Cost to replace a serpentine belt? Yeah, that’s a thing. It’s not exactly the most glamorous car repair, but when that little rubber belt gives out, your whole engine can go kaput. This isn’t some rocket science, though – we’re breaking down everything you need to know about the cost, from DIY fixes to pro jobs, and everything in between.
Get ready to become a serpentine belt whisperer!
We’ll cover the average costs, what factors inflate (or deflate!) the price, and even walk you through how to replace it yourself if you’re feeling adventurous. Think of it as your one-stop shop for all things serpentine belt – because nobody wants to be stranded on the side of the road with a dead engine. We’ll even tackle some of those tricky questions you might have about your car’s specific needs.
Average Cost of Serpentine Belt Replacement

Replacing a serpentine belt is a relatively common and usually affordable car repair. However, the exact cost can vary depending on several factors. This section will break down the average costs, considering different vehicle types and influencing factors.The total cost of a serpentine belt replacement is primarily determined by two components: the cost of the belt itself (the part) and the labor cost charged by the mechanic.
Labor rates fluctuate based on geographical location, the shop’s reputation, and the mechanic’s experience. Part costs vary depending on the vehicle’s make, model, and year, as well as the brand of replacement belt chosen (OEM vs. aftermarket). Choosing a higher-quality, more durable belt might cost a bit more upfront but could potentially extend its lifespan.
Serpentine Belt Replacement Cost Breakdown by Vehicle Type
The following table provides a general estimate of the average costs associated with serpentine belt replacement for different vehicle types. Keep in mind that these are averages and actual costs may vary significantly. For instance, a luxury SUV will likely have a higher labor cost due to potentially more complex engine bays and higher hourly rates charged by the mechanic.
| Vehicle Type | Average Part Cost (USD) | Average Labor Cost (USD) | Total Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Car | $20 – $50 | $50 – $150 | $70 – $200 |
| Truck | $30 – $75 | $75 – $200 | $105 – $275 |
| SUV | $30 – $75 | $75 – $200 | $105 – $275 |
Factors Affecting Serpentine Belt Replacement Costs: Cost To Replace A Serpentine Belt
The cost of replacing a serpentine belt isn’t a fixed number; it varies depending on several interconnected factors. Understanding these variables can help you budget accurately and avoid unexpected expenses when your car needs this relatively common repair. Let’s delve into the key influences on the final price tag.
Vehicle Make and Model Impact on Replacement Costs
The make and model of your vehicle significantly influence the cost. Luxury cars, for example, often require more expensive parts, and accessing components in some vehicles might necessitate more labor-intensive disassembly. A simple belt replacement on a compact car might only require basic tools and straightforward access, while a high-end SUV might involve more complex procedures, potentially increasing labor costs.
Furthermore, the specific design of the engine bay can impact accessibility, adding time to the repair process. For instance, a car with a tightly packed engine bay will likely cost more to repair than a vehicle with ample space. The cost of the belt itself can also vary greatly. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) belts for certain models are pricier than those for others, due to material quality and brand reputation.
Geographic Location’s Influence on Pricing
Your geographic location plays a critical role in both labor rates and part pricing. Labor costs in major metropolitan areas tend to be higher than in smaller towns or rural areas due to higher cost of living and increased demand for skilled mechanics. Similarly, parts pricing can fluctuate based on local taxes, distribution networks, and even the prevalence of competition among auto parts retailers.
So, you’re wondering about the cost to replace a serpentine belt? It’s usually pretty cheap, a few bucks for the part and maybe an hour of labor. But, if you’re driving a Rolls-Royce, you probably aren’t sweating the small stuff – you’re more likely to use services like those offered by VIP concierge services for Rolls-Royce owners to handle even minor maintenance.
Back to that serpentine belt though, even for a Rolls, it’s still a relatively inexpensive fix.
A replacement belt purchased in a densely populated urban center might be more expensive than one bought in a less populated region. This is due to factors such as higher rent for retail spaces and increased transportation costs in busy cities.
Additional Services and Cost Implications
Often, a serpentine belt replacement isn’t an isolated repair. Mechanics might identify other issues during the process, leading to additional services and costs. For instance, if the belt is worn, it might indicate problems with the pulleys or tensioners. Replacing these components alongside the belt increases the total cost. Similarly, a mechanic might recommend replacing other related components like the water pump or idler pulleys, if they show signs of wear or damage.
These preventative measures, while adding to the immediate expense, can help avoid more costly repairs down the road. Ignoring these recommendations could lead to further damage and more extensive repairs in the future.
OEM vs. Aftermarket Parts: A Cost Comparison
The choice between OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) and aftermarket parts significantly impacts the total cost.
