How much weight can a Chevy 2500HD tow? That’s a seriously important question if you’re planning any serious hauling. This isn’t just about hitching up a small camper; we’re talking about boats, horse trailers, and everything in between. Understanding your truck’s towing capacity is crucial for safety and avoiding potential damage. We’ll break down everything you need to know, from the different models and their capabilities to essential safety tips and maintenance practices.
This guide will delve into the factors affecting towing capacity, like engine type, cab configuration, and even the weather. We’ll also cover payload capacity and its relationship to towing, showing you how to distribute weight properly in your truck bed. Plus, we’ll help you understand terms like GVWR and GCWR, so you can stay safe and legal on the road.
Get ready to become a towing pro!
Towing Capacity Variations
The Chevy 2500HD boasts impressive towing capabilities, but the exact amount varies considerably depending on several key factors. Understanding these variations is crucial for choosing the right truck for your specific needs and ensuring safe towing practices. This section will break down the factors affecting towing capacity and provide a clearer picture of what you can expect from different 2500HD configurations.
Factors Influencing Towing Capacity
Several interconnected factors determine the maximum towing capacity of a Chevy 2500HD. These factors work together, and a change in one can significantly impact the overall towing capacity. Ignoring these variations could lead to overloading and potentially dangerous situations.
The most significant factors include:
- Engine Type and Horsepower: A more powerful engine, like the Duramax diesel, naturally provides greater towing capacity than a gasoline engine. More horsepower and torque translate directly to the ability to pull heavier loads.
- Cab Configuration: A crew cab, with its larger passenger space, typically has a slightly lower towing capacity compared to a regular cab due to the increased vehicle weight.
- Bed Length: A longer bed might slightly reduce towing capacity because of the increased weight of the truck itself. The difference is usually minimal but still worth noting.
- Optional Equipment: Adding features like heavy-duty towing packages, fifth-wheel hitches, or gooseneck hitches can affect the truck’s weight distribution and, therefore, its towing capacity. These packages often include upgraded components designed to handle increased stress during towing.
- Drivetrain: Four-wheel drive (4WD) systems generally reduce towing capacity slightly compared to two-wheel drive (2WD) because of added weight and mechanical complexity. However, the enhanced traction in off-road conditions might be worth the trade-off for some users.
Gasoline vs. Diesel Towing Capacity
The choice between a gasoline and a diesel engine significantly impacts towing capacity. Diesel engines, particularly the Duramax in the 2500HD, are renowned for their high torque output at lower RPMs, making them exceptionally well-suited for heavy towing. Gasoline engines, while offering advantages in other areas like fuel efficiency under lighter loads, generally provide considerably lower towing capacities.
This difference is not simply a matter of a few hundred pounds; it can be a difference of several thousand pounds. Choosing the right engine is crucial based on your anticipated towing needs.
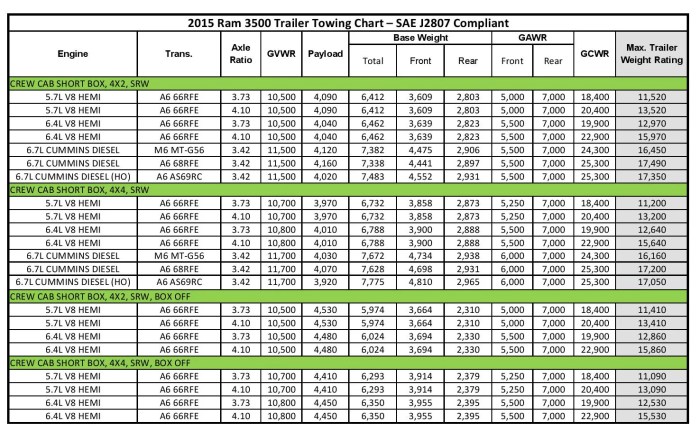
Towing Capacity Comparison Table
The following table provides a general comparison of towing capacities. Note that these figures are approximate and can vary based on specific configurations and options. Always consult the official specifications for your particular model year and trim level.
