EV regenerative braking system repair cost? Yeah, that’s a thing. It’s not always cheap to fix your electric car’s fancy braking system, and the price can vary wildly depending on what’s broken, your car’s make and model, and where you get it fixed. We’re diving into the nitty-gritty of what makes these repairs so expensive, from the tiny parts to the hefty labor bills, so you can be a little more prepared if (or when) something goes wrong.
This isn’t just about throwing money at the problem; we’ll cover DIY options, warranty considerations, and how to keep your regenerative braking system running smoothly for years to come.
Think of your EV’s regenerative braking system as a mini power plant in your car. It captures energy during braking, converting it back into electricity to recharge your battery. But like any complex system, it can malfunction. Understanding the different components, common issues, and the factors affecting repair costs is crucial to avoiding unexpected expenses. We’ll explore the ins and outs of regenerative braking, from the most frequent problems to how much you can expect to pay for repairs, and how to possibly avoid those hefty bills.
Understanding EV Regenerative Braking Systems: EV Regenerative Braking System Repair Cost
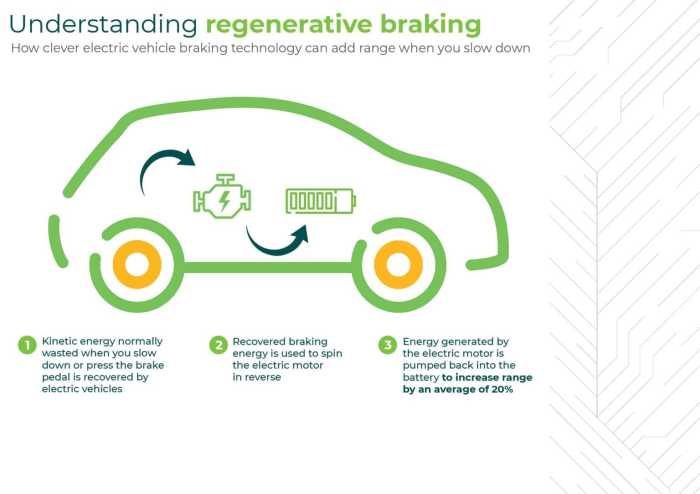
Regenerative braking is a key technology enabling the increased efficiency and range of electric vehicles (EVs). It’s a system that converts some of the kinetic energy lost during braking into electricity, recharging the vehicle’s battery. This differs significantly from traditional braking systems that dissipate energy as heat. Understanding how this system works, its components, and variations is crucial for anyone interested in EVs.Regenerative braking systems, at their core, cleverly reuse energy that would otherwise be wasted.
This leads to improved fuel efficiency (or, more accurately, energy efficiency) and contributes to a smoother driving experience. Different manufacturers implement this technology in various ways, resulting in a range of performance characteristics.
Components of a Typical EV Regenerative Braking System
A typical regenerative braking system involves several key components working together. These include the electric motor, the power inverter, the battery management system (BMS), and the braking control unit. The electric motor acts as both a motor and a generator, converting kinetic energy into electrical energy during braking. The power inverter manages the flow of electricity between the motor and the battery, ensuring efficient energy conversion and storage.
The BMS monitors the battery’s state of charge and prevents overcharging or damage. Finally, the braking control unit coordinates the regenerative braking with the friction brakes, ensuring smooth and safe deceleration.
How Regenerative Braking Works in Different EV Models
The implementation of regenerative braking varies significantly across EV models. Some systems offer a single level of regenerative braking, automatically engaging when the driver releases the accelerator pedal. Others provide multiple levels of adjustable regenerative braking, allowing the driver to customize the intensity of energy recovery. For example, some vehicles allow drivers to select “low,” “medium,” or “high” regeneration settings, offering a range from gentle deceleration to more aggressive energy recapture.
The higher the setting, the more significant the energy recovery but potentially also the more abrupt the deceleration. Tesla vehicles, for example, are known for their highly customizable regenerative braking systems, allowing for one-pedal driving in some modes.
