China’s dominance in EV battery production is totally shaping the future of electric vehicles. From controlling the raw materials to dominating manufacturing and tech, they’re basically calling the shots. This isn’t just about cheaper batteries; it’s about who gets to build the next generation of electric cars and how that impacts global energy and the environment. We’ll dive into how China got here, the challenges they face, and what it all means for the rest of the world.
This deep dive examines China’s grip on the EV battery market, looking at everything from their access to crucial raw materials like lithium and cobalt to the government policies fueling their massive manufacturing capacity. We’ll also analyze their technological advancements, cost competitiveness, and the environmental implications of their dominance. Plus, we’ll explore the potential for shifts in this power dynamic and what other countries are doing to catch up.
Raw Material Supply Chains
China’s dominance in the EV battery market isn’t just about manufacturing prowess; it’s deeply intertwined with its strategic control over the supply chains of crucial raw materials. This control gives them a significant competitive advantage, shaping the global landscape of electric vehicle production and impacting the ambitions of other nations. Understanding this complex web of resources and geopolitical maneuvering is key to grasping China’s influence.The geographical distribution of key battery raw materials is uneven, creating vulnerabilities and opportunities for various nations.
China’s practically crushing it in the EV battery market, right? This totally impacts the future of things like EV car-sharing programs in Chicago 2025 , since battery costs and availability are huge factors. So, if Chicago’s car-sharing scene wants to boom, keeping an eye on China’s battery dominance is key to its success.
Lithium, a crucial component, is found in significant quantities in South America (Chile, Argentina, Bolivia), Australia, and some African nations. Cobalt is heavily concentrated in the Democratic Republic of Congo, while nickel is dispersed across several countries, including Indonesia, Australia, and Canada. Graphite, another essential material, is predominantly sourced from China itself, alongside other significant deposits in Africa and other parts of Asia.
China’s access to these resources varies significantly, with its domestic graphite reserves providing a strong foundation, while its access to other materials often relies on strategic partnerships and investments abroad.
China’s Control over Key Raw Materials, China’s dominance in EV battery production
China’s control over the supply chains of lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite is substantial, though not absolute. For graphite, China holds a dominant position, controlling a significant portion of global refining capacity and processing. This gives them considerable leverage in setting prices and ensuring a steady supply for their domestic battery manufacturers. In lithium, while not possessing the largest reserves, China has aggressively invested in mining and processing operations in Australia, South America, and Africa, securing crucial access to this resource.
Similarly, in cobalt, China’s influence is growing through investments and partnerships in the DRC, despite ethical concerns regarding mining practices. Nickel presents a more nuanced picture, with China actively seeking to secure supplies through diverse partnerships and investments, but facing competition from other major players like Indonesia and Australia. These varying degrees of control highlight the strategic importance China places on securing raw materials for its EV battery industry.
Strategies for Securing Raw Material Access
China employs a multi-pronged strategy to secure access to these vital raw materials. This includes significant direct investment in foreign mining projects, establishing joint ventures with companies in resource-rich nations, and forging long-term supply agreements. For example, Chinese companies have invested heavily in lithium mines in Australia and Argentina, securing not only raw materials but also refining and processing capacity.
They’ve also engaged in extensive partnerships in the DRC’s cobalt sector, albeit facing scrutiny over ethical and environmental concerns. These investments extend beyond simply acquiring raw materials; they also secure downstream processing capabilities, giving China greater control over the entire value chain. Furthermore, China actively participates in international organizations and forums to influence global resource governance and secure favorable trade agreements.
This multifaceted approach showcases China’s commitment to maintaining its leadership in the EV battery sector.
