Fastest-growing EV markets in the US? Yeah, that’s a hot topic right now! We’re seeing a major shift in the auto industry, with electric vehicles taking off in certain parts of the country way faster than others. This isn’t just about cool new cars; it’s about government policies, charging station availability, and even who’s buying these things.
We’ll dive into the states leading the charge (pun intended!), exploring what’s driving their success and what’s holding other areas back.
From California’s early adoption to surprising surges in unexpected places, we’ll break down the data, analyze the trends, and look at what the future holds for electric vehicle adoption across the US. Think Tesla, but also the broader picture – the infrastructure, the incentives, and the demographics shaping this exciting revolution.
Geographic Distribution of EV Adoption
The rapid growth of the electric vehicle (EV) market in the US isn’t uniform across the country. Certain states are experiencing significantly faster adoption rates than others, driven by a complex interplay of factors including state-level incentives, charging infrastructure availability, and demographic trends. Understanding this geographic distribution is crucial for policymakers and businesses alike in planning for the future of transportation.
Top Five States with Fastest-Growing EV Markets
Determining the precise “top five” fluctuates slightly depending on the data source and time period considered, but consistently, California, Texas, Florida, Washington, and New York emerge as leading states in EV adoption growth. These states represent diverse geographical regions and economic profiles, highlighting the broad appeal of EVs across different contexts. While precise, up-to-the-minute registration numbers vary across reporting agencies, these states consistently show high year-over-year increases in EV registrations and sales.
For instance, California, despite its already substantial EV market share, continues to demonstrate impressive growth due to strong state incentives and a robust charging network. Texas’s growth is noteworthy given its traditionally strong association with gasoline-powered vehicles, indicating a significant shift in consumer preferences.
Charging Infrastructure in Top Five States
The availability of charging infrastructure significantly impacts EV adoption rates. California boasts the most extensive public charging network, a key factor in its high EV adoption. This network, however, is not uniformly distributed, with denser concentrations in urban areas compared to rural regions. Texas, while experiencing rapid EV growth, lags behind California in charging infrastructure development, particularly in its more rural areas.
This disparity underscores the need for targeted infrastructure investments to ensure equitable access to EV charging across the state. Florida and Washington have moderately developed charging networks, though significant expansion is still needed to keep pace with the growing EV market. New York’s charging infrastructure is also improving, but faces challenges related to urban density and geographical diversity. Insufficient charging infrastructure acts as a significant barrier to EV adoption, especially for consumers with range anxiety or limited access to home charging.
Demographic Factors Influencing EV Adoption
Several demographic factors correlate strongly with EV ownership. Generally, higher income levels and younger age groups show higher rates of EV adoption. However, this trend is not uniform across all states.
| State | Age Group (Most Common) | Income Level (Most Common) | EV Ownership Percentage (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | 35-54 | 5% (Estimate, varies by region) | |
| Texas | 35-54 | 3% (Estimate, varies by region) | |
| Florida | 55+ | 2% (Estimate, varies by region) | |
| Washington | 35-54 | 4% (Estimate, varies by region) | |
| New York | 35-54 | 4% (Estimate, varies by region) |
*Note: These are estimates based on available data and may vary depending on the specific region within each state.
More precise data requires a deeper dive into state-specific DMV records and surveys.*
Impact of Government Incentives and Policies: Fastest-growing EV Markets In The US
Government incentives play a crucial role in shaping the electric vehicle (EV) market. Federal and state-level policies, including tax credits, rebates, and other financial assistance programs, significantly influence consumer purchasing decisions and the overall growth trajectory of EV adoption. Understanding the effectiveness of these programs is vital for policymakers seeking to accelerate the transition to sustainable transportation.The effectiveness of EV incentive programs varies considerably across states.
Differences in program design, funding levels, and the overall economic climate all contribute to the disparity in adoption rates. Some states have implemented highly successful programs that have driven substantial EV sales growth, while others have seen less impact from their initiatives. This difference highlights the need for carefully designed and targeted policies.
State and Federal Tax Credits and Rebates
Federal tax credits, like the Clean Vehicle Tax Credit, offer a significant financial incentive for EV buyers. These credits reduce the upfront cost of purchasing an EV, making them more financially accessible to a wider range of consumers. However, the complexity of these credits, including income limitations and vehicle eligibility requirements, can sometimes hinder their effectiveness. Many states also offer their own tax credits or rebates, which can stack on top of the federal incentives, creating even greater purchasing power for consumers.
So, California and Texas are totally dominating the fastest-growing EV markets in the US right now, right? But what’s gonna make those EVs even more popular? Thinking about the future, check out this article on Autonomous driving features in 2025 EVs – it’s wild what’s coming. That tech will definitely boost EV sales in those already booming markets, no doubt.