| Year | Engine | Drivetrain | Max Towing Capacity (lbs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 6.6L Duramax Turbo-Diesel V8 | 4WD | 18,500 |
| 2023 | 6.6L Duramax Turbo-Diesel V8 | 2WD | 20,000 |
| 2023 | 6.6L Gas V8 | 4WD | 11,500 |
| 2023 | 6.6L Gas V8 | 2WD | 12,000 |
Payload Capacity and its Relation to Towing
Payload capacity and towing capacity are intrinsically linked in a Chevy 2500HD, or any pickup truck for that matter. Understanding this relationship is crucial for safe and legal operation. Simply put, the weight of everything in the truckbesides* the truck itself (passengers, cargo, accessories) directly impacts how much it can tow. Exceeding the payload capacity reduces the truck’s overall stability and can severely compromise its towing capabilities.The maximum towing capacity advertised by Chevy is only achievable under ideal conditions and with a minimal payload.
As you add weight to the truck bed or to the cab (passengers, gear, etc.), the amount you can safely tow decreases. This is because the added weight shifts the truck’s center of gravity, reducing its stability and increasing stress on the suspension, drivetrain, and braking systems. Think of it like this: the more weight you’re already carrying, the less weight you have available to safely pull.
Overloading the truck can lead to a dangerous situation, potentially resulting in accidents, equipment damage, and even injury.
Payload Capacity’s Impact on Towing and Safety
Exceeding the payload capacity has several significant consequences when towing. First, it increases the risk of sway, which is when the trailer begins to wobble or fishtail. This can be incredibly difficult to control, even for experienced drivers. Second, it significantly reduces braking performance. A heavier truck requires more stopping distance, and an overloaded truck will need even more.
This increased stopping distance is compounded when towing a trailer, which also adds to the overall weight. Third, it puts added stress on the truck’s components, potentially leading to premature wear and tear or even catastrophic failure of parts like axles, suspension components, or the transmission. Imagine trying to tow a heavy boat while already carrying a full load of lumber in the bed – the strain on the truck is immense.
The consequences of overloading, especially when towing, can be quite serious.
Best Practices for Weight Distribution
Proper weight distribution is paramount for safe towing. Here’s a breakdown of best practices to optimize weight distribution within the truck bed:
- Distribute Weight Evenly: Avoid concentrating weight in one area. Spread heavier items across the bed, aiming for a balanced distribution from front to back and side to side. Think of it like balancing a scale.
- Heavier Items Low and Forward: Place the heaviest items as low to the ground as possible and towards the front of the bed. This helps lower the center of gravity and improves stability.
- Secure All Cargo: Use appropriate tie-down straps or other securing mechanisms to prevent cargo from shifting during transit. Loose or shifting cargo can dramatically impact stability and control.
- Utilize Weight Distribution Hitches: For heavy loads, consider a weight distribution hitch. These hitches transfer a portion of the trailer’s tongue weight to the truck’s front axle, reducing the load on the rear axle and improving stability. This is particularly important for larger trailers.
- Regularly Check Tire Pressure and Load Ratings: Ensure your tires are properly inflated to the recommended pressure for your load and that they meet or exceed the load ratings for the weight you are carrying.
Factors Affecting Towing Performance
Towing a heavy load with your Chevy 2500HD, even with its impressive capabilities, isn’t just about the truck’s specs; environmental conditions and driving style play a significant role in overall performance, fuel efficiency, and safety. Understanding these factors allows for better planning and safer towing practices.Environmental factors and driving techniques significantly impact the performance and fuel economy of your Chevy 2500HD while towing.
Altitude, terrain, and weather conditions can dramatically affect your truck’s power and efficiency, while your driving style directly influences fuel consumption. Optimizing your approach to these factors is key to a smooth and efficient towing experience.
Environmental Factors Affecting Towing Performance
Altitude, steep inclines, and adverse weather conditions all contribute to decreased towing performance. Higher altitudes reduce engine power due to thinner air, making it harder to maintain speed and requiring more engine effort. Steep grades demand more power from the engine and transmission, leading to increased fuel consumption and potentially overheating. Adverse weather, such as heavy rain, snow, or strong winds, can reduce traction, increase braking distances, and negatively impact fuel economy.
