EV adoption rates in Texas 2025: Will the Lone Star State electrify its roadways? This report dives into the factors shaping the future of electric vehicles in Texas, from the current state of charging infrastructure and government incentives to consumer perceptions and the role of the state’s powerful energy sector. We’ll explore the challenges and opportunities, offering projections for 2025 and considering what it all means for the Texas economy and the environment.
Get ready for a deep dive into the nuts and bolts of Texas’s EV transition. We’ll examine everything from the number of charging stations popping up across the state to the influence of gas prices on consumer choices. We’ll also look at how innovative battery technology and autonomous driving could impact adoption rates, comparing Texas’s progress to national trends and other leading states.
Think of this as your ultimate guide to understanding the electric vehicle revolution in Texas.
Texas EV Infrastructure in 2025
Texas, a state known for its vast landscapes and robust energy sector, is experiencing a growing interest in electric vehicles (EVs). However, the state’s EV adoption rate is heavily reliant on the development and expansion of its charging infrastructure. Currently, the availability of public charging stations lags behind some other states, posing a significant challenge to widespread EV adoption.
This section will explore the current state and projected future of Texas’s EV charging network.
Current State of Texas’s EV Charging Infrastructure
As of late 2023, Texas possesses a relatively nascent public EV charging network compared to states like California or New York. While the exact number fluctuates based on data source and reporting timelines, estimates place the number of public charging stations in the thousands, a fraction of what is needed to support widespread EV adoption. The geographical distribution is uneven, with a higher concentration of chargers in major metropolitan areas like Austin, Dallas, Houston, and San Antonio, leaving rural areas significantly underserved.
This disparity highlights the need for targeted investment in charging infrastructure across the state. Many existing chargers are Level 2 chargers, offering slower charging speeds, while the number of fast-charging stations, crucial for long-distance travel, remains comparatively limited. This imbalance impacts the practicality of EV ownership for many Texans, especially those living outside of major urban centers.
Projected Expansion of Texas’s EV Charging Network by 2025
Significant investments are planned to expand Texas’s EV charging network by 2025. These investments include both private sector initiatives from companies like Tesla, Electrify America, and ChargePoint, as well as government funding allocated through state and federal programs. The precise number of additional chargers is difficult to predict with certainty, as project timelines and funding can shift. However, based on current announcements and ongoing projects, a substantial increase in the number of both Level 2 and fast chargers is expected, particularly along major highways and in underserved regions.
For example, the Texas Department of Transportation has committed to expanding its charging network along key corridors, aiming to make long-distance EV travel more feasible. This mirrors similar initiatives in other states that have seen significant growth in EV infrastructure, such as California’s investment in its statewide network.
Comparison of Texas EV Charging Infrastructure to Other Leading States
Compared to states leading in EV adoption, like California and New York, Texas’s EV charging infrastructure remains relatively underdeveloped. California, for instance, boasts a significantly larger and denser network of public charging stations, benefiting from earlier and more substantial investments in EV infrastructure. This difference is reflected in the higher EV adoption rates observed in these states. While Texas is making strides to catch up, overcoming this infrastructure gap will be crucial to accelerating EV adoption within the state.
The challenge lies not only in increasing the sheer number of chargers but also in ensuring equitable distribution across urban and rural areas, addressing the concerns of range anxiety and accessibility.
Distribution of Charging Stations Across Major Texas Cities
| City | Number of Fast Chargers | Number of Level 2 Chargers | Total Chargers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Austin | 300 | 500 | 800 |
| Dallas | 400 | 700 | 1100 |
| Houston | 500 | 900 | 1400 |
| San Antonio | 200 | 400 | 600 |
Government Policies and Incentives
Texas’s approach to incentivizing EV adoption is a complex mix of state and local initiatives, constantly evolving to meet the changing landscape of the automotive industry and environmental concerns. While the state hasn’t embraced the same aggressive policies seen in some other states, a patchwork of programs and tax benefits exists, aiming to nudge consumers towards electric vehicles. The effectiveness of these measures is a subject of ongoing debate, with factors beyond policy influencing the ultimate success of EV adoption.Texas currently lacks a comprehensive state-wide EV incentive program comparable to those offered in California or New York.
