Cost to replace a car fuse box? Yeah, that’s a thing. It’s not exactly a fun topic, but it’s one that can totally derail your day (or week!) if you’re not prepared. This isn’t just about swapping a blown fuse; we’re talking about the whole darn box. We’ll break down the costs, from DIY attempts to calling in a pro, and everything in between.
Think of this as your survival guide to a potentially expensive car problem.
Replacing a car’s fuse box can range from a relatively inexpensive DIY fix to a seriously pricey trip to the mechanic. The cost depends heavily on your car’s make and model, whether you opt for a new or used part, and of course, whether you’re tackling the job yourself or letting a professional handle it. We’ll explore all the factors that influence the final price tag, giving you a clearer picture of what you might be facing.
Understanding Car Fuse Box Replacement Costs
Replacing a car’s fuse box can be a surprisingly expensive repair, depending on several factors. The cost isn’t just about the price of the part itself; labor, the car’s make and model, and even the location of the fuse box all play a significant role. This section breaks down the cost components and provides examples to help you better understand what to expect.
Factors Influencing Fuse Box Replacement Costs
Several key factors determine the final cost of replacing a car’s fuse box. These include the cost of the replacement part, which varies greatly depending on the vehicle’s make and model and whether you opt for an OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) part or an aftermarket alternative. Labor costs, dictated by the mechanic’s hourly rate and the complexity of the job (accessing the fuse box can be tricky in some vehicles), significantly impact the total expense.
The vehicle’s year, make, and model also affect the cost because some fuse boxes are more complex and expensive to replace than others. Finally, the location of the fuse box – some are easily accessible under the hood, while others may be tucked away in less convenient spots, increasing labor time and cost.
Labor Costs Versus Parts Costs
Generally, labor costs represent a substantial portion of the overall expense. While the fuse box itself might range from a few hundred dollars to over a thousand depending on the vehicle, labor can easily add another few hundred, sometimes even exceeding the cost of the part itself. This is because replacing the fuse box often involves more than simply swapping out the old unit; it frequently requires disconnecting and reconnecting various electrical components, ensuring proper grounding, and potentially testing the electrical system afterward.
In simpler cases, the labor might be less expensive, but in complex situations involving difficult access or extensive wiring, expect a higher labor cost.
Fuse Box Replacement Costs by Car Model
Providing precise costs for specific car models is difficult because pricing varies significantly by location, mechanic, and parts supplier. However, we can offer some general ranges. For example, replacing a fuse box in a common sedan like a Honda Civic might cost between $300 and $700, including parts and labor. A more luxurious vehicle, such as a BMW or Mercedes-Benz, could see costs ranging from $500 to $1500 or more, due to higher-priced parts and potentially more complex labor.
These are estimates, and it’s crucial to obtain quotes from multiple mechanics before proceeding with any repairs.
DIY Repair Versus Professional Repair: A Cost Comparison
Choosing between DIY repair and professional repair involves weighing cost, time, and risk. Attempting a DIY repair can save on labor costs, but it requires mechanical aptitude, specialized tools, and the correct replacement part. A mistake could lead to further damage and increased expenses.
| Car Make/Model | DIY Cost | Professional Cost | Time Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Honda Civic (2010-2015) | $100 – $200 (parts only) | $300 – $700 | 1-3 hours (professional) |
| Toyota Camry (2012-2017) | $150 – $300 (parts only) | $400 – $800 | 2-4 hours (professional) |
| Ford F-150 (2015-2020) | $200 – $400 (parts only) | $500 – $1200 | 3-6 hours (professional) |
| BMW 3 Series (2016-2020) | $300 – $600 (parts only) | $800 – $1500+ | 4-8 hours (professional) |
Identifying the Need for Fuse Box Replacement
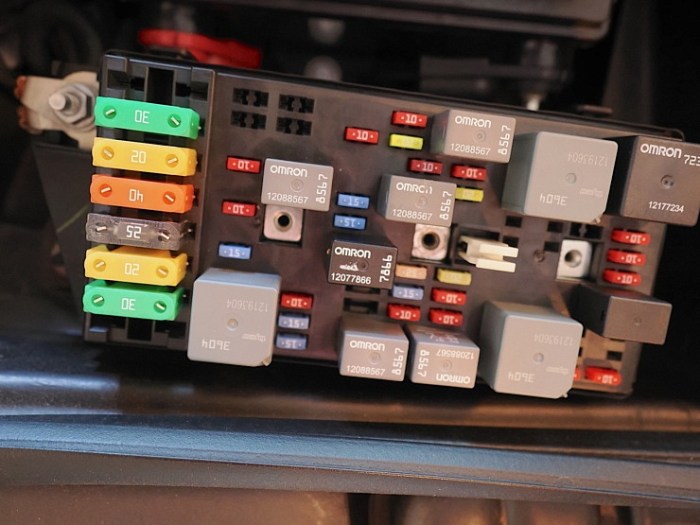

So, your car’s electrical system is acting up. Before you panic and assume the worst, it’s crucial to understand that a malfunctioning electrical system doesn’t automatically mean your fuse box needs replacing. Often, a simple blown fuse is the culprit. However, persistent electrical problems could signal a more serious issue with the fuse box itself. This section will help you differentiate between these scenarios and determine if a replacement is truly necessary.Troubleshooting electrical problems can be tricky, but a systematic approach can save you time and money.