Types of Regenerative Braking Systems
Several types of regenerative braking systems exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. One common type is the “series” regenerative braking system, where the motor is directly connected to the wheels and acts as a generator during braking. Another type is the “parallel” hybrid system, where the regenerative braking system works in conjunction with a traditional friction braking system.
The specific type employed often depends on the overall vehicle architecture and design goals. More sophisticated systems might even incorporate predictive braking, using navigation data and sensor information to anticipate braking events and optimize energy recovery.
Energy Recovery Efficiency Comparison
The efficiency of regenerative braking systems varies depending on several factors, including the type of system, the driving style, and the environmental conditions. Generally, systems with adjustable regenerative braking settings tend to offer greater flexibility and potential for higher energy recovery. However, even the most efficient systems are not able to recover 100% of the kinetic energy during braking.
Factors such as heat loss in the motor and inverter, and limitations in battery charging rates, all contribute to losses. While precise figures are hard to pin down without specific system details, studies have shown that regenerative braking can recover anywhere from 10% to 30% of the total braking energy, significantly reducing overall energy consumption.
Common EV Regenerative Braking System Failures
Regenerative braking, while offering efficiency and performance benefits in electric vehicles, isn’t immune to malfunctions. Understanding the common points of failure and their symptoms is crucial for both EV owners and mechanics. This section will Artikel frequent issues, typical causes, and illustrative real-world scenarios.While the entire system can be complex, failures often stem from specific components experiencing wear and tear or encountering unexpected stresses.
These failures can manifest in subtle ways, initially impacting performance before escalating into more significant problems. Early diagnosis is key to preventing larger, more costly repairs.
Frequent Causes of Regenerative Braking System Malfunctions
Several factors contribute to regenerative braking system failures. These include degradation of components due to age and use, manufacturing defects, and damage from external sources such as impacts or exposure to extreme environmental conditions. Over time, components like the motor, inverter, and high-voltage battery experience wear and tear, increasing the likelihood of malfunction. Additionally, software glitches in the control systems can also lead to regenerative braking problems.
EV regenerative braking system repair can be pricey, depending on the issue. A major component failure might mean a hefty bill, especially considering the battery’s role in the system. Learning about responsible battery disposal is key, though, so check out this article on How to recycle EV batteries in 2025 to understand the long-term implications. Ultimately, understanding battery recycling helps put the cost of regenerative braking repairs in perspective.
Symptoms of a Failing Regenerative Braking System
A failing regenerative braking system may present various symptoms, depending on the specific component affected. Reduced regenerative braking effect is the most obvious sign; you might notice less engine braking than usual, requiring more reliance on friction brakes. Error messages displayed on the vehicle’s dashboard are another common indicator. In more severe cases, the regenerative braking system may completely fail, leaving you reliant solely on friction brakes, potentially leading to reduced stopping power and increased brake wear.
Unusual noises emanating from the motor or drivetrain could also point towards a problem.
Components Prone to Failure and Typical Lifespan
The lifespan of components within the regenerative braking system varies significantly depending on factors like driving style, environmental conditions, and vehicle usage. However, some components are more prone to failure than others. The inverter, a critical component responsible for controlling the power flow to the motor, is susceptible to overheating and eventual failure, potentially lasting anywhere from 5 to 10 years, depending on usage.
The high-voltage battery, while generally robust, can degrade over time, reducing its capacity to effectively support regenerative braking. Its lifespan is typically projected to be around 8-10 years, but this is heavily influenced by charging habits and environmental factors. The electric motor itself, while durable, can suffer from wear and tear on its bearings or windings, eventually leading to reduced efficiency or complete failure.
A well-maintained motor could last for 10+ years but may require periodic maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Real-World Scenarios Illustrating Common Regenerative Braking System Issues, EV regenerative braking system repair cost
Imagine a scenario where an EV driver frequently uses aggressive regenerative braking in hilly terrain. The constant high-current demands could lead to premature overheating and failure of the inverter. Another example could be a vehicle exposed to extreme temperatures (e.g., prolonged periods of intense heat or cold). This could cause degradation of the battery cells, reducing their ability to effectively support regenerative braking.