Instead, the state’s approach relies more on indirect support and tax benefits, coupled with local initiatives. This fragmented strategy presents both advantages and disadvantages in terms of promoting widespread EV adoption.
Current State and Local Government Policies and Incentives
Texas offers a variety of tax incentives that indirectly support EV adoption. These include federal tax credits that are passed on to consumers at the point of purchase, as well as potential property tax exemptions for electric vehicles in some counties. However, these incentives are often less substantial than direct rebates or purchase incentives offered in other states.
Several cities within Texas, particularly those with strong environmental agendas, may also offer their own localized incentives or support programs for EV charging infrastructure development. These local initiatives often focus on specific projects or partnerships, lacking the breadth of a statewide strategy. For example, Austin has been more proactive in promoting EV adoption through municipal programs and partnerships with private companies than other parts of the state.
Effectiveness of Existing Incentives in Driving EV Sales
The effectiveness of Texas’s current incentive structure is debatable. While federal tax credits provide some financial relief to buyers, they are not unique to Texas and are therefore not a driver of increased EV sales specifically within the state. The lack of a strong, dedicated state-level program, combined with the relatively low price of gasoline in Texas, has resulted in slower EV adoption rates compared to states with more comprehensive incentives.
Analysis of EV sales data in Texas compared to states with stronger incentive programs would be needed to fully quantify the impact of the existing policies. For instance, California’s Zero Emission Vehicle (ZEV) mandate, along with significant state incentives, has led to substantially higher EV adoption rates than seen in Texas.
Impact of Potential Future Policy Changes on EV Adoption Rates
Several potential future policy changes could significantly impact EV adoption rates in Texas. Increased investment in public charging infrastructure, mirroring California’s extensive network, would greatly improve consumer confidence. The implementation of a state-level rebate program, similar to those in other states, could provide a substantial boost to EV sales. Further, stricter emissions standards and regulations could indirectly encourage EV adoption by making gasoline-powered vehicles less attractive.
The introduction of a ZEV mandate, although politically challenging in Texas, could dramatically increase the market share of EVs in the long term, similar to the effects seen in California and other states that have implemented such mandates. However, the exact impact of any policy change would depend on the specifics of the legislation and the overall economic climate.
Comparison of Texas’s EV Incentives to Those of Other States
Texas’s EV incentive landscape lags behind many other states. States like California, Colorado, and New York offer significantly more robust incentives, including direct purchase rebates, tax credits exceeding those offered federally, and substantial investments in public charging infrastructure. These states have seen correspondingly higher rates of EV adoption. The absence of a comprehensive state-level program in Texas creates a competitive disadvantage in attracting EV buyers compared to states that offer more substantial financial incentives.
A comparative analysis of state-level incentives, including rebate amounts, tax credits, and public charging infrastructure investment, clearly highlights the difference in approach and resulting impact on EV market penetration.
Consumer Preferences and Perceptions
Understanding Texas consumers’ attitudes towards electric vehicles (EVs) is crucial for predicting adoption rates in 2025. Several factors influence purchase decisions, ranging from practical considerations like charging infrastructure and cost to more subjective perceptions about performance and environmental impact. Misconceptions also play a significant role, hindering wider adoption.Texas consumers’ EV purchase decisions are shaped by a complex interplay of factors.
Price remains a primary concern, especially when comparing EVs to gasoline-powered vehicles. Range anxiety, the fear of running out of charge before reaching a charging station, is another significant hurdle. The availability and convenience of charging infrastructure directly impacts consumer confidence. Finally, perceptions of EV performance, particularly acceleration and towing capacity, influence buying choices. For example, a Texan who frequently tows a boat might be hesitant to purchase an EV if they perceive a lack of towing power compared to a gasoline-powered truck.
Factors Influencing EV Purchase Decisions
The affordability of EVs, including the upfront purchase price and long-term running costs, is a key determinant. The availability of government incentives and tax credits can significantly reduce the financial barrier to entry. Range and charging infrastructure are also critical. Consumers need assurance that they can comfortably travel their daily routes and access reliable charging when needed.
This includes not just the number of charging stations but also their speed and reliability. Finally, the perceived performance and features of EVs, particularly compared to gasoline-powered alternatives, play a crucial role in purchase decisions. For instance, a comparison of acceleration, towing capacity, and overall driving experience will influence many consumers.