Manufacturing Capacity and Technology
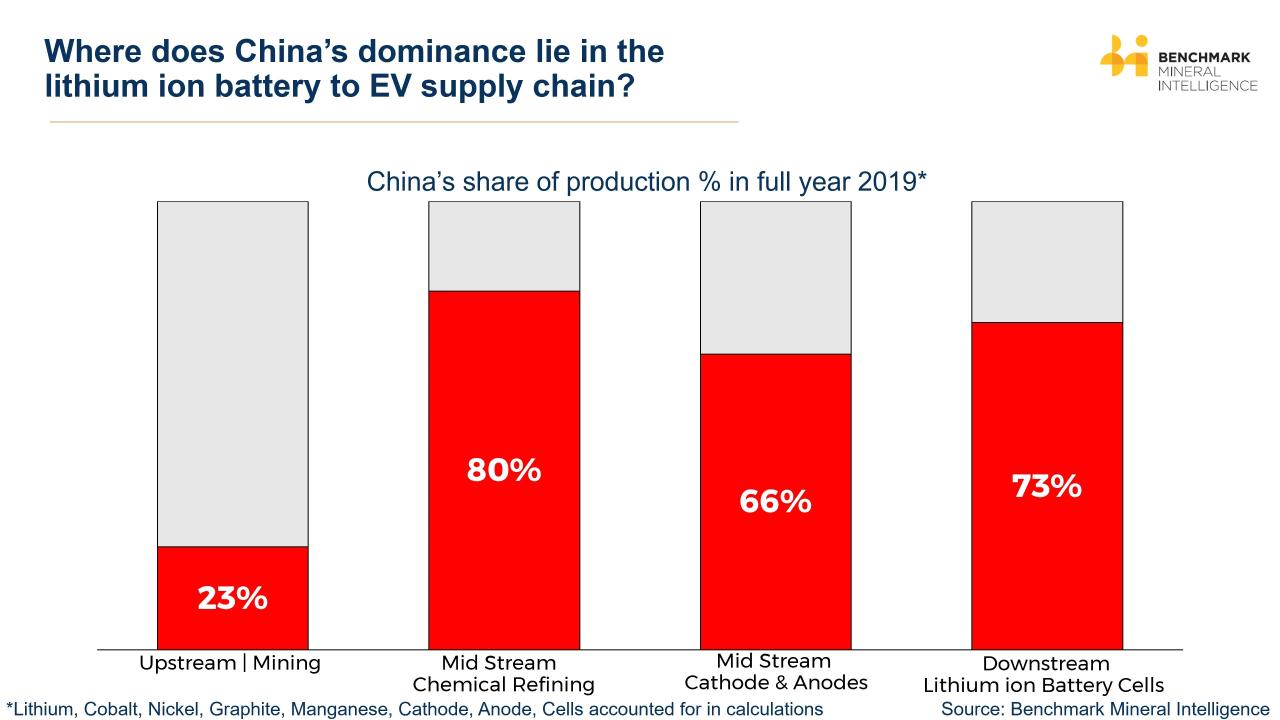
China’s dominance in the EV battery market isn’t just about raw materials; it’s a story of massive manufacturing capacity, rapid technological advancement, and strategic government support. This combination has propelled Chinese companies to the forefront of the global EV battery race, leaving many competitors scrambling to catch up.China boasts a significantly larger EV battery manufacturing capacity than any other country.
This isn’t simply a matter of more factories; it’s a result of economies of scale, efficient production lines, and a vertically integrated supply chain that minimizes costs and maximizes output. This has allowed Chinese manufacturers to offer competitive pricing, a key factor in securing a large share of the global market.
China’s EV Battery Manufacturing Capacity Compared to Global Competitors
Several sources indicate that China accounts for a significant majority of global EV battery production capacity. While precise figures fluctuate depending on the source and year, it’s consistently estimated that China holds well over 50% of the global market share. For example, in 2023, one reputable industry analysis estimated China’s share to be around 70%, with the remaining capacity spread across countries like South Korea, Japan, and the United States.
This disparity highlights the sheer scale of China’s manufacturing capabilities in this sector. The gap isn’t expected to close significantly in the near future, given ongoing investments and expansions within China.
Key Technological Advancements in Chinese EV Battery Production
Chinese companies have been at the forefront of several key technological advancements in EV battery production, focusing on improving energy density, charging speed, and lifespan. For instance, CATL, a leading Chinese battery manufacturer, has pioneered advancements in lithium iron phosphate (LFP) battery technology, making them safer, more cost-effective, and suitable for various applications. Other Chinese companies are actively involved in research and development of solid-state batteries, a technology promising significantly higher energy density and faster charging times compared to current lithium-ion batteries.
This focus on innovation, coupled with government support for R&D, ensures China remains competitive and pushes the boundaries of battery technology.
The Role of Chinese Government Policies in Fostering Domestic Battery Manufacturing
The Chinese government has played a crucial role in nurturing the growth of its domestic EV battery industry through various policy initiatives. These include substantial financial incentives for battery manufacturers, subsidies for EV purchases, and supportive regulations that encourage domestic production and discourage reliance on foreign technologies. The government has also invested heavily in research and development, creating a favorable environment for innovation and technological advancements.