For example, towing a 10,000-pound trailer up a steep mountain pass in snowy conditions will require significantly more power and fuel than towing the same trailer on a flat, dry road at sea level.
Driving Techniques and Fuel Economy While Towing
Driving techniques significantly impact fuel economy while towing. Maintaining a consistent speed, avoiding sudden acceleration and braking, and using cruise control when appropriate can improve fuel efficiency. For instance, accelerating gradually instead of aggressively reduces the amount of fuel consumed. Similarly, anticipating stops and slowing down gradually, instead of using hard braking, reduces wear and tear on the brakes and improves fuel economy.
Overloading the truck beyond its recommended towing capacity will also drastically reduce fuel economy and increase wear and tear on the vehicle’s components. Proper tire inflation is also crucial; under-inflated tires increase rolling resistance, leading to reduced fuel efficiency.
Choosing the Appropriate Gear Ratio While Towing
The selection of the appropriate gear ratio is crucial for efficient and safe towing. A lower gear ratio (higher numerical value) provides more torque at lower speeds, making it ideal for steep inclines and heavy loads. Conversely, a higher gear ratio (lower numerical value) is better suited for maintaining higher speeds on level terrain. The decision-making process involves considering the terrain, load weight, and desired speed.
Safety Considerations for Towing with a Chevy 2500HD
Towing with a Chevy 2500HD, while capable, demands a serious commitment to safety. Overlooking even minor details can lead to accidents, property damage, and serious injury. Understanding and adhering to best practices is crucial for a safe and successful towing experience.
Before you even think about hooking up your trailer, a thorough pre-trip inspection is essential. Neglecting this step is like driving without brakes – a recipe for disaster. It’s not just about the truck; the trailer itself needs a comprehensive check-up too.
So you’re wondering how much a Chevy 2500HD can tow? That depends on the configuration, but it’s a serious hauler. If you’re on a tighter budget and fuel efficiency is a concern, though, check out this list of Cheapest trucks under $30k with good MPG 2025 to see what lighter-duty options might fit your needs. Ultimately, the towing capacity of a Chevy 2500HD far surpasses most of those, making it the better choice for heavy loads.
Pre-Towing Safety Checks
A comprehensive pre-trip inspection involves checking both your vehicle and the trailer for potential issues that could compromise safety. This isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s about identifying potential mechanical failures or unsafe conditions that could lead to accidents.
- Check tire pressure and condition on both the truck and trailer: Under-inflated tires increase the risk of blowouts, while worn tires reduce traction and braking performance. Ensure all tires are properly inflated to the recommended pressure (found on the tire sidewall and in your vehicle’s owner’s manual).
- Inspect lights and signals on both the truck and trailer: Confirm that all lights (brake lights, turn signals, running lights, and taillights) are functioning correctly on both your truck and trailer. Faulty lights can lead to accidents caused by poor visibility.
- Verify hitch connection security: Make absolutely sure your trailer hitch is securely connected to your truck’s receiver hitch. A loose connection could lead to the trailer separating from the truck while driving.
- Examine trailer brakes and wiring: Ensure the trailer brakes are functioning correctly and that the wiring is properly connected to the truck’s electrical system. This is crucial for safe and controlled stopping.
- Check cargo securement: If you’re hauling cargo, make sure it’s properly secured to prevent shifting or falling during transit. Use straps, tie-downs, or other appropriate securing devices.
- Inspect safety chains: Safety chains are a critical backup in case the hitch fails. Ensure they are properly crossed and connected to both the trailer and the truck, with appropriate slack.
Proper Use of Trailer Brakes and Weight Distribution Hitches
Using trailer brakes and weight distribution hitches correctly is paramount for safe towing. These systems significantly improve braking performance and handling, especially when towing heavier loads. Improper use can negate their benefits and increase the risk of accidents.