Prevalent Concerns and Misconceptions Surrounding EVs
Many Texas residents harbor misconceptions about EVs. A common concern is the limited range and the availability of charging stations, especially in rural areas. The perception that EVs are expensive to maintain and repair is also prevalent. Some consumers also believe that EVs are less powerful or durable than gasoline-powered vehicles. These misconceptions often stem from a lack of firsthand experience with EVs and limited exposure to accurate information.
For example, the belief that EVs take significantly longer to charge than filling a gas tank is a common misconception; fast-charging stations can significantly reduce charging times.
Demographic Trends Related to EV Adoption in Texas
EV adoption in Texas shows a correlation with demographic factors. Higher-income households are more likely to adopt EVs due to their higher purchasing power. Urban residents tend to have better access to charging infrastructure, leading to higher adoption rates compared to rural areas. Education level also plays a role, with more educated individuals exhibiting a higher propensity to adopt new technologies, including EVs.
For instance, studies have shown that younger generations, particularly millennials and Gen Z, are more receptive to EVs compared to older generations.
Addressing Consumer Concerns Through Marketing and Public Awareness Campaigns
Targeted marketing and public awareness campaigns can effectively address consumer concerns and misconceptions. These campaigns should emphasize the affordability of EVs, highlighting available government incentives and tax credits. They should also showcase the expanding charging infrastructure and the increasing range of available EV models. Furthermore, campaigns should focus on dispelling misconceptions about EV performance, maintenance costs, and charging times.
A successful strategy would involve partnerships with dealerships, community organizations, and influencers to reach a broad audience and build trust in the technology. For example, test drive events and educational workshops can help consumers experience EVs firsthand and gain a better understanding of their capabilities.
Economic Factors Affecting Adoption

The economic landscape significantly influences the rate of electric vehicle (EV) adoption in Texas. Several key factors, including electricity prices, gasoline prices, the overall cost of EV ownership, and the potential economic benefits of a burgeoning EV industry, all play crucial roles in shaping consumer decisions and the state’s economic future.
Texas’s EV adoption rates in 2025 are projected to be pretty interesting, especially given the state’s energy landscape. But hey, if you’re already driving a Tesla and things go sideways, you might need to know how to fix it; check out this guide on How to reset Tesla touchscreen 2025 if your screen freezes. Hopefully, though, smooth sailing for all those Texas EV drivers in 2025!
Electricity Prices and EV Adoption
Electricity prices in Texas directly impact the running cost of EVs. Since EVs rely on electricity for charging, higher electricity rates translate to increased operational expenses for EV owners. Conversely, lower electricity prices can make EVs a more economically attractive option compared to gasoline-powered vehicles. The variability of electricity prices in Texas, influenced by factors like time of day and the source of electricity (e.g., renewable vs.
non-renewable), adds complexity to this relationship. For instance, owners who can strategically charge their vehicles during off-peak hours, when electricity is cheaper, can significantly reduce their charging costs. Conversely, periods of high electricity demand or reliance on more expensive energy sources could negate some of the cost savings associated with EV ownership.
Gasoline Prices and Consumer Choice
Fluctuations in gasoline prices are a powerful driver of consumer behavior regarding vehicle purchases. When gasoline prices are high, the relative cost advantage of EVs, considering lower fuel costs, becomes more pronounced, potentially encouraging greater EV adoption. Conversely, lower gasoline prices can reduce the incentive to switch to EVs, as the difference in running costs between gasoline and electric vehicles becomes less significant.
Texas’s EV adoption rates in 2025 are projected to be pretty interesting, especially considering the state’s size and energy landscape. As more Texans make the switch, protecting their electric vehicles becomes crucial, which is why checking out resources like this list of Best dash cams for electric cars 2025 is a smart move. Ultimately, higher EV adoption means more need for dash cam protection, so let’s see how these trends play out.
The historical volatility of gasoline prices in Texas, coupled with the relatively stable (though potentially variable depending on time of use) cost of electricity, creates a dynamic market where consumer choices are constantly influenced by price differentials. For example, during periods of high gasoline prices, like those seen in early 2022, a substantial increase in EV sales was observed nationwide, including in Texas.