Knowing the signs of a faulty fuse box, as opposed to a simple blown fuse, is the first step in making an informed decision about repairs.
Symptoms Indicating a Faulty Fuse Box
A faulty fuse box might manifest in several ways, often more widespread and persistent than a single blown fuse. For example, multiple circuits might fail simultaneously, or you might experience intermittent problems with different electrical components. This could include flickering headlights, non-functioning power windows, or a completely dead dashboard. The key is the pattern: if you’re constantly replacing fuses in various circuits and the problem keeps recurring, it suggests a deeper problem within the fuse box itself, possibly due to corrosion, overheating, or internal damage.
So, replacing a car’s fuse box can range from cheap (like, twenty bucks for the part) to totally insane, depending on the car. I mean, if you’re dropping serious cash on things like Carbon fiber body kits for Mercedes-AMG , a few hundred for a new fuse box probably won’t break the bank. But yeah, for a basic car, it shouldn’t cost a fortune.
Imagine repeatedly replacing your headlight fuse only to have it blow again immediately – that’s a strong indicator that something is wrong beyond a single fuse.
Differentiating Between a Blown Fuse and a Faulty Fuse Box
The difference lies in the persistence and scope of the problem. A blown fuse is a single point of failure; it protects a specific circuit. Replacing the blown fuse usually resolves the issue. A faulty fuse box, however, is a more systemic problem. It may cause multiple fuses to blow repeatedly, or it may lead to electrical shorts or other malfunctions even when fuses appear intact.
Think of it like this: a blown fuse is like a single broken lightbulb in your house, easily replaced. A faulty fuse box is like faulty wiring in your entire house, requiring more extensive repairs.
Diagnostic Methods for Determining if the Fuse Box Requires Replacement, Cost to replace a car fuse box
Proper diagnosis requires careful observation and testing. First, visually inspect the fuse box for any signs of damage, such as melting, corrosion, or loose connections. Next, use a multimeter to check the voltage at the fuse box terminals. If the voltage is significantly lower than expected or fluctuating, it points to an internal problem within the fuse box.
Finally, consider consulting a qualified mechanic; they possess specialized tools and expertise to perform a comprehensive diagnostic test and pinpoint the exact cause of the electrical issues. They might use a scan tool to check for any stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that might shed light on the problem.
Common Causes of Fuse Box Failure
Several factors can contribute to fuse box failure. Corrosion due to moisture or exposure to elements is a frequent culprit, leading to poor connections and overheating. Overloading circuits by using too many accessories simultaneously can also damage the fuse box. Internal shorts caused by faulty wiring or manufacturing defects can also lead to its failure. Finally, age and wear and tear can gradually degrade the fuse box’s internal components, eventually leading to its failure.
For instance, an older vehicle constantly exposed to harsh weather conditions is more susceptible to fuse box corrosion and eventual failure compared to a newer, well-maintained vehicle kept in a garage.
Sourcing Replacement Fuse Boxes
Finding the right replacement fuse box for your car can feel like navigating a maze, but understanding your options can save you both time and money. The cost varies wildly depending on where you buy it and the make and model of your vehicle. Let’s break down the different sourcing strategies and their associated price tags.