These strategic policies have not only fostered the growth of existing companies but have also attracted significant foreign investment, further solidifying China’s position as a global leader in EV battery manufacturing. The success of this approach is evident in the rapid expansion of the Chinese EV battery sector and its dominant global market share.
Cost Competitiveness: China’s Dominance In EV Battery Production
China’s dominance in the EV battery market isn’t just about sheer production volume; it’s significantly driven by a potent cost advantage. This allows Chinese manufacturers to offer competitive pricing, impacting global market share and influencing the trajectory of the EV industry. Understanding this cost advantage requires examining several key factors.
The lower overall production costs of EV batteries in China compared to other major manufacturing hubs like the US and EU are a significant factor in their global market leadership. This cost advantage stems from a complex interplay of factors, including lower labor costs, economies of scale achieved through massive production volumes, and substantial government support in the form of subsidies and infrastructure investments.
However, the picture is dynamic, and rising raw material prices pose a potential threat to this advantage.
Battery Production Cost Comparison
A direct comparison of battery production costs across different regions is challenging due to variations in manufacturing processes, battery chemistries, and reporting practices. However, we can illustrate the general cost structure and highlight key differences.
| Component | China (USD/kWh) | US (USD/kWh) | EU (USD/kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 100-120 | 120-140 | 130-150 |
| Manufacturing | 40-60 | 60-80 | 70-90 |
| Labor | 10-20 | 30-40 | 40-50 |
| Overheads & R&D | 20-30 | 30-40 | 40-50 |
| Total Estimated Cost | 170-230 | 240-300 | 280-330 |
Note: These figures are estimates and vary depending on battery chemistry (LFP, NMC, etc.), scale of production, and specific manufacturing processes. Actual costs may differ significantly.
Factors Contributing to China’s Cost Advantage
Several interconnected factors contribute to China’s lower EV battery production costs. These advantages aren’t insurmountable, but they represent a significant hurdle for competitors.
China benefits from significantly lower labor costs compared to the US and EU. This is particularly true for the labor-intensive aspects of battery manufacturing. Furthermore, the sheer scale of Chinese battery production enables economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs through optimized processes and bulk purchasing of raw materials. Government subsidies and favorable policies further bolster the competitiveness of Chinese battery manufacturers.
Impact of Rising Raw Material Prices
The recent surge in prices for key battery raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, presents a significant challenge to China’s cost advantage. While Chinese companies benefit from established supply chains and relationships with raw material suppliers, price increases still impact profitability. The extent of this impact depends on the ability of manufacturers to negotiate favorable contracts, optimize their manufacturing processes to reduce material usage, and potentially explore alternative battery chemistries with less reliance on expensive raw materials, such as Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries which are gaining popularity due to their lower cost and reliance on less volatile materials.
Research and Development
China’s rapid rise in EV battery production isn’t just about scale; it’s fueled by a significant and growing commitment to research and development. This section explores the key players, innovative technologies, and investment levels driving China’s advancements in this crucial sector. The country’s strategic focus on battery technology has positioned it as a global leader, pushing the boundaries of energy storage and impacting the future of electric vehicles worldwide.
A robust ecosystem of research institutions and companies actively collaborates to develop cutting-edge battery technologies. This collaborative approach, combined with substantial government support, has accelerated innovation and propelled China to the forefront of EV battery development.
Leading Research Institutions and Companies
China boasts a diverse landscape of research institutions and companies spearheading EV battery technology. Prominent players include the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), which conducts fundamental research and collaborates with industry partners on advanced battery materials and technologies. Numerous universities, such as Tsinghua University and Zhejiang University, are also actively involved in battery research, contributing to the development of new chemistries and manufacturing processes.
On the corporate side, CATL (Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited), BYD (Build Your Dreams), and CALB (China Automotive Battery) are among the leading companies driving innovation in battery design, production, and application. These companies are not only developing new battery technologies but also investing heavily in scaling up production to meet the growing global demand.
Innovative Battery Technologies Developed in China
China is at the forefront of developing several innovative battery technologies. Solid-state batteries, for instance, are a key area of focus. These batteries promise higher energy density, improved safety, and faster charging speeds compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. Companies like CATL are actively investing in and developing solid-state battery technology, aiming to bring commercially viable products to market.