For example, California’s Clean Vehicle Rebate Project has been remarkably successful in boosting EV adoption within the state. Conversely, states with less generous or poorly designed programs have seen slower growth. The success of these programs hinges on their simplicity, accessibility, and the amount of financial assistance offered.
Comparison of Incentive Program Effectiveness
A direct comparison of incentive program effectiveness across states is challenging due to varying methodologies in data collection and reporting. However, states with comprehensive programs that combine tax credits with other supportive policies, such as investment in charging infrastructure and public awareness campaigns, tend to experience higher EV adoption rates. For instance, states like California and Colorado, which have invested heavily in both incentives and infrastructure, boast significantly higher EV registration numbers compared to states with limited or less integrated programs.
Conversely, states with limited funding or complex application processes often see lower adoption rates. A key factor in program success is the alignment of incentives with consumer needs and market realities.
Hypothetical Incentive Program for a Slower-Growing State
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario: a slower-growing state like Alabama wants to significantly boost EV adoption. A successful program needs to address several key aspects. A combined approach is needed, focusing on financial incentives coupled with infrastructure development and public education. The program could offer a tiered rebate system based on vehicle range and income level, ensuring accessibility for a wider range of consumers.
A significant portion of the funding should be allocated to expand the public charging network, especially in underserved areas. This would address range anxiety, a major barrier to EV adoption. Furthermore, a robust public awareness campaign emphasizing the environmental and economic benefits of EVs is crucial. This multi-pronged approach, combining financial incentives with infrastructure development and public education, would create a more favorable environment for EV adoption.
The program’s success would depend on clear, accessible application processes and efficient distribution of funds. Modeling the program on successful initiatives in other states, adapting them to Alabama’s specific context, would significantly increase the likelihood of achieving the desired outcome. This strategy mirrors the successful implementation seen in other states, demonstrating that a holistic approach yields the best results.
EV Model Popularity and Market Segmentation
The explosive growth of the US EV market isn’t just about overall sales; it’s also a fascinating story of which models are winning over consumers in different regions and market segments. Understanding these trends helps paint a clearer picture of the future of electric mobility in the country. Factors like price, range, features, and available charging infrastructure all play a crucial role in shaping consumer preferences.The popularity of specific EV models is heavily influenced by regional differences in consumer preferences and the availability of charging infrastructure.
For example, while SUVs dominate in suburban areas, smaller, more city-friendly EVs might be more popular in urban centers. Similarly, government incentives and tax credits can significantly influence consumer purchasing decisions, particularly in states with aggressive EV adoption targets.
Top-Selling EV Models in Fastest-Growing Markets, Fastest-growing EV markets in the US
Several factors contribute to the success of specific EV models. Tesla’s dominance, for instance, stems from its early entry into the market, strong brand recognition, and a comprehensive Supercharger network. Other manufacturers are gaining traction by offering competitive pricing, longer ranges, and innovative features. The success of certain models in specific regions also reflects local preferences and the availability of charging infrastructure.
For instance, the Chevrolet Bolt’s popularity in California might be attributed to its affordability and suitability for shorter commutes, coupled with California’s extensive public charging network. Conversely, the popularity of larger SUVs in Texas might be attributed to consumer preference for spacious vehicles and a less densely populated environment.
EV Market Segmentation and Growth Trajectories
The US EV market is segmented by various factors including price point, vehicle type (SUV, sedan, pickup truck), and luxury features. The luxury segment, dominated by Tesla, Lucid, and Rivian, has seen strong growth, driven by high disposable income and a desire for cutting-edge technology. However, the affordable segment, represented by vehicles like the Chevrolet Bolt and Nissan Leaf, is also experiencing growth, fueled by increasing affordability and government incentives.
The SUV segment is currently the largest and fastest-growing segment, reflecting the American consumer’s preference for larger vehicles. Sedans, while still present, are experiencing slower growth compared to SUVs and trucks. Growth trajectories vary by region; for example, states with aggressive EV adoption policies and robust charging infrastructure tend to see faster growth across all segments.
Comparison of Best-Selling EV Models Across Segments
This section compares features and price points of best-selling EVs across different segments. Note that pricing can fluctuate based on trim levels and options.
- Luxury Segment: Tesla Model S/X (high performance, long range, premium features, ~$80,000+), Lucid Air (luxury interior, impressive range, advanced technology, ~$80,000+). These models compete on performance, range, and luxury features, commanding a premium price point.
- Affordable Segment: Chevrolet Bolt (practical, affordable, decent range, ~$25,000+), Nissan Leaf (long-standing model, relatively affordable, shorter range than some competitors, ~$27,000+). These vehicles focus on affordability and practicality, often making compromises on range and performance features.