- OEM Parts: These are parts manufactured by the vehicle’s original manufacturer. They typically come with a higher price tag due to quality control, warranty, and brand reputation. However, they usually offer better performance and longevity. For example, an OEM serpentine belt for a high-end German sedan could cost significantly more than an aftermarket alternative.
- Aftermarket Parts: These are parts manufactured by companies other than the vehicle’s original manufacturer. They generally offer a lower price point, providing a cost-effective alternative. However, quality can vary, impacting durability and lifespan. A comparable aftermarket serpentine belt for the same German sedan would likely be cheaper but might not last as long.
DIY Serpentine Belt Replacement
Replacing your serpentine belt yourself can save you some serious cash, but it’s crucial to approach it safely and methodically. This isn’t rocket science, but a little know-how and the right tools are essential for a successful repair. Remember, if you’re uncomfortable with any step, it’s always best to take your car to a professional mechanic.
Necessary Tools and Safety Precautions
Before you even think about touching your car’s engine, safety should be your top priority. Always work in a well-ventilated area, and make sure your car is securely parked on a level surface and the engine is completely cool. Never work under a car supported only by a jack; use jack stands for stability. Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris, and consider using gloves to keep your hands clean.
| Tool | Purpose | Where to Find It |
|---|---|---|
| Wrench Set (metric and standard) | To loosen and tighten various bolts and fasteners. You’ll likely need different sizes depending on your car’s make and model. | Auto parts stores, hardware stores, or online retailers. |
| Socket Set (metric and standard) | Similar to a wrench set, but with sockets that fit over bolts for easier turning. Often comes with a ratchet for faster work. | Auto parts stores, hardware stores, or online retailers. |
| Screwdrivers (Phillips and flathead) | For removing various covers and panels that might be in the way. | Auto parts stores, hardware stores, or online retailers. |
| New Serpentine Belt | The replacement part. Make sure you get the correct belt for your car’s make, model, and year. | Auto parts stores, online retailers, or your car’s dealership. |
Step-by-Step Guide to Serpentine Belt Replacement
This guide provides a general overview; specific steps might vary slightly depending on your vehicle. Consult your car’s repair manual for detailed instructions specific to your model.
- Locate the Serpentine Belt: Identify the serpentine belt; it’s a long, rubber belt that wraps around several pulleys in your engine bay.
- Loosen the Tensioner: Most serpentine belts are held in place by a tensioner pulley. You’ll need to loosen this pulley using the appropriate wrench or socket to release tension on the belt.
- Remove the Belt: Once the tension is released, carefully guide the belt off the pulleys. Take note of the routing of the belt; this will help you install the new one correctly.
- Install the New Belt: Carefully route the new belt onto the pulleys, following the same path as the old belt. Ensure it sits correctly on all pulleys.
- Tighten the Tensioner: Tighten the tensioner pulley to secure the new belt. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual for the correct torque specifications.
- Check Belt Alignment and Tension: Visually inspect the belt to ensure it’s properly aligned and has adequate tension. A slightly loose or misaligned belt can lead to premature wear.
- Start the Engine: Start the engine and listen for any unusual noises. If you hear squealing or other problems, turn off the engine immediately and re-check your work.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
Replacing a serpentine belt is generally straightforward, but you might encounter a few hurdles.
- Difficulty Accessing the Tensioner: Some tensioners are located in tight spaces, making access challenging. Using the right tools and employing different angles can help.
- Broken or Stuck Bolts: If a bolt is rusted or stripped, applying penetrating oil and using the correct tools can help. In stubborn cases, you might need a professional’s assistance.
- Incorrect Belt Routing: If the belt isn’t routed correctly, it won’t function properly. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual or a diagram for the correct routing.
- Improper Tension: Too much or too little tension can damage the belt or other components. Consult your vehicle’s repair manual for the recommended tension specifications.
Professional Serpentine Belt Replacement

So, you’re facing a potentially troublesome serpentine belt issue. While tackling it yourself might seem appealing, professional replacement offers several key advantages, especially considering the potential consequences of a botched DIY job. Let’s dive into what a professional service entails and why it might be the better option for you.Professional replacement provides expertise, specialized tools, and often, a warranty – things you won’t necessarily have at your disposal at home.
This ultimately translates to peace of mind and a higher chance of a long-lasting, correctly installed belt.
Replacing a serpentine belt isn’t too expensive, usually under $100 for the part and labor, but preventative maintenance is key. Thinking about that cost, it makes you wonder about other regular maintenance like oil changes; check out this article on how often you should change your synthetic oil: How often should I change synthetic oil in my car?