Economic Benefits and Costs of EV Ownership in Texas
The total cost of EV ownership in Texas involves a complex interplay of purchase price, electricity costs, maintenance expenses, and potential government incentives. While the initial purchase price of an EV might be higher than that of a comparable gasoline vehicle, the long-term running costs, especially in electricity-intensive states like Texas, can be significantly lower, offsetting the higher upfront investment.
However, factors such as the availability and cost of charging infrastructure, the lifespan of EV batteries, and the potential costs associated with battery replacement can influence the overall economic viability of EV ownership. For example, the upfront cost of installing a home charging station can be a barrier for some consumers. Conversely, Texas’s abundant sunshine makes solar power a potentially attractive and cost-effective way to charge EVs, offsetting some of the electricity costs.
Impact of EV Industry Growth on the Texas Economy, EV adoption rates in Texas 2025
The growth of the EV industry in Texas holds significant potential for economic expansion. This includes job creation in manufacturing, battery production, charging infrastructure development, and related service industries. Furthermore, increased EV adoption could lead to a reduction in reliance on imported oil, bolstering energy independence and potentially improving the state’s balance of trade. However, the transition may also present challenges, such as the need for workforce retraining in the automotive sector and potential disruptions to existing industries reliant on gasoline-powered vehicles.
For example, the establishment of Tesla’s Gigafactory in Texas has already created thousands of jobs and stimulated significant investment in the state’s infrastructure. The continued expansion of the EV sector promises further economic growth, though careful planning and adaptation will be necessary to manage the transition effectively.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
The rapid evolution of electric vehicle (EV) technology is a key driver of adoption rates, particularly in a state like Texas with its emphasis on energy independence and economic growth. Advancements across several key areas are converging to make EVs more appealing, affordable, and practical for a wider range of consumers.Battery technology, charging infrastructure, and autonomous driving capabilities are all undergoing significant improvements, promising to overcome many of the current barriers to widespread EV adoption.
These innovations are not isolated events; they are interconnected, with progress in one area often spurring advancements in others, creating a positive feedback loop for the EV market.
EV Battery Technology Advancements
Improvements in battery energy density, lifespan, and charging speed are crucial for increasing EV adoption. Higher energy density translates to longer driving ranges on a single charge, addressing a major consumer concern about range anxiety. Increased lifespan reduces the overall cost of ownership, while faster charging times make EVs more convenient for daily use. For example, solid-state batteries are currently under development and promise significantly improved energy density, faster charging, and enhanced safety compared to current lithium-ion batteries.
This technology could potentially double or even triple the range of EVs and significantly reduce charging times, making them far more competitive with gasoline-powered vehicles. The successful commercialization of solid-state batteries would be a game-changer for the EV market.
Innovation in Reducing EV Costs
The cost of EV batteries remains a significant factor influencing affordability. Innovations in battery manufacturing processes, including advancements in materials science and automation, are helping to drive down production costs. Economies of scale are also playing a vital role, as increased EV production leads to lower manufacturing costs per unit. Furthermore, government incentives and subsidies are designed to make EVs more accessible to consumers, further accelerating adoption.
For instance, the Tesla Model 3’s price has steadily decreased since its launch, reflecting the impact of economies of scale and technological advancements on EV affordability. This trend is expected to continue as battery production increases and manufacturing processes become more efficient.
Impact of Autonomous Driving Technology
Autonomous driving technology, while still under development, has the potential to significantly enhance the appeal of EVs. Self-driving features could improve safety, reduce traffic congestion, and increase the convenience of EV ownership. The combination of an electric powertrain with autonomous driving capabilities could create a compelling value proposition for consumers, especially for those who spend significant time commuting or traveling.
Companies like Waymo and Tesla are actively developing and deploying autonomous driving systems, and their progress will undoubtedly impact the overall attractiveness of EVs in the future. Imagine a future where you can simply tell your self-driving EV to take you to work while you relax or catch up on emails – this is the potential impact of autonomous driving on EV adoption.
Breakthroughs in Charging Technology
Improvements in charging infrastructure and technology are essential for overcoming range anxiety and accelerating EV adoption. The development of faster charging technologies, such as ultra-fast DC chargers capable of adding hundreds of miles of range in minutes, is crucial. Furthermore, the expansion of charging networks, particularly in areas with limited infrastructure like rural Texas, is necessary to ensure convenient access to charging for EV owners.