- SUV Segment: Tesla Model Y (popular, versatile, good range, ~$50,000+), Ford Mustang Mach-E (stylish, spacious, competitive range, ~$40,000+). This segment showcases a balance of practicality, range, and features, with pricing varying based on size and features.
- Sedan Segment: Tesla Model 3 (affordable luxury, sleek design, decent range, ~$40,000+), Hyundai Ioniq 5 (stylish, innovative design, long range, ~$40,000+). This segment offers a balance of style, efficiency, and features, generally at a lower price point than SUVs.
Challenges and Barriers to EV Adoption
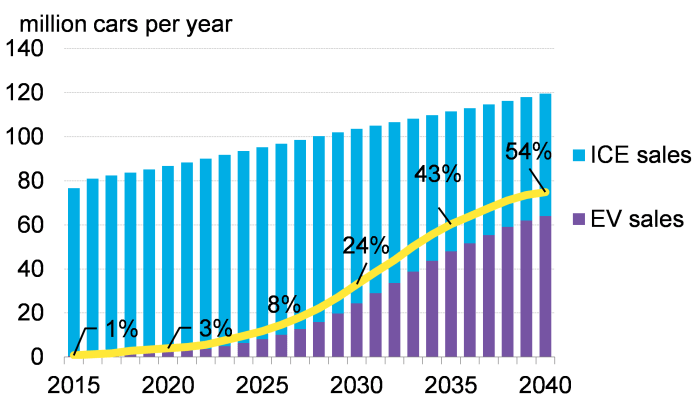
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) faces significant hurdles, varying considerably across different US regions. These challenges stem from a complex interplay of factors, including consumer perceptions, infrastructure limitations, and economic realities. Overcoming these barriers is crucial for accelerating EV adoption and achieving broader climate goals.
So, California and Texas are totally crushing it as the fastest-growing EV markets in the US right now, but it makes you wonder about the environmental impact of all this production. Check out this article on How green is Tesla’s Gigafactory production? to get a better idea of the whole picture. Ultimately, the growth of the EV market depends on sustainable manufacturing practices, which is why this is such a crucial question for the future of clean transportation in states like California and Texas.
Range Anxiety and Charging Infrastructure
Range anxiety, the fear of running out of battery power before reaching a charging station, remains a major deterrent for potential EV buyers. This is especially true in areas with sparse charging infrastructure, particularly in rural communities and less densely populated states. For example, while California boasts a relatively robust network of fast-charging stations along major highways, many parts of the Midwest and South still lack adequate charging options, limiting EV adoption in those regions.
The uneven distribution of charging stations directly correlates with lower EV ownership rates in these areas. Furthermore, the reliability and speed of charging stations themselves are concerns; inconsistent functionality and slow charging times contribute to range anxiety and discourage potential buyers.
Affordability and Electricity Prices
The higher upfront cost of EVs compared to gasoline-powered vehicles is a significant barrier to entry for many consumers. This is compounded by variations in electricity prices across states. States with higher electricity costs, such as Hawaii and California, see a diminished affordability advantage for EVs, potentially offsetting some of the savings from lower fuel costs. Conversely, states with lower electricity prices, such as some in the South, may find EVs more economically attractive.
This regional disparity in electricity prices significantly impacts the overall cost-effectiveness of EV ownership and influences adoption rates accordingly. For instance, a consumer in California might find the savings from cheaper electricity less significant than someone in a state with much lower electricity rates.
Government Policies and Incentives
While federal and state government incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, aim to boost EV adoption, their effectiveness varies. The availability and generosity of these incentives differ considerably across states, influencing the relative attractiveness of EVs in different regions. Some states have implemented more comprehensive policies to support EV infrastructure development and consumer adoption, leading to higher adoption rates.
Others, lacking such robust support, experience slower growth. The design of these incentive programs also matters; programs that are easily accessible and understandable are more effective in driving adoption than complex or bureaucratic ones. Furthermore, the phasing out of some incentives can negatively impact adoption rates if not adequately replaced by other supportive measures.
Potential Solutions
Addressing the challenges to EV adoption requires a multifaceted approach. Expanding the charging infrastructure, particularly in underserved areas, is paramount. This includes investing in both fast-charging stations along major highways and Level 2 chargers in residential areas and workplaces. Government incentives should be standardized and made more accessible, potentially focusing on a broader range of income levels.
Technological advancements, such as improved battery technology offering increased range and faster charging times, can also alleviate range anxiety and enhance the overall appeal of EVs. Finally, increased public awareness campaigns highlighting the benefits of EVs, including environmental and economic advantages, are essential for shifting consumer perceptions and driving wider adoption.