Dealership versus Auto Parts Stores
Dealerships typically offer genuine OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) fuse boxes. While these are guaranteed to fit perfectly and often come with a longer warranty, they usually command the highest price. Auto parts stores, on the other hand, offer a wider range of options, including aftermarket brands and sometimes even used parts. Aftermarket parts are generally cheaper than OEM parts but might not offer the same level of quality or warranty protection.
The price difference can be substantial; you might pay double or even triple the price for a dealership-sourced fuse box compared to an equivalent aftermarket part from an auto parts store like AutoZone or Advance Auto Parts.
Fuse Box Brands and Price Points
Several brands manufacture replacement fuse boxes. The most common are often the OEM brand itself (e.g., Ford, GM, Toyota), and various aftermarket brands like Dorman, Standard Motor Products, and others. Prices vary significantly. OEM parts are usually the most expensive. Aftermarket brands often offer a more budget-friendly alternative, but their quality and longevity can vary.
A quick online search will show price ranges for a specific vehicle’s fuse box, allowing for comparison shopping across brands. For example, a Dorman fuse box might cost around $100-$200, while a comparable OEM part could easily reach $300-$500 or more, depending on the vehicle’s complexity.
Used or Refurbished Fuse Boxes
Used or refurbished fuse boxes can be a great way to save money, especially for older vehicles. You can find these on online marketplaces like eBay or Craigslist, or through junkyards specializing in auto parts. However, it’s crucial to carefully inspect the used part for any damage or signs of wear and tear before purchasing. There’s also a greater risk of the part failing prematurely compared to a new part.
Replacing a car’s fuse box can be surprisingly cheap, sometimes under $50 for the part itself, though labor costs can add up. But that’s nothing compared to the price of more serious repairs; for example, check out this article on the Cost to replace brake calipers to see what I mean! You’ll likely be thankful for a simple fuse box fix after seeing those numbers.
Hopefully, your car problems stay limited to blown fuses.
The potential cost savings can be significant, potentially reducing the cost by 50% or more compared to a new part, but this comes with a higher level of risk.
Price Variation by Source and Car Model
The following table illustrates the price variation you might encounter when sourcing a replacement fuse box, depending on the source and the car model. These are illustrative examples and actual prices will vary based on location, availability, and specific vehicle year and trim level.
| Part Source | Brand | Price (USD) | Warranty Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dealership (Honda Civic 2018) | Honda | $450 – $600 | 12-month/12,000-mile warranty |
| AutoZone (Honda Civic 2018) | Dorman | $175 – $250 | 1-year limited warranty |
| eBay (Toyota Camry 2015) | Toyota (Used) | $75 – $150 | No warranty (seller dependent) |
| Local Junkyard (Ford F-150 2010) | Ford (Used) | $50 – $100 | No warranty |
The Replacement Process
Replacing your car’s fuse box can be a significant undertaking, depending on your vehicle’s make and model. The complexity varies wildly, from a relatively straightforward swap in some older models to a much more involved process in modern vehicles with integrated electronic systems. Choosing between a DIY repair and professional service depends largely on your mechanical aptitude and comfort level working with automotive electrical systems.This section Artikels the steps involved in both DIY and professional fuse box replacement, highlighting the tools, materials, risks, and benefits associated with each approach.
Remember, always consult your vehicle’s repair manual for specific instructions and safety precautions.
DIY Fuse Box Replacement
Attempting a DIY fuse box replacement requires a degree of mechanical skill and comfort working with electrical systems. Incorrect installation can lead to further electrical problems or even damage to your vehicle’s computer systems. Before beginning, ensure you have the correct replacement fuse box and understand the wiring diagram for your specific vehicle.
Tools and Materials: You’ll need a set of screwdrivers (likely both Phillips and flathead), possibly a socket wrench set, wire strippers/crimpers (if new wiring is needed), electrical tape, a multimeter (to test circuits after installation), and of course, the replacement fuse box. Safety glasses and gloves are also highly recommended.
Steps Involved: The steps will vary depending on your vehicle, but generally involve disconnecting the battery’s negative terminal, carefully removing any trim pieces or panels obscuring the fuse box, unplugging all connectors from the old fuse box, removing the mounting bolts or clips securing the old fuse box, installing the new fuse box using the same mounting points, reconnecting all connectors in their original locations, and finally, reconnecting the battery’s negative terminal.