In a different scenario, a sudden impact, like a collision, could damage the motor or its wiring harness, resulting in a complete loss of regenerative braking functionality. These scenarios highlight the importance of regular maintenance and mindful driving habits to prolong the lifespan of the regenerative braking system.
Repair Costs
Repairing a malfunctioning regenerative braking system in an electric vehicle can be a significant expense, varying widely depending on several interconnected factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for EV owners to budget effectively and make informed decisions regarding repairs. This section delves into the key cost drivers, providing a framework for estimating potential repair bills.
Factors Influencing Repair Costs
The total cost of repairing an EV’s regenerative braking system is determined by a complex interplay of factors. These can be broadly categorized as labor costs, part costs, and diagnostic fees. Labor costs are influenced by the mechanic’s hourly rate and the time required for the repair. Part costs vary dramatically depending on the specific component needing replacement and whether OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts or aftermarket alternatives are used.
Diagnostic fees cover the initial assessment and troubleshooting of the problem, often involving specialized diagnostic equipment. The severity of the issue—a minor component failure versus a major system overhaul—significantly impacts the overall expense.
Repair Cost Comparison Across EV Makes and Models
Predicting precise repair costs is difficult due to the wide range of EV models and the variability in labor rates across different service centers. However, a general comparison can illustrate the potential cost differences. The following table provides illustrative examples, and actual costs may vary considerably based on location, specific repair needs, and the chosen repair facility. Remember, these figures are estimations and should not be considered definitive.
| Make/Model | Part Cost (USD) | Labor Cost (USD) | Total Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tesla Model 3 (minor sensor replacement) | 200 | 300 | 500 |
| Chevrolet Bolt (major inverter failure) | 2000 | 1000 | 3000 |
| Nissan Leaf (regenerative braking module repair) | 1500 | 800 | 2300 |
| Ford Mustang Mach-E (brake caliper replacement) | 500 | 500 | 1000 |
Cost Differences: Minor vs. Major System Failures
Repair costs differ drastically between minor component failures and major system malfunctions. A minor repair, such as replacing a faulty sensor or a damaged wire, might only cost a few hundred dollars. In contrast, a major failure, such as a damaged inverter or a malfunctioning regenerative braking control unit, could easily cost several thousand dollars due to the high cost of these components and the extensive labor involved in their replacement or repair.
For example, replacing a single sensor might only require a couple of hours of labor, while replacing a major component like an inverter could take a full day or more.
Hierarchical Structure of Factors Affecting Repair Costs
The most significant factor influencing repair cost is the severity of the system failure. This encompasses the specific component that failed and the extent of the damage. Following this, part costs play a substantial role, with OEM parts generally more expensive than aftermarket options. Finally, labor costs and diagnostic fees contribute to the overall cost, but their impact is typically less than the cost of the parts themselves, especially in cases of major system failures.
DIY Repair vs. Professional Service
So, you’re facing a potential repair on your EV’s regenerative braking system. The big question is: DIY or pro? Both options have their own set of advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice depends heavily on your mechanical aptitude, comfort level, and the specific nature of the repair.Attempting a DIY repair can seem appealing – potentially saving you a chunk of cash.
However, working on an EV’s braking system is significantly different from working on a gas-powered car’s brakes. High-voltage systems are involved, posing serious risks if you’re not familiar with proper safety protocols. Professional mechanics possess specialized knowledge and tools, guaranteeing a safer and often more efficient repair.
DIY Repair Advantages and Disadvantages
DIY repairs offer the potential for significant cost savings, providing a sense of accomplishment and a deeper understanding of your vehicle. However, incorrect repairs can lead to serious safety hazards, void warranties, and ultimately, cost more in the long run than professional service. Lack of specialized tools and expertise is another significant disadvantage. The complexity of EV systems makes DIY repair challenging, even for experienced mechanics.
Professional Service Advantages and Disadvantages
Professional service offers peace of mind, ensuring the repair is completed correctly and safely. Professionals have the specialized tools and knowledge to diagnose and fix problems efficiently, minimizing downtime. However, professional repairs are significantly more expensive than DIY repairs. Finding a qualified EV mechanic might also be a challenge depending on your location.