. Regular oil changes, just like a timely belt replacement, can save you big bucks down the road by preventing engine problems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Professional vs. DIY Serpentine Belt Replacement
Choosing between professional and DIY replacement hinges on several factors. A professional mechanic brings experience and the right tools to the table, ensuring a smoother, more efficient repair. However, professional services come with a higher price tag. DIY, on the other hand, can save money but requires time, mechanical aptitude, and access to the necessary tools. A poorly executed DIY repair could lead to further damage and increased costs down the line.
The Typical Process of Professional Serpentine Belt Replacement
A professional serpentine belt replacement typically begins with a thorough inspection. The mechanic will assess the condition of the belt, looking for cracks, fraying, or glazing. They might also check the pulleys and tensioner for wear and tear. Once the diagnosis is complete, they’ll explain the necessary repairs and provide a cost estimate. The replacement itself involves removing the old belt, often using specialized tools to release tension, and installing the new belt, ensuring proper alignment and tension.
Finally, they’ll perform a test run to verify the system’s functionality.
Choosing a Mechanic: Reputation and Warranty
Selecting a reputable mechanic is crucial. Look for a shop with positive online reviews and a history of satisfied customers. Consider asking friends and family for recommendations. A good mechanic will be transparent about pricing and provide a detailed explanation of the work performed. Inquire about their warranty policy – a reputable shop will typically offer some form of warranty on parts and labor.
Warranty on Professional Serpentine Belt Replacements
Warranties on professional serpentine belt replacements vary depending on the shop and the specific parts used. Some shops might offer a 12-month/12,000-mile warranty, while others may offer a shorter or longer period. The warranty usually covers defects in materials and workmanship, but may not cover damage caused by other issues, such as neglect or misuse. Always carefully review the warranty terms and conditions before agreeing to the service.
For example, a shop might offer a 6-month warranty on the labor and parts, but this would not cover damage caused by a subsequent failure of a different component that places extra strain on the new belt.
Signs of a Worn Serpentine Belt
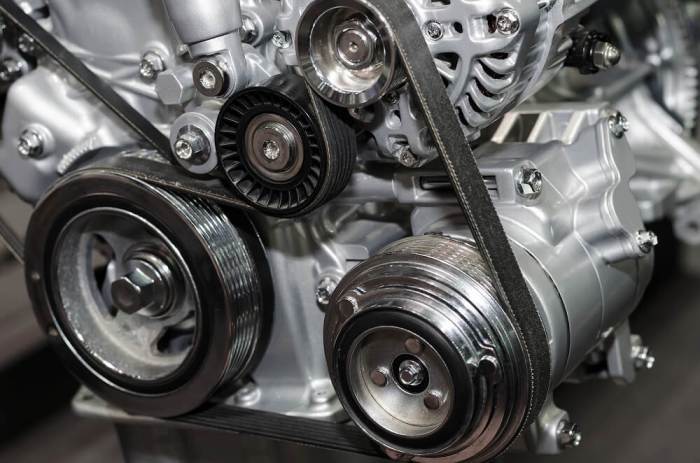

Ignoring a worn serpentine belt can lead to significant car trouble, so knowing the warning signs is crucial for preventing costly repairs. A failing belt can leave you stranded, and the damage it causes to other components can quickly escalate the repair bill. Regular checks are key to avoiding these problems.A worn serpentine belt shows several distinct signs, both visually and audibly.
These signs often develop gradually, giving you time to address the issue before complete failure. Catching these early indicators can save you money and hassle in the long run.
Visual Inspection of a Worn Serpentine Belt, Cost to replace a serpentine belt
Visually inspecting your serpentine belt is a simple yet effective way to identify potential problems. Compare your belt to the image of a new belt described below. A new belt will be smooth, uniformly colored, and show no signs of cracking or fraying. A worn belt will exhibit several distinct characteristics. Look for cracks along the edges or across the surface of the belt.
These cracks indicate weakening and impending failure. Also, check for glazing or a shiny appearance, suggesting that the rubber is becoming hard and losing its grip on the pulleys. Significant wear can lead to visible fraying, where the belt’s fabric begins to unravel. A worn belt might also show signs of significant stretching, appearing thinner or more elongated than a new belt.
Auditory Indicators of Serpentine Belt Wear
Besides visual cues, listen for unusual noises emanating from your engine compartment. A squealing or squeaking sound, especially when starting the engine or accelerating, is a classic sign of a slipping or worn serpentine belt. This noise happens because the belt is not gripping the pulleys properly due to wear, glazing, or a buildup of debris. Another potential indicator is a high-pitched whine, which often indicates that the belt is too tight or worn and rubbing against the pulleys or engine components.
