Measures in the Automotive Industry
By 2025, the automotive industry will need to adopt a more proactive approach to cybersecurity. This involves implementing comprehensive security architectures from the design phase, conducting regular security assessments and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities, and establishing robust incident response plans to handle security breaches effectively. Collaboration within the industry, sharing threat intelligence and best practices, is crucial for collective defense.
Furthermore, investment in cybersecurity research and development is essential to stay ahead of evolving threats and develop innovative security solutions. A key example is the increasing adoption of threat intelligence platforms which collate and analyze threat data from various sources, enabling proactive mitigation. This collaborative effort is critical, as single manufacturers are unlikely to anticipate every possible attack vector.
Final Review: Luxury Car Cybersecurity Risks 2025
So, are your luxury wheels safe in 2025? The short answer is: it’s complicated. While the tech is impressive, the security isn’t always keeping pace. The good news is that awareness is growing, and manufacturers are starting to take cybersecurity more seriously. But as these cars become more connected, the stakes only get higher.
Staying informed about the latest threats and pushing for better security practices is crucial – both for the manufacturers and for the drivers who rely on these vehicles every day. It’s a race against the hackers, and the future of luxury car security depends on who wins.