Trailer brakes help prevent jackknifing and provide controlled stopping, especially on inclines or in emergencies. A weight distribution hitch helps distribute the trailer’s weight more evenly across the truck’s axles, improving handling and stability. It also reduces sway and prevents the rear of the truck from sagging excessively. Consult your owner’s manual and a professional installer for proper installation and adjustment.
So you’re wondering how much weight a Chevy 2500HD can tow? It’s a beast, for sure, but that towing capacity can be affected by issues like transmission problems. If you’re experiencing a shudder, check out this guide on How to fix transmission shudder in Chevy trucks to keep your towing game strong. A smooth transmission is key to maximizing that impressive Chevy 2500HD towing power.
Connecting a Trailer to a Chevy 2500HD
Connecting a trailer to your Chevy 2500HD requires a methodical approach to ensure a secure and safe connection. Rushing this process can lead to dangerous consequences.
- Park on a level surface: This makes connecting the hitch and wiring much easier and safer.
- Engage the parking brake: This prevents the truck from rolling during the connection process.
- Align the trailer hitch with the truck’s receiver hitch: Carefully guide the trailer’s ball into the truck’s receiver hitch, ensuring a snug fit.
- Secure the hitch pin: Insert the hitch pin and secure it tightly. This is crucial to prevent the trailer from detaching.
- Connect the safety chains: Cross the safety chains and connect them to both the trailer and the truck, ensuring sufficient slack to allow for turning but not so much that they drag on the ground.
- Connect the trailer lights: Connect the trailer’s wiring harness to the truck’s connector. Test all lights to ensure they’re functioning properly.
- Check all connections: Before driving, double-check all connections to ensure everything is secure and properly connected. Take your time and don’t rush this step.
Trailer Types and Matching Them to the Chevy 2500HD
Choosing the right trailer for your Chevy 2500HD depends heavily on the type of trailer and its weight. The 2500HD’s impressive towing capacity makes it suitable for a wide variety of trailers, but understanding the specific requirements of each type is crucial for safe and efficient towing. Different trailers place different stresses on the truck and hitch, necessitating careful consideration of weight distribution and hitch type.
The Chevy 2500HD, with its robust build and powerful engine, is capable of handling a significant range of trailer types. However, optimizing towing performance and safety requires matching the right truck configuration to the specific trailer. Factors such as the trailer’s weight, length, and the type of hitch used all play a critical role.
Trailer Type Suitability and Chevy 2500HD Configurations
The following table Artikels suitable Chevy 2500HD configurations for various trailer types. Remember that the actual towing capacity will vary depending on the specific truck configuration (engine, drivetrain, options), payload, and other factors. Always consult your owner’s manual for precise figures.
| Trailer Type | Suitable Chevy 2500HD Configurations | Typical Hitch Type | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boat Trailers | Most configurations are suitable, especially those with higher payload capacities. Consider a heavier-duty model if towing larger boats. | Weight-distribution hitch recommended for larger boats. A ball hitch might suffice for smaller, lighter boats. | Proper weight distribution is crucial to prevent sway and maintain control. Ensure the boat is properly secured to the trailer. |
| Fifth-Wheel Trailers | Generally requires a long-bed model and a fifth-wheel hitch installation. Higher GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating) configurations are preferred. | Fifth-wheel hitch, properly installed and rated for the trailer’s weight. | Proper weight distribution is paramount, requiring careful attention to pin weight. A weight distribution system may still be necessary, depending on the trailer weight. |
| Gooseneck Trailers | Similar to fifth-wheel trailers, a long-bed model is recommended. High GVWR configurations are essential. Gooseneck hitches require specific bed-mounted hitches. | Gooseneck hitch, properly installed and rated for the trailer’s weight. | Goosenecks offer superior weight distribution compared to other hitch types, making them ideal for heavy loads. Ensure proper ball size and hitch installation. |
| Utility/Cargo Trailers | Most configurations are suitable, depending on the trailer’s weight. | Ball hitch or weight-distribution hitch, depending on the trailer’s weight and cargo. | Properly secure all cargo to prevent shifting during transit. Ensure the trailer’s weight is within the truck’s towing capacity. |
Suitable Trailer Hitch Characteristics, How much weight can a Chevy 2500HD tow?