Simple Repair Guide: Replacing a Worn Brake Pad
Replacing a worn brake pad is one of thefew* regenerative braking system repairs that might be suitable for a DIY approach, provided you have basic mechanical skills and understand the safety precautions. Remember, this is a simplified example and may not apply to all EV models. Always consult your vehicle’s service manual before attempting any repair.
- Safety First: Disconnect the vehicle’s battery and ensure the high-voltage system is deactivated before starting any work. Consult your owner’s manual for specific procedures.
- Gather Tools: You’ll need a jack, jack stands, wheel chocks, socket wrench set, brake caliper tool (to compress the piston), new brake pads, and gloves.
- Remove the Wheel: Securely lift the vehicle using the jack and place it on jack stands. Remove the wheel.
- Access the Brake Caliper: Locate the brake caliper and carefully remove the retaining pins or bolts.
- Compress the Caliper Piston: Use the brake caliper tool to compress the piston, creating space for the new brake pads.
- Install New Brake Pads: Carefully install the new brake pads, ensuring they are properly seated.
- Reassemble: Reinstall the retaining pins or bolts, the wheel, and lower the vehicle.
- Test the Brakes: Carefully test the brakes in a safe area, ensuring they function correctly.
Potential Risks and Liabilities of DIY Repairs
DIY repairs carry inherent risks, including:
- Electrical Shock: High-voltage systems in EVs pose a significant risk of electric shock, potentially leading to serious injury or death.
- Brake Failure: Improper repair can result in brake failure, leading to accidents and injuries.
- Warranty Voiding: DIY repairs may void your vehicle’s warranty, leaving you responsible for any future issues.
- Damage to Components: Improper tools or techniques can damage other components, increasing repair costs.
Tools and Equipment Checklist for Basic Regenerative Braking System Repair
This checklist is for basic repairs, like pad replacement. More complex repairs will require additional specialized tools.
- Jack and Jack Stands
- Wheel Chocks
- Socket Wrench Set (Metric)
- Brake Caliper Compression Tool
- New Brake Pads (correct specification for your vehicle)
- Gloves (work gloves and possibly insulated gloves for electrical work)
- Safety Glasses
- Vehicle Service Manual
- Multimeter (to check for voltage and continuity – essential for high-voltage systems)
Warranty Coverage and Repair Options
Navigating the complexities of EV warranties, especially when it comes to expensive components like the regenerative braking system, can feel like decoding a secret language. Understanding your coverage and available repair options is crucial to avoiding unexpected costs. This section clarifies how warranties typically address regenerative braking system issues and Artikels alternative repair strategies.Your EV’s warranty likely covers defects in materials and workmanship for the regenerative braking system, but the specifics vary widely between manufacturers and models.
The warranty period itself might range from 3 to 8 years or a certain mileage limit, and certain conditions must be met, such as regular maintenance according to the manufacturer’s schedule. Exclusions often exist for damage caused by accidents, misuse, or modifications. Knowing the precise terms of your warranty is key.
Warranty Claim Process
Filing a warranty claim typically begins with contacting your dealership or authorized service center. You’ll need to provide details about the issue, including when it started, the symptoms, and any relevant documentation like purchase records. The service center will then diagnose the problem. If the issue is covered under warranty, they’ll typically repair or replace the faulty components at no cost to you.
However, if the problem stems from misuse or neglect, the warranty may not apply, and you’ll be responsible for the repair costs. Some manufacturers have online portals for submitting warranty claims, streamlining the process.
Alternative Repair Options
If your warranty doesn’t cover the repair or has expired, several alternative options exist. Using certified pre-owned parts can significantly reduce costs compared to new components from the dealership. These parts are usually inspected and tested to ensure they meet certain quality standards. Third-party repair shops specializing in EVs might also offer more competitive pricing than dealerships, though it’s crucial to ensure they have experience with your specific EV model and possess the necessary diagnostic tools and expertise.
Always verify the shop’s reputation and certifications before entrusting your vehicle to them.