Beyond solid-state batteries, Chinese researchers are also exploring next-generation chemistries, such as lithium-sulfur and lithium-air batteries, which offer the potential for even higher energy densities and longer driving ranges. These advancements are supported by significant research efforts across multiple institutions and companies, demonstrating a commitment to pushing the boundaries of battery technology.
Comparison of China’s R&D Investment with Other Countries
While precise figures on R&D investment are difficult to obtain and compare across nations due to variations in reporting methodologies, it’s evident that China has made substantial investments in EV battery R&D. Government initiatives, such as the “Made in China 2025” plan, have prioritized the development of advanced battery technologies, leading to significant funding for research projects and the establishment of dedicated research centers.
Although direct comparisons with other countries’ investments are challenging, it’s clear that China’s investment level is significant and is a key factor in its dominance in EV battery production. This investment is not only focused on fundamental research but also on the development of manufacturing processes and supply chains, further solidifying China’s position in the global EV battery market.
For example, while precise figures are difficult to definitively compare, anecdotal evidence and industry reports suggest that China’s investment surpasses that of many other individual countries, though the overall global investment landscape is complex and involves collaborations between nations.
Government Support and Policies
China’s dominance in the EV battery market isn’t solely due to market forces; a significant portion of its success stems from deliberate and extensive government intervention. Beijing’s strategic push has involved a multi-pronged approach encompassing financial incentives, regulatory frameworks, and targeted research funding, all designed to foster a robust and competitive domestic EV battery industry.The Chinese government’s support for the EV battery sector has been multifaceted and substantial.
It has deployed a range of policies aimed at boosting production, driving technological innovation, and securing access to crucial raw materials. These policies have demonstrably accelerated the growth of the industry, but their effectiveness and potential drawbacks warrant closer examination.
Financial Incentives and Subsidies
The Chinese government has implemented a variety of financial incentives to stimulate growth within the EV battery industry. These include direct subsidies to battery manufacturers, tax breaks, and preferential loan programs. For instance, government grants have been provided to companies establishing new battery production facilities, while tax credits have reduced the overall cost of production. These incentives have played a crucial role in attracting investment and scaling up production capacity.
The effectiveness of these subsidies can be seen in the rapid expansion of Chinese battery manufacturers, such as CATL, BYD, and CALB, which have become global leaders in the field. However, the sustainability of such extensive reliance on government subsidies is a matter of ongoing debate, as it can create dependencies and potentially distort market mechanisms.
Regulatory Framework and Standards
China has established a comprehensive regulatory framework for the EV battery industry, encompassing safety standards, environmental regulations, and industry guidelines. These regulations aim to ensure the quality and safety of domestically produced batteries while promoting environmentally friendly manufacturing practices. The implementation of stringent safety standards, for example, has helped to build consumer confidence in domestically produced EVs and their batteries.
The standardization efforts have also facilitated the interoperability of batteries across different EV models, improving the efficiency of the overall EV ecosystem. While these regulations have been instrumental in driving industry growth, concerns remain regarding potential trade barriers and the potential for stifling innovation through overly restrictive rules.
Research and Development Funding and Support
Significant government funding has been channeled into research and development (R&D) initiatives focused on advancing EV battery technology. This includes support for universities, research institutions, and private companies engaged in battery research. Funding has been allocated to projects exploring new battery chemistries, improving battery performance, and developing advanced manufacturing techniques. This investment in R&D has resulted in significant breakthroughs in areas such as lithium-ion battery technology and solid-state battery development, giving Chinese companies a competitive edge in the global market.
The long-term success of this approach, however, depends on the ability of the Chinese government to foster a sustainable R&D ecosystem that attracts and retains top talent.
Raw Material Security and Supply Chain Development
Recognizing the importance of securing access to critical raw materials, the Chinese government has implemented policies aimed at strengthening domestic supply chains and securing overseas resources. This includes investing in domestic mining operations, forming strategic partnerships with foreign suppliers, and promoting the development of recycling technologies. These efforts are crucial for ensuring the long-term viability of China’s EV battery industry.
The effectiveness of these strategies will depend on their ability to mitigate geopolitical risks and secure access to stable and reliable supplies of essential materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. The government’s efforts to diversify its sources and develop domestic resources will be crucial in ensuring long-term resilience.