A grinding sound, on the other hand, suggests severe belt wear or damage, possibly involving pulley damage as well.
Consequences of Driving with a Worn Serpentine Belt
Driving with a worn serpentine belt is risky. The belt’s primary function is to drive essential engine components like the alternator, power steering pump, and water pump. Failure of the belt means these components stop working. This can lead to a loss of power steering, making steering difficult or impossible, especially at low speeds. The alternator’s failure will drain your battery, potentially leaving you stranded with a dead battery.
A malfunctioning water pump will cause your engine to overheat, leading to potentially catastrophic engine damage. In short, a broken serpentine belt can result in expensive repairs, and even render your vehicle immobile.
Preventative Maintenance for Serpentine Belt Longevity
Regular preventative maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of your serpentine belt. This proactive approach will help you avoid unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs.
- Regular Visual Inspections: Visually inspect your serpentine belt every few months, looking for cracks, glazing, or fraying.
- Check Belt Tension: Periodically check the tension of the belt. A properly tensioned belt should have a slight give when pressed with your thumb.
- Clean the Belt: Use a clean cloth to wipe away any dirt, grease, or debris that may accumulate on the belt.
- Scheduled Replacements: Consult your owner’s manual for recommended replacement intervals. Generally, serpentine belts should be replaced every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, or as recommended by the manufacturer.
Serpentine Belt Types and Materials
Choosing the right serpentine belt is crucial for optimal engine performance and longevity. While they all perform the same basic function – driving various engine accessories – different types and materials offer varying levels of durability, performance, and cost. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision when replacing your belt.Different belt constructions and materials offer different advantages and disadvantages.
The material selection impacts factors like heat resistance, tensile strength, and overall lifespan, directly affecting both performance and the cost of replacement.
Serpentine Belt Construction Types
Serpentine belts are typically constructed using either a ribbed design or a cogged design. Ribbed belts have multiple parallel ribs that grip the pulleys, providing good traction and power transmission. Cogged belts, on the other hand, feature a series of teeth or cogs that mesh with the pulley grooves, offering potentially improved grip, especially in high-torque applications or under harsh conditions.
While both effectively transmit power, the choice between them might depend on the specific vehicle’s engine design and the manufacturer’s specifications.
Serpentine Belt Material Properties
The material used in a serpentine belt significantly impacts its performance and lifespan. Common materials include:
- EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): This is a very common rubber material known for its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering. EPDM belts are a good all-around choice for many vehicles and offer a balance of performance and cost. They’re generally suitable for a wide range of operating conditions.
- Neoprene: Another popular rubber choice, neoprene offers good flexibility and resistance to oil and grease. However, it might not be as resistant to heat or ozone as EPDM, potentially leading to a shorter lifespan in high-temperature applications.
- Nitrile: This material provides exceptional resistance to oils and fuels, making it suitable for vehicles exposed to harsh conditions or those with potential for oil leaks. However, it might be less resistant to ozone and weathering than EPDM.
- Hypalon: This material offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals. It is a more premium option often used in demanding applications or high-performance vehicles, resulting in a longer lifespan but a higher initial cost.
Belt Material and Replacement Cost
The material of the serpentine belt directly influences its cost. Premium materials like Hypalon, offering superior durability and longevity, tend to be more expensive upfront. Conversely, more common materials like EPDM, while offering good performance, are generally less costly. This trade-off between initial cost and long-term durability is a key consideration when choosing a replacement belt. A longer-lasting, higher-priced belt might ultimately be more cost-effective over its lifespan than a cheaper belt requiring more frequent replacements.
Comparison of Serpentine Belt Materials
| Material | Lifespan (Approximate) | Cost (Relative) | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | 3-5 years | Low | Good heat, ozone, and weathering resistance; good all-around performance | May not be ideal for extreme conditions |
| Neoprene | 2-4 years | Low to Moderate | Good flexibility, oil and grease resistance | Lower heat and ozone resistance than EPDM |
| Nitrile | 2-4 years | Moderate | Excellent oil and fuel resistance | Lower ozone and weathering resistance than EPDM |
| Hypalon | 5-7+ years | High | Superior heat, ozone, and chemical resistance; longest lifespan | Higher initial cost |
Closing Summary
So, there you have it – the lowdown on serpentine belt replacement costs. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or prefer leaving it to the pros, understanding the factors that influence the price will help you make an informed decision. Remember, a little preventative maintenance goes a long way. Keep an eye on your belt, and you’ll avoid a potentially expensive headache down the road (pun intended!).
Now go forth and conquer those serpentine belt woes!