Examples of Warranty Clauses
While specific wording varies, here are illustrative examples reflecting common warranty approaches to regenerative braking systems:
Example 1 (Manufacturer A): “The regenerative braking system is covered under the vehicle’s limited warranty for a period of 5 years or 60,000 miles, whichever comes first, against defects in materials and workmanship under normal use and maintenance.”
Example 2 (Manufacturer B): “The high-voltage components of the regenerative braking system, including the motor and inverter, are covered for 8 years or 100,000 miles, excluding damage resulting from accidents or unauthorized modifications.”
So, you’re thinking about EV repair costs? Regenerative braking system repair can be pricey, depending on the issue. But, before you freak out about that, consider the long-term savings; check out this article on EV charging cost per mile vs gas in 2025 to see how much you could save on fuel. Ultimately, those savings might offset some of the potential regenerative braking repair expenses down the line.
These examples highlight the variation in warranty periods and exclusions. Always carefully review your specific vehicle’s warranty documentation for precise details concerning regenerative braking system coverage. Don’t hesitate to contact your manufacturer’s customer service if you have any questions or require clarification.
Preventive Maintenance and System Longevity

Keeping your EV’s regenerative braking system in top shape isn’t just about avoiding costly repairs; it’s about maximizing efficiency and ensuring a smooth, safe driving experience. Regular maintenance and mindful driving habits significantly impact the system’s lifespan and performance. Think of it like regularly changing the oil in a gas car – preventative care pays off big time.Regular maintenance and careful driving significantly impact the longevity and efficiency of your EV’s regenerative braking system.
Neglecting these aspects can lead to premature wear and tear, ultimately resulting in costly repairs. By understanding the system’s vulnerabilities and adopting preventative measures, you can significantly extend its lifespan and enjoy optimal performance.
Driving Habits and Regenerative Braking System Longevity
Aggressive driving habits, such as frequent hard braking and rapid acceleration, put considerable stress on the regenerative braking system. These actions generate excessive heat, which can damage components like the motor, inverter, and battery. Conversely, smooth and predictable driving, with gentle braking and acceleration, minimizes stress on the system, promoting longevity. For example, anticipating traffic slowdowns and gently easing off the accelerator allows for more efficient energy recapture via regenerative braking, reducing the need for friction braking.
This reduces wear on the brake pads and extends the lifespan of the entire system.
Importance of Regular Inspections and Diagnostics
Regular inspections and diagnostic checks are crucial for early detection of potential problems within the regenerative braking system. These checks should include visual inspections for any signs of damage or wear, as well as electronic diagnostics to assess the performance of the system’s various components. A qualified technician can identify issues such as faulty sensors, degraded motor windings, or problems with the power electronics before they escalate into major failures.
Think of it like a regular checkup at the doctor – catching problems early can prevent more serious, and costly, issues down the line. Many modern EVs offer onboard diagnostic capabilities, providing early warning signs of potential problems. Paying attention to these warnings is essential.
Preventive Maintenance Recommendations
A comprehensive preventive maintenance plan should incorporate several key aspects. Firstly, adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals is essential. These schedules often include software updates that can optimize the regenerative braking system’s performance and address potential bugs. Secondly, regularly inspecting the brake pads and rotors for wear is crucial, as these components play a supporting role in the regenerative braking process.
Excessive wear on these friction-based components suggests potential issues with the regenerative system’s ability to manage braking effectively. Finally, keeping the vehicle’s battery in optimal condition is vital, as a degraded battery can negatively impact the regenerative braking system’s efficiency and performance. This includes ensuring proper charging practices and avoiding extreme temperatures.
Concluding Remarks
So, while the cost of repairing an EV’s regenerative braking system can definitely be a sticker shock, understanding the factors involved empowers you. Whether you’re facing a minor component replacement or a major system failure, knowing your options – from DIY fixes to warranty claims – can save you money and frustration. Remember, preventative maintenance and smart driving habits can significantly extend the life of your system, minimizing the chances of expensive repairs down the line.
Stay informed, stay safe, and keep those electrons flowing!