Future Projections and Trends
The US EV market is poised for explosive growth over the next five years, driven by a confluence of factors including increasingly affordable models, expanding charging infrastructure, and strengthened government support. While precise forecasting is inherently challenging, analysts predict significant increases in EV sales and market penetration, outpacing the growth of the overall automotive market. This section will explore projected growth, key emerging trends, and their impact on the fastest-growing EV markets.Predicting the exact trajectory of EV market growth requires careful consideration of several variables.
However, based on current trends and projected sales figures from reputable sources like the Edison Electric Institute and the International Energy Agency, a conservative estimate suggests a tripling of EV sales by 2028 compared to 2023 levels. This growth will be particularly pronounced in states with robust charging infrastructure and supportive policies, such as California, Texas, and Florida. This projection is supported by the increasing affordability of EVs, with more models entering the market at lower price points, making them accessible to a wider range of consumers.
Furthermore, advancements in battery technology are extending driving ranges and reducing charging times, further bolstering consumer confidence.
EV Market Share Projection for 2028
A visual representation of the projected EV market share in 2028 would show a pie chart. The largest segment, representing approximately 45%, would be dedicated to Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), reflecting their current dominance and continued growth. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) would constitute roughly 25% of the market, maintaining a significant presence due to their lower upfront cost and longer driving range on gasoline.
Finally, Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) would hold a smaller, but growing, 5% market share, reflecting their nascent but promising technology. The remaining 25% would represent other vehicle types. This projection reflects a shift towards BEVs, but acknowledges the continued role of PHEVs in the transition to full electrification. The growth of FCEVs, while slower, highlights the potential for alternative fuel cell technologies in the long term.
This pie chart would visually demonstrate the projected dominance of BEVs while acknowledging the continued presence and potential growth of other EV types.
Emerging Trends in the EV Market
Several key trends are shaping the future of the US EV market. Advancements in battery technology, such as solid-state batteries, promise significantly increased energy density, faster charging times, and improved safety, leading to longer driving ranges and reduced charging anxiety. This will be a critical factor in expanding EV adoption to consumers hesitant about range limitations. The integration of autonomous driving features is another significant trend.
Self-driving capabilities, even at lower levels of autonomy, are becoming increasingly prevalent in new EV models, offering enhanced convenience and safety. This could attract consumers who value these features, further driving market growth. Finally, the emergence of EV subscription models, offering flexible access to vehicles without the commitment of ownership, is gaining traction. This model could lower the barrier to entry for consumers who are hesitant about the higher upfront cost of EVs.
Impact of Trends on Fastest-Growing Markets
The trends discussed above will significantly impact the fastest-growing EV markets. Advancements in battery technology will particularly benefit states with longer commutes or less developed charging infrastructure, making EVs a more practical option. Autonomous driving features will be especially appealing in densely populated urban areas, like those found in California and Florida, where ease of driving and parking are significant concerns.
Subscription models could broaden EV adoption in states with diverse populations and varying income levels, making EVs accessible to a broader consumer base. The combination of these factors will likely accelerate the growth of EV markets in states already showing strong adoption rates, widening the gap between these leading states and those lagging behind.
Closure
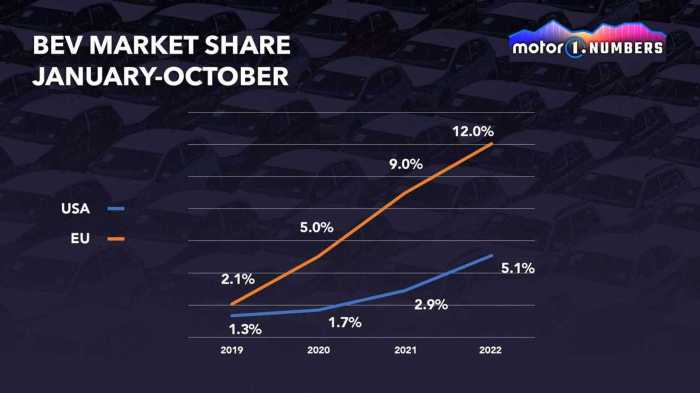
So, the race to electrify America’s roads is on, and it’s not a uniform sprint. Some states are blazing ahead, fueled by a combination of supportive policies, robust charging infrastructure, and a population eager to embrace electric vehicles. Others lag behind, hampered by cost concerns, range anxiety, and a lack of convenient charging options. But the overall trend is clear: EV adoption is accelerating, and understanding the factors driving this growth in different regions is crucial for shaping the future of transportation in the US.
The next five years will be key in seeing how these trends solidify and which states truly become EV powerhouses.