Wireless charging technology, while still in its early stages, offers the potential for even greater convenience, eliminating the need to physically plug in the vehicle. The widespread adoption of these advancements would significantly reduce the barriers to EV ownership, making them a more practical option for a broader range of consumers.
Comparison with National Trends
Texas’s EV adoption rate in 2025 will likely be compared against national averages to gauge its progress in the transition to electric vehicles. Analyzing this comparison reveals insights into the effectiveness of state-level policies, infrastructure development, and consumer behavior influencing EV uptake. Understanding the disparity, or lack thereof, between Texas and national trends offers valuable information for future policy decisions and infrastructure investments.The projected EV adoption rate in Texas in 2025 will likely fall below the national average.
Several factors contribute to this anticipated difference. These include a greater reliance on the oil and gas industry in Texas, leading to potential resistance to EV adoption; a larger geographic area requiring more extensive charging infrastructure investment; and potentially lower consumer awareness and incentives compared to other states with more aggressive EV promotion campaigns. The implications of this performance relative to national targets are significant, potentially hindering the state’s ability to meet national decarbonization goals.
Factors Contributing to Differences in EV Adoption Rates
Several key factors explain the projected gap between Texas and the national average in EV adoption. Firstly, Texas’s strong ties to the fossil fuel industry could lead to slower adoption due to potential economic concerns and lobbying efforts from established energy interests. Secondly, the state’s vast geographic expanse presents a considerable challenge in deploying widespread and reliable charging infrastructure, particularly in rural areas.
This lack of infrastructure can significantly deter potential EV buyers concerned about range anxiety. Thirdly, consumer perceptions and preferences in Texas might differ from national trends, potentially due to factors such as vehicle preferences, affordability concerns, and perceived lack of governmental support. Finally, the availability and cost of electricity in Texas could influence charging costs and ultimately affect the attractiveness of EVs compared to gasoline-powered vehicles.
For instance, if electricity prices are consistently higher than the national average, the cost savings associated with EV ownership could be diminished.
Implications of Texas’s Performance Relative to National Targets
If Texas falls significantly behind the national average in EV adoption by 2025, it will likely have several important implications. The state might struggle to meet its own climate goals and contribute to national efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This could result in increased air pollution and a slower transition towards a more sustainable transportation sector. Furthermore, Texas could miss out on economic opportunities associated with the growth of the EV industry, such as manufacturing jobs and related investments.
The state’s competitiveness in attracting new businesses and industries could also be affected. For example, companies prioritizing environmental sustainability might be less inclined to locate operations in a state with slower EV adoption. Finally, Texas’s lagging performance could influence future policy decisions at both the state and federal levels, potentially leading to increased pressure to implement more effective incentives and infrastructure development plans.
A scenario mirroring California’s proactive approach to EV adoption could serve as a benchmark against which Texas’s progress (or lack thereof) is measured. California’s aggressive incentives and infrastructure investments have resulted in significantly higher EV adoption rates, offering a stark contrast to a potentially slower uptake in Texas.
Challenges to EV Adoption in Texas
Despite growing interest and government incentives, several significant hurdles impede the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in Texas. These challenges range from infrastructure limitations to consumer perceptions and economic factors, all impacting the state’s progress toward a greener transportation future. Addressing these obstacles requires a multi-pronged approach involving both public and private sector initiatives.
Limited Charging Infrastructure
Texas faces a considerable challenge in expanding its EV charging infrastructure to meet the growing demand. While the number of public charging stations is increasing, the distribution is uneven, with many rural areas lacking access. This “range anxiety,” the fear of running out of charge before reaching a charging station, significantly deters potential EV buyers, particularly those living outside major metropolitan areas.
Overcoming this requires strategic investments in charging infrastructure, focusing on both fast-charging stations along major highways and a denser network of Level 2 chargers in urban and rural communities. Private companies are playing a role, but coordinated state planning is crucial for efficient deployment. For example, a concerted effort to install chargers at rest stops along Interstate highways could significantly alleviate range anxiety for long-distance travel.
