How to finance a car with bad credit 2025? It’s a question a lot of people are asking, especially with the economy the way it is. Buying a car is a huge decision, and it can feel even tougher when your credit score isn’t exactly stellar. But don’t worry, it’s not impossible! This guide breaks down everything you need to know about getting approved for a car loan even with less-than-perfect credit, from understanding your credit report to negotiating the best loan terms.
We’ll cover different financing options, strategies for improving your credit, and how to avoid predatory lenders. Let’s get you behind the wheel!
This guide will walk you through the entire process, from understanding your credit score and its impact on loan interest rates to exploring various financing options specifically designed for individuals with bad credit. We’ll cover strategies to improve your creditworthiness, tips for negotiating favorable loan terms, and crucial budgeting techniques to ensure you can comfortably manage your car payments. We’ll also discuss how to protect yourself from predatory lenders and explore alternative financing methods such as leasing or buying a used car.
Finally, we’ll provide a clear visual explanation of key loan terms to help you make informed decisions.
Understanding Your Credit Score and its Impact
Your credit score is like a financial report card, summarizing your history of borrowing and repayment. Lenders use it to assess your risk – how likely you are to repay a loan. A higher credit score means you’re seen as a lower risk, leading to better loan terms. Conversely, a lower score can significantly impact your ability to get a car loan and the interest rate you’ll pay.Understanding the factors that influence your credit score is crucial for securing the best possible car loan.
Your payment history is the most important factor, accounting for roughly 35% of your score. Late or missed payments significantly damage your score. Amounts owed (30%) reflects how much debt you carry relative to your available credit. Length of credit history (15%) considers how long you’ve had credit accounts open. New credit (10%) impacts your score when you open many new accounts in a short period.
Finally, credit mix (10%) refers to the variety of credit accounts you have (credit cards, loans, etc.).
Credit Score Ranges and Loan Options
Credit scores typically range from 300 to 850, with higher scores indicating better creditworthiness. Different score ranges generally correlate with different loan options and interest rates. Individuals with scores above 750 (excellent credit) usually qualify for the lowest interest rates and best loan terms. Those with scores between 700-749 (good credit) often still receive favorable terms, though potentially with slightly higher rates.
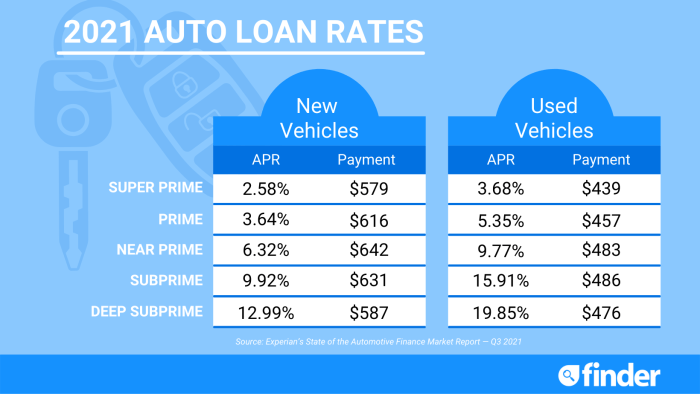
People with scores between 650-699 (fair credit) might find it more challenging to secure a loan, possibly facing higher interest rates and stricter requirements. Those with scores below 650 (poor credit) may struggle to obtain financing through traditional lenders and might need to explore alternative options like buy-here-pay-here dealerships, which often come with significantly higher interest rates. For example, someone with excellent credit might qualify for a 3% interest rate on a car loan, while someone with poor credit might face an interest rate exceeding 15%.
Obtaining and Understanding Your Credit Report
You are entitled to a free credit report from each of the three major credit bureaus – Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion – once a year through AnnualCreditReport.com. This is the official source; be wary of sites that charge for this service. The process involves providing personal information to verify your identity. Once you receive your report, review it carefully.
It will detail your credit history, including accounts you’ve opened, balances, payment history, and any inquiries made by lenders. Look for any inaccuracies or errors; if you find any, dispute them immediately with the credit bureau. Understanding your report empowers you to take steps to improve your credit score and ultimately secure a more favorable car loan.
For instance, if you notice a late payment that was actually made on time, you can contact the credit bureau to correct the error. This correction can significantly improve your credit score.
Exploring Financing Options for Bad Credit
Securing a car loan with less-than-perfect credit can feel daunting, but it’s definitely achievable. Several financing options cater specifically to individuals with bad credit, each with its own set of pros and cons. Understanding these differences is key to finding the best fit for your financial situation. This section will explore the major options available, helping you navigate the process and make informed decisions.