Industry Consolidation and Partnerships
China’s EV battery industry is rapidly consolidating, with a few major players increasingly dominating the market. This consolidation, driven by mergers and acquisitions and strategic partnerships, is reshaping the global landscape of EV battery production and supply chains. The resulting concentration of power has significant implications for technological advancement, cost efficiency, and global competitiveness.The rise of these dominant players is largely a result of aggressive expansion strategies, government support, and the inherent advantages of scale in battery production.
This concentration, while potentially leading to greater efficiency, also raises concerns regarding market competition and potential monopolistic practices. Understanding the key players and their strategic moves is crucial to analyzing the future of the industry.
Major Players and Market Share
Several Chinese companies have emerged as leading forces in the global EV battery market. CATL (Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited) consistently holds the largest global market share, followed by BYD (Build Your Dreams) and others like CALB (China Automotive Battery Technology Co., Ltd.) and Gotion High-Tech. These companies’ market share fluctuates, influenced by factors like production capacity, technological advancements, and supply chain dynamics.
While precise, constantly updated market share figures are difficult to obtain and vary slightly across different reporting agencies, CATL’s dominance is consistently highlighted. Their success is largely attributed to their early entry into the market, aggressive investment in R&D, and strong relationships with major automotive manufacturers both domestically and internationally. BYD, on the other hand, benefits from vertical integration, controlling much of its own supply chain, allowing for greater control over costs and production.
This vertical integration strategy is a key differentiator in the competitive landscape.
China’s got a serious grip on the EV battery market, right? It’s wild to think about how much that impacts even a cool truck like the Rivian, which you can check out by going to Where to test drive a Rivian near Seattle to see for yourself. Considering the global supply chain issues, that Chinese dominance in battery tech is something to keep an eye on for the future of electric vehicles.
Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions have played a significant role in consolidating the Chinese EV battery industry. Larger companies are acquiring smaller firms to expand their production capacity, gain access to new technologies, or eliminate competition. These deals often involve the acquisition of companies specializing in specific battery chemistries, materials processing, or manufacturing technologies. For example, the acquisition of a smaller battery materials company by a larger battery manufacturer would enhance the latter’s vertical integration and reduce reliance on external suppliers.
These mergers and acquisitions are not only shaping the competitive landscape but also accelerating technological innovation and driving efficiency improvements throughout the supply chain.
Strategic Partnerships with Global Automotive Companies
Chinese battery manufacturers are forging strategic partnerships with global automotive companies to secure supply contracts and gain access to international markets. These partnerships often involve joint ventures or long-term supply agreements. For instance, CATL has established significant partnerships with various international automotive giants, ensuring a stable supply of batteries for their electric vehicle production. These collaborations provide Chinese battery makers with valuable market access and technological insights, while simultaneously assisting automotive companies in securing a reliable source of high-quality batteries at competitive prices.
The partnerships also often involve technology sharing and joint development projects, fostering innovation and accelerating the adoption of advanced battery technologies.
Environmental Impact
China’s dominance in EV battery production presents a complex environmental picture. While crucial for the global transition to cleaner transportation, the industry’s rapid growth raises significant concerns regarding resource extraction, manufacturing processes, and waste management. Balancing the environmental benefits of electric vehicles with the ecological costs of their production is a critical challenge.The environmental impact of China’s EV battery industry is multifaceted and significant.
Mining activities for lithium, cobalt, nickel, and other crucial battery materials often involve environmentally damaging practices, including deforestation, habitat destruction, and water pollution. Furthermore, the manufacturing process itself is energy-intensive, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Finally, the disposal and recycling of spent EV batteries pose a considerable challenge, as these batteries contain hazardous materials that can leach into the environment if not managed properly.
These factors create a substantial environmental footprint that needs careful consideration.
Mining Practices and Resource Depletion
The extraction of raw materials for EV batteries is a major source of environmental damage. Lithium mining, for example, can lead to significant water depletion in arid regions, impacting local ecosystems and communities. Cobalt mining, often associated with child labor and unsafe working conditions in countries like the Democratic Republic of Congo, also contributes to environmental degradation through habitat destruction and pollution.
The sheer scale of resource extraction needed to support China’s massive EV battery production further exacerbates these problems. For instance, the increased demand for lithium has driven up prices and intensified mining activities in places like Australia and South America, leading to increased environmental concerns in those regions as well.