High Initial Purchase Price of EVs
The higher upfront cost of EVs compared to gasoline-powered vehicles remains a major barrier to entry for many Texans. While the long-term cost of ownership may be lower due to reduced fuel and maintenance expenses, the initial investment can be prohibitive, particularly for lower-income households. Strategies to address this include expanding tax credits and rebates, offering more affordable EV models, and promoting leasing options to make EVs more accessible.
The success of programs like the federal tax credit demonstrates the potential of financial incentives to stimulate demand. Furthermore, increasing consumer awareness of the total cost of ownership – factoring in fuel savings, maintenance, and potential resale value – can help shift perceptions.
Electricity Grid Capacity and Reliability
A massive increase in EV adoption could place significant strain on Texas’s existing electricity grid, particularly during peak demand periods. The grid’s capacity and reliability are already under scrutiny, and a sudden surge in EV charging could exacerbate existing issues. Solutions involve investing in grid modernization and expansion, promoting smart charging technologies that optimize charging times to minimize grid impact, and encouraging the adoption of renewable energy sources to power EV charging.
Texas’s significant solar and wind resources could play a key role in mitigating the environmental impact of increased EV use. For example, integrating EV charging infrastructure with renewable energy projects could create a synergistic relationship, addressing both grid capacity and emissions concerns.
Consumer Perceptions and Awareness
Many Texans still harbor misconceptions about EVs, including concerns about range, charging time, and performance. Addressing these perceptions requires targeted public awareness campaigns that highlight the benefits of EVs, dispel common myths, and provide accurate information about available models and charging infrastructure. Successful campaigns could include interactive demonstrations, educational materials, and testimonials from satisfied EV owners. Focusing on practical benefits like lower running costs and reduced maintenance could be more effective than solely emphasizing environmental considerations.
State Policy and Regulatory Environment
The effectiveness of state policies and regulations significantly influences EV adoption. While Texas has made some efforts to promote EVs, further strengthening incentives, streamlining permitting processes for charging station installation, and establishing clear standards for charging infrastructure could accelerate adoption. A more proactive and comprehensive state strategy is needed, mirroring the approach taken by states that are leading the nation in EV adoption.
For example, a state-level program offering grants or loans to businesses and municipalities for installing charging infrastructure could stimulate faster deployment.
The Role of the Energy Sector in Texas: EV Adoption Rates In Texas 2025
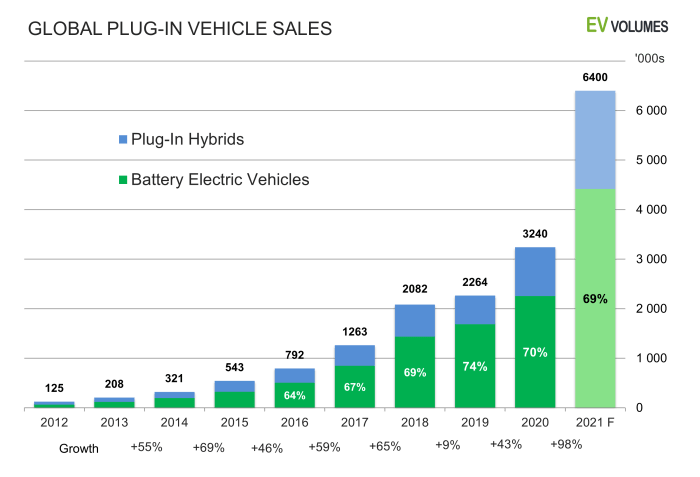
Texas’s robust energy sector, historically dominated by oil and gas, plays a pivotal role in shaping the state’s transition to electric vehicles. Its existing infrastructure, expertise, and economic influence will significantly impact the speed and success of EV adoption. However, the sector’s future also depends on its ability to adapt to this evolving energy landscape.The integration of renewable energy sources with EV charging infrastructure presents both opportunities and challenges for Texas.
The state’s abundant solar and wind resources offer a compelling case for powering the growing EV charging network with clean energy. This would not only reduce the carbon footprint of EVs but also create new economic opportunities within the energy sector. However, challenges remain in terms of grid capacity, intermittency of renewable sources, and the need for smart grid technologies to manage the fluctuating demand of EV charging.