Secured Loans
Secured loans require collateral, meaning you pledge an asset (like a savings account or another vehicle) to guarantee the loan. If you default, the lender can seize the collateral. This reduces the risk for the lender, making it easier to qualify even with bad credit. However, the risk of losing your collateral is significant. The interest rates on secured loans are typically lower than unsecured options because of the reduced risk for the lender.
For example, someone might use a savings account as collateral to secure a lower interest rate on an auto loan.
Subprime Loans
Subprime loans are specifically designed for borrowers with poor credit scores. These loans come with higher interest rates and potentially stricter terms than loans offered to individuals with good credit. Lenders understand the increased risk involved, and that’s reflected in the cost. While the interest rates are higher, subprime loans provide an avenue for car ownership that might otherwise be unavailable.
A common example would be a loan offered through a credit union that specializes in working with borrowers who have experienced past financial difficulties.
Buy-Here-Pay-Here Dealerships
Buy-here-pay-here (BHPH) dealerships offer financing directly through their dealership. This can be a convenient option for those struggling to get approved elsewhere, as they often have less stringent credit requirements. However, BHPH loans typically carry extremely high interest rates and may include additional fees. It’s crucial to carefully review all terms and conditions before agreeing to a BHPH loan.
So, you’re trying to figure out how to finance a car with bad credit in 2025? That can be tough, but securing a loan is often easier if you have good insurance. Check out this comparison of USAA vs Progressive for military families in 2025 to see which might offer better rates, potentially impacting your loan approval.
Lower premiums could improve your financial picture, making it easier to get that car loan you need.
For instance, a BHPH dealership might offer a loan with a very high APR and a short repayment period, making it difficult to manage.
Examples of Lenders Specializing in Bad Credit Auto Loans
Finding a lender willing to work with bad credit requires research. Many lenders specialize in this area, but it’s essential to compare offers carefully. Interest rates, loan terms, and additional fees can vary significantly.
| Lender Name | Interest Rate Range | Loan Term Options | Special Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Credit Union (Example: Local Credit Union) | Varies greatly depending on credit score and loan amount; often higher than prime loans. | 12-72 months | Membership requirements may apply. May require a larger down payment. |
| Online Lender (Example: LendingTree) | Varies significantly based on credit score and market conditions; generally higher than prime loans. | 24-84 months | Requires thorough application process; may request additional documentation. |
| Subprime Auto Lender (Example: Carvana) | Typically high, reflecting the higher risk; exact range varies greatly. | 36-72 months | May require a larger down payment or proof of income. |
| Buy-Here-Pay-Here Dealership (Example: Local BHPH Dealership) | Very high, often exceeding 20%; varies widely. | Often shorter terms (12-36 months) | Often requires a large down payment; may involve additional fees. |
Improving Your Creditworthiness
Getting approved for a car loan with bad credit is tough, but it’s not impossible. Improving your credit score takes time and effort, but the rewards are significant. By focusing on a few key areas, you can significantly boost your creditworthiness and qualify for better loan terms in the near future. This section Artikels a plan to help you achieve this goal.
A solid credit repair strategy involves consistent effort across multiple fronts. It’s not a quick fix, but a gradual process of rebuilding your financial reputation. Remember, patience and persistence are key. Small, consistent improvements over time will yield much better results than sporadic bursts of activity.
Credit Score Improvement Plan
This plan Artikels concrete steps and timelines for improving your credit score. It’s crucial to remember that the exact timeframe depends on your individual circumstances and the severity of your credit issues. However, consistent application of these steps will lead to noticeable progress.
- Months 1-3: Address Immediate Issues. This phase focuses on resolving any immediate problems impacting your score, such as late payments or collections. Contact creditors to negotiate payment plans and work towards settling any outstanding debts. Begin monitoring your credit report regularly for accuracy.
- Months 4-6: Debt Reduction Strategy. Implement a debt reduction plan, prioritizing high-interest debts. Consider methods like the debt snowball or debt avalanche methods. Track your progress meticulously and celebrate small victories to stay motivated. For example, if you have $5,000 in credit card debt, aim to pay an extra $100-$200 each month beyond the minimum payment.
- Months 7-12: Responsible Credit Card Use. Maintain a low credit utilization ratio (the amount of credit used compared to your total available credit). Aim for under 30%, ideally under 10%. Pay your credit card bills on time, every time. Consider closing unnecessary credit cards, as having too many open accounts can sometimes negatively impact your score.
- Months 13-18: Continue Good Habits. Continue practicing responsible financial behavior. Monitor your credit report and score regularly. Consider adding a secured credit card if you don’t already have one to help build credit history. A secured credit card requires a security deposit that acts as your credit limit. This helps build your credit responsibly.