The correct hitch is vital for safe and effective towing. The hitch type must be compatible with both the trailer and the Chevy 2500HD. The hitch’s weight rating must exceed the tongue weight (the weight on the hitch ball) of the trailer.
Ball hitches are commonly used for smaller trailers, offering simplicity and ease of use. Weight-distribution hitches are recommended for heavier trailers to better distribute weight and prevent sway. Fifth-wheel and gooseneck hitches are specialized for their respective trailer types and offer superior weight distribution for large and heavy trailers. Always consult a professional for hitch installation and ensure the hitch is properly rated for the specific trailer being towed.
Maintenance and Upkeep for Towing
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring your Chevy 2500HD performs reliably and safely when towing heavy loads. Neglecting this can lead to breakdowns, accidents, and costly repairs. A proactive approach to maintenance will extend the life of your truck and enhance your peace of mind on the road.Proper maintenance goes beyond routine oil changes and tire rotations. It specifically addresses the increased stress placed on your vehicle’s components when towing.
This includes paying close attention to the towing system itself, ensuring your brakes are in top condition, and regularly inspecting your trailer’s safety features.
Regular Maintenance Schedule for Towing
A comprehensive maintenance schedule for a Chevy 2500HD used for towing should include more frequent checks than for a truck used solely for everyday driving. These checks should be performed before each towing trip and at regular intervals as Artikeld in your owner’s manual.
- Engine Oil and Filter: Change more frequently than recommended for standard driving, especially when towing in hot climates or mountainous terrain. Consult your owner’s manual for recommendations based on towing conditions.
- Transmission Fluid: Towing puts extra strain on your transmission. Regular fluid checks and changes, again according to your owner’s manual guidelines for towing, are vital. Consider using a synthetic transmission fluid for extended life and improved performance under heavy loads.
- Coolant: Check coolant levels before each trip and ensure the cooling system is functioning correctly. Overheating is a serious risk when towing, and a low coolant level can lead to catastrophic engine failure.
- Brakes: Thorough brake inspections are paramount (discussed further below). This includes checking pad thickness, rotor wear, and fluid levels.
- Tires: Maintain proper tire inflation, especially when towing. Under-inflated tires increase rolling resistance, reduce fuel economy, and increase the risk of blowouts. Check tire pressure before each trip and regularly inspect for wear and tear.
- Hitch and Wiring: Visually inspect the hitch for damage or loose connections before each towing trip. Ensure the trailer wiring is securely connected and functioning correctly.
- Suspension and Steering Components: Regularly inspect for wear and tear on shocks, struts, ball joints, and tie rod ends. These components are heavily stressed when towing and require more frequent attention.
Brake Inspections and Maintenance for Towing
Regular brake inspections are critical when towing heavy loads. The increased weight significantly increases the demands on your braking system. Neglecting brake maintenance can lead to brake failure, a potentially catastrophic event.
- Brake Pad Thickness: Check brake pad thickness regularly. Thin brake pads reduce braking effectiveness and can lead to rotor damage.
- Rotor Wear: Inspect brake rotors for scoring, grooves, or excessive wear. Worn rotors reduce braking performance and can cause vibrations.
- Brake Fluid Level: Maintain the correct brake fluid level. Low fluid levels indicate a potential leak and should be addressed immediately.
- Brake Lines and Hoses: Inspect brake lines and hoses for cracks, leaks, or damage. Damaged brake lines can lead to complete brake failure.
- Brake System Bleeding: Periodically bleed the brake system to remove air bubbles that can compromise braking effectiveness. Consult your owner’s manual or a qualified mechanic for the correct procedure.
Trailer Light and Safety Feature Inspection
Before each towing trip, a thorough inspection of the trailer’s lights and safety features is essential for safe operation. Faulty lights can significantly reduce visibility and increase the risk of accidents.