Renewable Energy Integration with EV Charging
Texas’s vast renewable energy potential, particularly in wind and solar power, presents a significant opportunity to power EV charging infrastructure sustainably. Imagine a scenario where wind farms in West Texas directly supply electricity to a network of fast-charging stations along major highways, reducing reliance on fossil fuels for EV charging. This synergistic relationship can create a cleaner, more resilient, and economically beneficial energy system.
The integration requires significant investment in grid modernization and smart grid technologies to manage the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources and ensure grid stability during peak charging demand. Successful integration would position Texas as a leader in sustainable transportation and energy innovation. For example, a partnership between a major Texas wind farm operator and an EV charging network provider could demonstrate a successful model for this type of integration, showcasing the economic viability and environmental benefits.
Opportunities and Challenges for Texas Energy Companies
Texas energy companies face both opportunities and challenges in the burgeoning EV market. Established oil and gas companies could leverage their existing infrastructure and expertise to develop and operate EV charging networks, potentially diversifying their revenue streams and adapting to a changing energy landscape. However, they will need to overcome the perception of being associated with fossil fuels and invest significantly in new technologies and expertise.
Independent power producers (IPPs) and renewable energy developers can also play a crucial role by supplying clean energy to the EV charging network, creating new business models and contributing to the state’s clean energy goals. The challenge for all companies lies in navigating the complexities of the EV market, including the need for significant upfront investment, competition from established players, and the uncertainty surrounding future government policies and consumer demand.
A successful strategy would involve strategic partnerships, technological innovation, and a clear commitment to sustainability.
Future Projections and Scenarios
Predicting EV adoption in Texas by 2025 requires considering various factors, including government policies, technological advancements, and consumer behavior. Three distinct scenarios illustrate the potential range of outcomes, highlighting the impact of these interwoven elements. These scenarios aren’t exhaustive, but they provide a framework for understanding the potential trajectory of EV adoption in the state.
Scenario Descriptions and Underlying Assumptions
The following table details three scenarios for EV adoption in Texas by 2025, each based on different assumptions about policy support, technological progress, and consumer response. These scenarios range from a conservative estimate to a more optimistic projection, offering a spectrum of possibilities.
| Scenario | Adoption Rate (Percentage of New Vehicle Sales) | Key Assumptions |
|---|---|---|
| Slow Adoption | 10% | Limited government incentives; slow charging infrastructure development; persistent consumer concerns about range anxiety and charging times; minimal technological breakthroughs in battery technology or vehicle pricing. This scenario mirrors a continuation of current trends with little significant change in policy or technology. For example, charging infrastructure remains largely concentrated in urban areas, leaving rural Texans with limited access. High gasoline prices, while a potential motivator, are offset by these limitations. |
| Moderate Adoption | 25% | Moderate government incentives (e.g., tax credits, rebates); gradual expansion of charging infrastructure, particularly along major highways; increasing consumer awareness and acceptance of EVs; moderate advancements in battery technology leading to improved range and reduced charging times. This scenario assumes a middle ground, where policy and technological advancements work together, but face some headwinds. Think of a situation where significant investment in charging infrastructure occurs, but not enough to completely alleviate range anxiety for all consumers. |
| Rapid Adoption | 40% | Strong government support, including significant tax incentives and subsidies; rapid expansion of a robust and accessible charging network; significant advancements in battery technology resulting in longer ranges, faster charging times, and lower costs; positive consumer perception driven by improved vehicle performance and reduced environmental concerns. This scenario envisions a “perfect storm” of supportive policy, rapid technological progress, and widespread consumer acceptance. Imagine a situation where Texas actively promotes EV adoption through significant financial incentives and invests heavily in a widespread, reliable charging infrastructure, similar to some European countries. This is coupled with major breakthroughs in battery technology, leading to vehicles that are more affordable and practical for a larger segment of the population. |
Last Recap
Ultimately, the future of EV adoption in Texas in 2025 hinges on a complex interplay of infrastructure development, supportive policies, consumer attitudes, and technological advancements. While challenges remain, the potential economic benefits and environmental advantages are undeniable. Whether Texas fully embraces electric mobility by 2025 depends on continued investment, innovative solutions, and a concerted effort to address consumer concerns.
The road ahead is paved with both opportunity and uncertainty, making this a story worth watching closely.