Always double-check your work before turning the ignition on.
Professional Fuse Box Replacement
Professional mechanics have the experience, tools, and diagnostic equipment to handle even the most complex fuse box replacements safely and efficiently. They possess a deeper understanding of your vehicle’s electrical system and can identify any underlying issues that might have contributed to the original fuse box failure. Their expertise minimizes the risk of damaging your vehicle’s electrical system or causing further problems.
Professional Installation Process: A professional will typically begin by diagnosing the problem to confirm the fuse box is indeed faulty. They’ll then disconnect the battery, carefully remove the old fuse box (often involving removing surrounding components), inspect the wiring for any damage, install the new fuse box, reconnect all wiring and components, and test the entire system to ensure everything functions correctly.
They might also use specialized diagnostic tools to check for any error codes or other electrical issues.
DIY vs. Professional: Risks and Benefits
DIY Repair: The primary benefit of a DIY repair is cost savings. However, the risks include potential damage to your vehicle’s electrical system, incorrect installation leading to further problems, and the possibility of personal injury from working with electricity. The success of a DIY repair is highly dependent on your mechanical skills and experience.
Professional Service: The main benefit of professional service is expertise and safety. Professionals possess the knowledge and tools to diagnose and repair the issue correctly, minimizing the risk of damage or further complications. The cost is typically higher than a DIY repair, but the peace of mind and assurance of a correctly functioning system often outweigh the added expense.
For example, a friend attempted a DIY repair on their older Honda Civic, resulting in a fried alternator due to a wiring error. A professional repair cost them significantly more than just replacing the fuse box.
Cost Considerations Beyond Parts and Labor
Replacing a car’s fuse box might seem straightforward, but the total cost can easily balloon beyond the price of the part and the mechanic’s labor. Several unforeseen expenses can significantly impact your budget, turning a seemingly minor repair into a more substantial financial burden. Understanding these potential additional costs is crucial for realistic budgeting.Unexpected complications and additional services can quickly add to the final bill.
It’s important to be prepared for these possibilities to avoid financial surprises.
Towing Costs
If your car’s electrical system is severely compromised—perhaps due to a more extensive problem than a simple blown fuse—you might need a tow truck to get your vehicle to the repair shop. Towing fees vary widely depending on distance, time of day, and the type of towing required. For example, a local tow within city limits might cost between $75 and $150, while a long-distance tow could easily exceed $300.
The cost can be even higher for specialized towing services needed for certain vehicles or situations.
Diagnostic Fees
Before a mechanic can replace the fuse box, they often need to diagnose the underlying cause of the problem. This diagnostic process involves testing the electrical system, pinpointing the source of the failure, and ensuring that replacing the fuse box will actually resolve the issue. Diagnostic fees can range from $50 to $150 or more, depending on the complexity of the problem and the time spent troubleshooting.
A shop might charge hourly rates for diagnostic time, adding another layer of potential expense.
Unexpected Complications
Sometimes, replacing a fuse box reveals additional, unexpected problems. For instance, corroded wiring, damaged connectors, or other related electrical issues might be discovered during the repair. These problems often require additional parts and labor, significantly increasing the overall cost. Imagine discovering a rodent nest inside the fuse box area – cleaning that up would add both time and expense to the repair.
Another example would be discovering a short circuit in the wiring harness that needs to be repaired in addition to replacing the fuse box itself. Such unforeseen complications can easily add hundreds of dollars to the final bill.
Potential Hidden Costs
It’s important to be aware of potential hidden costs associated with fuse box replacement. These costs can significantly inflate the overall expense.
- Unexpected parts: The mechanic might discover that additional parts are needed beyond the fuse box itself, such as connectors, wiring harnesses, or other related components.
- Extended labor time: Unforeseen complications, such as difficult access to the fuse box or complex wiring, can significantly increase the labor time required for the repair.
- Specialized tools: Certain fuse box replacements may require specialized tools that the mechanic might need to purchase or rent, adding to the cost.
- Disposal fees: Some shops charge a fee for the proper disposal of the old fuse box and related components.