So, you’re trying to figure out how to finance a car with bad credit in 2025? That’s tough, but definitely doable. A big factor is insurance, and knowing the Texas minimum liability coverage cost 2025 will help you budget. Understanding those costs will help you better manage your overall car expenses and potentially secure a loan.
Ultimately, planning ahead with insurance is key to successfully financing a car, even with less-than-perfect credit.
Strategies for Debt Reduction and Credit Card Management
Effectively managing debt and credit card usage is crucial for improving your creditworthiness. These strategies can help you get a handle on your finances and improve your credit score over time.
- Debt Snowball Method: Pay off your smallest debt first, regardless of interest rate. The psychological boost of quickly eliminating a debt can help maintain motivation.
- Debt Avalanche Method: Pay off your highest-interest debt first, minimizing the total interest paid over time. This method is mathematically more efficient but can be less motivating initially.
- Budgeting and Tracking: Create a detailed budget to track your income and expenses. Identify areas where you can cut back to allocate more funds towards debt repayment.
- Negotiating with Creditors: Contact your creditors to discuss options like lower interest rates or payment plans. Be polite and persistent, and document all communications.
Importance of Timely Bill Payments
On-time payments are the single most important factor influencing your credit score. Even one missed payment can significantly impact your score, while consistent on-time payments demonstrate responsible financial behavior.
Late payments remain on your credit report for seven years, negatively affecting your creditworthiness for that entire period. Automating bill payments through online banking or setting reminders can help ensure timely payments and prevent late fees. A consistent history of on-time payments is crucial for building a strong credit profile.
Negotiating Loan Terms and Conditions
Securing a car loan with bad credit can feel like navigating a minefield, but understanding how to negotiate is key to getting a deal that works for you. Remember, lenders are businesses, and they want your business. Knowing your options and asking the right questions can significantly impact your monthly payments and overall loan cost.Negotiating a car loan, especially with less-than-perfect credit, requires preparation and a clear understanding of your financial situation.
The better informed you are, the stronger your position will be. Don’t be intimidated – you have leverage, even with bad credit.
Interest Rate Negotiation
A lower interest rate can save you thousands of dollars over the life of your loan. Before you even step foot in a dealership or contact a lender, know your credit score and what interest rates are typical for borrowers with similar credit profiles. You can use online tools to get a general idea. Armed with this knowledge, you can confidently discuss interest rates with lenders, highlighting your research and proposing a rate that aligns with your creditworthiness.
For example, if you find that similar borrowers are getting 10% interest, you could start by proposing a rate around that number and work your way down from there, emphasizing your commitment to repayment. Remember to be polite but firm.
Loan Term Length
The length of your loan directly impacts your monthly payments. A longer loan term means lower monthly payments, but you’ll pay significantly more in interest over time. A shorter term means higher monthly payments but less interest paid overall. Consider your budget and long-term financial goals when deciding on a loan term. For example, a 60-month loan will have lower monthly payments than a 36-month loan, but the total interest paid will be considerably higher.
Carefully weigh the pros and cons before committing.
Fees and Charges
Understanding all fees associated with the loan is crucial. Ask about origination fees, prepayment penalties, and late payment fees. These fees can add hundreds or even thousands of dollars to the total cost of the loan. Don’t hesitate to compare offers from multiple lenders to find the one with the lowest overall cost. For instance, one lender might offer a slightly higher interest rate but waive origination fees, making it the more economical option.
Scrutinize every detail of the loan agreement before signing. Don’t be afraid to ask for clarification on anything you don’t understand.
Questions to Ask Potential Lenders
Before committing to a loan, it’s essential to have all your questions answered. Knowing what to ask will help you compare lenders effectively and make an informed decision. Examples of crucial questions include: What is the Annual Percentage Rate (APR)? What are all the fees associated with the loan? What is the total amount I will pay over the life of the loan?
What happens if I miss a payment? What are your policies regarding loan modifications or hardship programs? These questions ensure transparency and protect you from unexpected costs and penalties.
Budgeting for Car Payments
Securing a car loan with bad credit often means higher interest rates and potentially larger monthly payments. Successfully managing these payments requires careful budgeting and a realistic understanding of the total cost of car ownership. Failing to account for all expenses can lead to financial strain and even default on your loan.Successfully integrating car payments into your monthly budget involves a multi-step process.
First, you need to determine your total monthly income after taxes and other deductions. Then, meticulously list all your current monthly expenses, from rent or mortgage to groceries and utilities. Subtracting your total expenses from your income reveals how much money you have left for discretionary spending, including your car payment. Remember to be thorough; unexpected expenses pop up, and leaving some buffer room is crucial.