- Turn Signals: Activate the turn signals on the trailer and verify they function correctly. Both left and right signals should blink appropriately.
- Brake Lights: Apply the brakes on the tow vehicle and check that the trailer’s brake lights illuminate brightly.
- Tail Lights: Ensure the tail lights on the trailer are functioning properly. These lights are crucial for visibility at night.
- Running Lights: Check that the running lights are illuminated when the vehicle’s headlights are on. These lights provide constant rear visibility.
- Safety Chains: Verify that the safety chains are correctly connected and properly secured to both the tow vehicle and the trailer. Safety chains are a critical backup in case the hitch fails.
- Reflectors: Check that all reflectors on the trailer are clean and visible. Reflectors are essential for night-time visibility.
- Tires: Inspect the trailer’s tires for proper inflation and signs of wear and tear. Under-inflated tires increase rolling resistance and the risk of blowouts.
- Wheel Chocks: Ensure you have wheel chocks and use them whenever you disconnect the trailer from the vehicle.
Understanding GVWR and GCWR: How Much Weight Can A Chevy 2500HD Tow?
Knowing your Chevy 2500HD’s Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) and Gross Combined Weight Rating (GCWR) is crucial for safe and legal towing. These ratings represent the maximum weights your truck and your truck-trailer combination can handle, respectively. Exceeding these limits significantly increases the risk of accidents, damage to your vehicle, and potential legal issues.GVWR refers to the maximum allowable weight of your Chevy 2500HD itself, including the vehicle, its contents (passengers, cargo, fluids), and any added equipment.
GCWR, on the other hand, is the maximum allowable weight of your entire towing setup: the weight of your Chevy 2500HD plus the weight of the trailer and everything inside it (cargo, passengers, etc.). Understanding these limits is paramount to responsible towing.
GVWR Calculation Example
Let’s say the GVWR for a specific Chevy 2500HD model is 10,000 lbs. This means the combined weight of the truck, its fuel, any cargo in the truck bed, and passengers cannot exceed 10,000 lbs. To calculate if you’re within the GVWR, weigh your truck fully loaded (including passengers, cargo, and fuel) using a certified scale. If the weight exceeds 10,000 lbs, you are overloaded and need to remove weight before driving.
GCWR Calculation Example
Suppose the GCWR for the same Chevy 2500HD is 22,000 lbs. Imagine you’re towing a trailer weighing 8,000 lbs fully loaded. To determine if you’re within the GCWR, add the weight of your fully loaded truck (let’s say 9,000 lbs from the previous example) to the weight of your fully loaded trailer (8,000 lbs). This gives you a total combined weight of 17,000 lbs (9,000 lbs + 8,000 lbs).
Since 17,000 lbs is less than the 22,000 lbs GCWR, you are within the safe operating limit. However, remember that this is just an example; always consult your owner’s manual for the precise GVWR and GCWR for your specific Chevy 2500HD model and year.
Best Practices for Staying Within Weight Limits
To ensure you always stay within the GVWR and GCWR limits, follow these best practices:
Always consult your owner’s manual for the exact GVWR and GCWR for your specific vehicle.
Regularly weigh your truck and trailer combination on a certified scale, especially before long trips or when hauling heavy loads.
Accurately estimate the weight of your cargo and passengers. It’s better to slightly underestimate than overestimate.
Distribute weight evenly in both the truck bed and the trailer to maintain balance and stability.
Avoid overloading your truck or trailer. If you need to haul more than your truck can handle, consider using a larger vehicle or making multiple trips.
Regularly check your tire pressure. Under-inflated tires can lead to overheating and failure, especially when towing heavy loads.
Last Recap
So, how much weight
-can* a Chevy 2500HD tow? The answer, as we’ve seen, depends on a lot of factors. From engine size and configuration to the type of trailer you’re pulling and even the weather conditions, there are many variables to consider. But by understanding these factors and following the safety guidelines we’ve discussed, you can confidently and safely haul whatever you need.
Remember to always check your owner’s manual for specific recommendations and never exceed your truck’s rated capacities. Happy hauling!