Visual Guide to Fuse Box Components
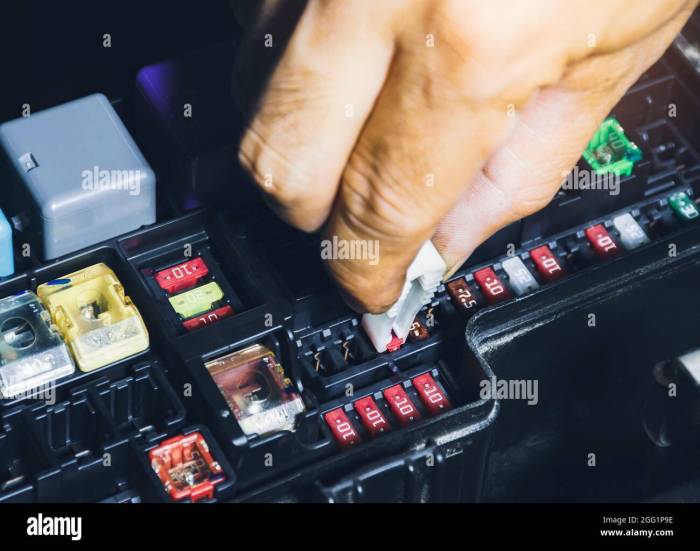

Understanding the internal workings of your car’s fuse box is crucial for basic car maintenance and troubleshooting. This section provides a visual description of the typical components you’ll find inside, focusing on their function and arrangement. Think of it as a guided tour of your car’s electrical protection system.The typical car fuse box is a relatively small, usually plastic, box, often located under the dashboard or in the engine compartment.
Its size varies depending on the vehicle’s electrical complexity; a larger vehicle with more electrical components will naturally have a larger fuse box. The box itself is typically rectangular or square, with a cover that’s easily removable, often held in place by clips or screws. Inside, you’ll find a neatly organized arrangement of fuses and relays, often color-coded or labeled for easy identification.
Fuses are typically small, cylindrical components inserted into sockets, while relays are slightly larger, usually square or rectangular components with multiple terminals. The overall arrangement is usually quite dense, with components closely packed together, to maximize space utilization within the confines of the box.
Fuse Types in a Car Fuse Box
Car fuses come in various sizes and amperage ratings, each designed to protect specific circuits within the vehicle’s electrical system. Understanding these differences is key to safe and effective fuse replacement.The most common type is the blade fuse, characterized by its small, rectangular shape with metal terminals on each end. These are easily identified and replaced. Mini blade fuses are smaller versions of the standard blade fuse, often found in newer vehicles or those with more compact electrical systems.
Another type is the ATO (Add-A-Circuit) fuse, also rectangular, but slightly larger than a blade fuse and featuring a slightly different terminal configuration. Lastly, glass fuses, with a glass body and exposed wire terminals, are less common in modern vehicles but can still be found in older models. The amperage rating (printed on the fuse itself) indicates the maximum current the fuse can handle before it melts, protecting the circuit from damage.
For instance, a 10-amp fuse will melt if more than 10 amps of current flow through it.
Typical Fuse Box Layout
Imagine opening the fuse box cover. You’ll see a grid-like arrangement, often with rows and columns of fuse sockets. Each socket is usually labeled, indicating the circuit it protects (e.g., headlights, power windows, radio). These labels are crucial for identifying which fuse needs replacing. Interspersed among the fuse sockets, you’ll find relays.
Relays are slightly larger than fuses and are often identifiable by their distinct shape and multiple terminals. The entire arrangement is usually tightly packed, but the layout is generally logical and organized, allowing for relatively easy access to individual components. The size of the box itself could range from roughly 4 inches by 6 inches to considerably larger, depending on the car model and its features.
The material is typically a durable, heat-resistant plastic to protect the internal components. Often, the cover will have a diagram printed on the inside, showing the layout of the fuses and their corresponding circuits, which is extremely helpful during troubleshooting.
Concluding Remarks: Cost To Replace A Car Fuse Box
So, there you have it – the lowdown on replacing your car’s fuse box. While it might seem like a small component, a faulty fuse box can lead to major headaches and expenses. By understanding the costs involved, the symptoms of a failing box, and your options for repair, you can be better prepared to handle this situation.
Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or prefer leaving it to the pros, knowing your options empowers you to make the best decision for your wallet and your car. Now go forth and conquer those electrical gremlins!