Sample Budget Incorporating Car Payments, How to finance a car with bad credit 2025
Let’s say your monthly net income is $3,000. After accounting for rent ($1,200), utilities ($200), groceries ($400), student loans ($300), and other expenses ($300), you have $600 left. If your car payment is $300, you’ll have $300 remaining for gas, maintenance, emergencies, and entertainment. This budget illustrates a tight but manageable situation. A higher car payment would necessitate adjustments elsewhere in the budget, perhaps by reducing discretionary spending or finding ways to lower existing expenses.
This detailed breakdown allows for a clear picture of financial feasibility.
Calculating Total Cost of Car Ownership
The monthly payment is only one piece of the puzzle. Total car ownership costs encompass several other significant expenses. Insurance premiums, fuel costs, maintenance (oil changes, tire rotations, repairs), and potential unexpected repairs all contribute to the overall cost. For instance, a car with a $300 monthly payment might also require $100 monthly for insurance, $150 for fuel (depending on mileage and gas prices), and $50 for regular maintenance.
This adds up to a total monthly expense of $600, significantly impacting your budget.
Total Cost of Car Ownership = Monthly Payment + Insurance + Fuel + Maintenance + Unexpected Repairs
Managing Unexpected Car Repair Costs
Unexpected car repairs can be financially devastating. A flat tire, a broken alternator, or a blown engine can lead to substantial expenses. To mitigate this risk, several strategies are crucial. First, establishing an emergency fund specifically for car repairs is highly recommended. Aim to save at least $1,000-$2,000.
Second, consider purchasing an extended warranty. While this adds to the initial cost, it can provide significant protection against expensive repairs. Third, regular car maintenance can help prevent major issues, reducing the likelihood of costly unexpected repairs. Finally, researching reputable mechanics and comparing prices before authorizing any work can help you avoid overpaying.
Protecting Yourself from Predatory Lending: How To Finance A Car With Bad Credit 2025
Securing a car loan with bad credit can feel like navigating a minefield, especially when dealing with lenders who prioritize profit over responsible lending practices. Predatory lenders often target individuals with less-than-perfect credit, preying on their desperation for transportation. Understanding their tactics is crucial to avoiding exploitation and making a financially sound decision.Predatory lenders employ various tactics to trap vulnerable borrowers.
These tactics often involve high interest rates, hidden fees, and complex loan terms designed to confuse and overwhelm the borrower. It’s vital to be aware of these methods to protect yourself from financial harm.
Common Tactics of Predatory Lenders
Predatory lenders frequently utilize deceptive strategies to lure in borrowers with bad credit. These tactics often involve misleading advertising, inflated interest rates, and aggressive sales pitches. For example, an advertisement might promise “easy financing for everyone,” without disclosing the extremely high interest rates associated with such loans. They might also pressure borrowers into signing contracts quickly, without giving them adequate time to review the terms.
Another common tactic is the use of balloon payments, requiring a significantly larger payment at the end of the loan term, which can easily lead to default. These practices make it difficult for borrowers to manage their payments and can result in a cycle of debt.
Warning Signs of Predatory Loans
Several warning signs can indicate a predatory loan. Excessively high interest rates, significantly above the average market rate, are a major red flag. Hidden fees, such as excessive application fees or prepayment penalties, are also common indicators. Loans with complex or confusing terms, deliberately designed to obscure important details, should raise concerns. Aggressive sales tactics, such as high-pressure sales calls or insistence on immediate decisions, should be viewed with suspicion.
If a lender is unwilling to clearly explain the terms of the loan or answer your questions, it’s a serious warning sign. Finally, a lender that focuses solely on your ability to make payments without regard to your overall financial situation could be acting in a predatory manner.
The Importance of Thorough Contract Review
Before signing any loan contract, it is absolutely crucial to read and understand every single detail. Don’t rush the process. Take your time, and if necessary, seek assistance from a trusted financial advisor or consumer protection agency. Pay close attention to the annual percentage rate (APR), which reflects the total cost of borrowing, including interest and fees. Understand the payment schedule, including the amount, frequency, and duration of payments.
Carefully review any additional fees, such as late payment fees or prepayment penalties. If any aspect of the contract is unclear or seems unreasonable, do not hesitate to ask questions and seek clarification. Remember, signing a contract is a legally binding agreement, and understanding its implications is vital to protecting your financial well-being. A poorly understood contract can lead to serious financial consequences.
Alternatives to Traditional Financing
Securing a car loan with bad credit can feel like navigating a minefield, but traditional financing isn’t your only option. Exploring alternatives like leasing or buying a used car can significantly improve your chances of getting behind the wheel. These options often come with different sets of advantages and disadvantages, so understanding the nuances is crucial.Leasing and purchasing a used car represent viable paths to car ownership for individuals with less-than-perfect credit.
Both options often involve lower upfront costs and potentially more manageable monthly payments compared to financing a new car. However, each approach presents unique financial implications that need careful consideration.
Leasing versus Buying a Used Car with Bad Credit
Leasing generally involves lower monthly payments than buying, because you’re only paying for the car’s depreciation during the lease term, not its full value. However, you don’t own the car at the end of the lease, and mileage limits and other restrictions can be costly. Buying a used car, on the other hand, means you eventually own the vehicle outright, building equity over time.
However, used car loans may still be challenging to obtain with bad credit, and you’ll need to factor in potential repair costs. For someone with bad credit, a used car might offer more favorable loan terms simply because the lender is lending less money. The lower loan amount reduces the lender’s risk, potentially leading to a higher approval rate.
Resources for Finding Affordable Used Cars
Finding a reliable used car at a fair price is key when dealing with bad credit. Several resources can help streamline the process. Websites like Carfax and Kelley Blue Book provide detailed vehicle history reports, helping you avoid potential lemons. Online marketplaces like Craigslist and Facebook Marketplace offer a wide selection of used cars, but buyer beware: thorough inspections are essential.
Reputable used car dealerships often specialize in working with individuals who have less-than-perfect credit, offering financing options tailored to their specific situations. Finally, consider consulting a trusted mechanic for pre-purchase inspections to ensure the car’s mechanical soundness before committing to a purchase. This step can save you significant money down the line by preventing unexpected repair bills.
Visual Guide to Understanding Loan Terms

Understanding the jargon associated with car loans is crucial, especially when you have bad credit and are navigating potentially less favorable terms. This visual guide simplifies key concepts, helping you make informed decisions. Imagine a colorful infographic, easily digestible at a glance.The infographic would be divided into four main sections, each representing a key loan term. A central image, perhaps a stylized car key, connects these sections.
Annual Percentage Rate (APR)
The APR section would visually represent the total cost of borrowing, expressed as a yearly percentage. A large, clear number displaying a sample APR (e.g., 12%) would be prominent. Below it, a concise explanation clarifies that the APR includes not only the interest rate but also other fees, like origination fees, which are often rolled into the loan.
A small bar graph could visually compare a lower APR with a higher APR, demonstrating the significant difference in total interest paid over the loan term. For example, it might show that a 12% APR on a $15,000 loan over 60 months results in approximately $3,000 in interest, while an 8% APR on the same loan would only result in approximately $2,000 in interest, a difference of $1,000.
Interest Rate
This section focuses solely on the interest charged on the principal loan amount. A simple formula is displayed:
Interest = Principal x Rate x Time
This is followed by a clear explanation that the rate is the percentage charged annually. The infographic would visually connect the interest rate to the total interest paid, showing how a higher interest rate directly impacts the overall loan cost. A small table could compare different interest rates (e.g., 6%, 8%, 10%) and their impact on the total interest paid for a fixed loan amount and term.
Loan Term
This section illustrates the duration of the loan. A timeline would visually represent different loan terms (e.g., 36 months, 48 months, 60 months). The infographic explains how a longer loan term reduces monthly payments but increases the total interest paid due to the extended repayment period. A comparison chart could showcase the monthly payment differences between a shorter and a longer loan term for the same loan amount and interest rate, highlighting the trade-off between affordability and total cost.
For instance, it might show that a $15,000 loan at 8% APR has a monthly payment of roughly $300 for a 60-month term and approximately $400 for a 48-month term.
Monthly Payment
This section visually emphasizes the amount due each month. A large, clear number showing a sample monthly payment (e.g., $300) would be featured. A breakdown of the monthly payment components (principal and interest) would be shown, illustrating how the proportion of principal versus interest changes over time. A simple graph could show this change over the loan’s lifespan.
A small note would highlight the importance of budgeting for this amount and avoiding missed payments, as this can negatively impact credit scores.
Closing Notes
So, you’re ready to tackle car financing with bad credit in 2025? Awesome! Remember, getting a car loan isn’t a race, it’s a process. By understanding your credit, exploring your options, and negotiating smart, you can find a car loan that works for you. Don’t let a less-than-perfect credit score hold you back from your dream ride. Use this guide as your roadmap, and remember to always do your research and ask questions.
Happy driving!