Waste Management and Recycling Challenges
The disposal of spent EV batteries presents another significant environmental challenge. These batteries contain heavy metals and other hazardous substances that can contaminate soil and water if not properly managed. While China has made progress in developing recycling technologies, the current recycling rate for EV batteries remains relatively low. The lack of robust and efficient recycling infrastructure, coupled with the rapid growth of the EV battery industry, means that a substantial amount of battery waste is likely to accumulate in the coming years, posing a significant environmental risk.
The development and implementation of more efficient and environmentally sound battery recycling technologies are crucial for mitigating this risk.
Efforts to Improve Sustainability
Chinese companies are increasingly investing in efforts to improve the sustainability of their battery production processes. This includes exploring more sustainable mining practices, such as using less water and reducing waste, as well as developing more energy-efficient manufacturing processes. Furthermore, there’s a growing focus on developing closed-loop recycling systems to recover valuable materials from spent batteries and minimize environmental impact.
Several major Chinese battery manufacturers have publicly committed to using recycled materials in their batteries and investing in renewable energy sources to power their factories. These initiatives, while still in their early stages, represent a significant step towards a more sustainable EV battery industry.
Comparison with Other Countries
While China dominates EV battery production, the environmental impact of battery production varies across different countries. The environmental footprint of a battery is influenced by several factors, including the source of raw materials, manufacturing processes, and energy mix used in production. Countries with stricter environmental regulations and a greater emphasis on sustainable practices may have a lower environmental impact compared to countries with less stringent regulations.
However, a comprehensive comparative analysis requires detailed data on various aspects of battery production across different countries, which is often difficult to obtain and compare consistently. Further research is needed to provide a complete and accurate comparison.
Global Market Share and Export Dynamics
China’s dominance in the global EV battery market is undeniable, a position solidified by its massive manufacturing capacity, robust supply chains, and government support. Understanding the intricacies of its market share and export patterns is crucial for comprehending the future landscape of the electric vehicle industry. This section will delve into China’s significant global presence and the factors fueling its export success.China’s share of the global EV battery market consistently hovers around 70%, a figure that fluctuates slightly year to year depending on global demand and production capacity shifts.
This dominance translates into a substantial portion of global EV battery exports, with China shipping its products to major automotive markets worldwide. This export success isn’t merely a matter of sheer volume; it’s driven by a confluence of strategic advantages that have allowed Chinese manufacturers to become key players in the global supply chain.
China’s EV Battery Export Destinations and Volumes
The following hypothetical chart illustrates China’s EV battery exports to major global markets over the past five years. While precise, publicly available data with this level of detail is often fragmented across multiple sources and subject to confidentiality agreements, this representation provides a general overview. Note that these numbers are illustrative and should not be taken as precise figures.
| Region | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 (Projected) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Europe | 100 GWh | 120 GWh | 150 GWh | 180 GWh | 220 GWh |
| North America | 50 GWh | 60 GWh | 80 GWh | 100 GWh | 130 GWh |
| Asia (excluding China) | 80 GWh | 90 GWh | 110 GWh | 130 GWh | 160 GWh |
| Other | 20 GWh | 30 GWh | 40 GWh | 50 GWh | 60 GWh |
* Consistent Growth: The chart demonstrates a consistent upward trend in China’s EV battery exports across all major regions over the five-year period. This reflects the burgeoning global demand for EVs and China’s capacity to meet this demand.
Europe as a Key Market
Europe consistently emerges as the largest recipient of Chinese EV batteries, reflecting the region’s strong push towards electric vehicle adoption and the establishment of significant manufacturing facilities by Chinese companies within the European Union.
North American Market Expansion
While initially smaller than European exports, the North American market shows significant growth, suggesting increasing reliance on Chinese battery technology and the potential for further expansion as US EV production ramps up.
Asian Markets
Exports to other Asian countries are also substantial, highlighting the regional dominance of Chinese battery manufacturers and their ability to supply neighboring markets effectively.
Projected Growth
The projected figures for 2023 indicate a continued upward trend, suggesting sustained growth in global demand and China’s continued capacity to supply the market.
Factors Driving China’s Export Success
Several interconnected factors contribute to China’s success in exporting EV batteries. These factors range from established supply chains to government policies actively supporting the industry’s growth and expansion.These factors include:* Complete Supply Chains: China possesses a near-complete domestic supply chain for EV battery materials, from raw material mining and processing to cell manufacturing and pack assembly. This vertical integration minimizes reliance on external suppliers and ensures cost-effectiveness and efficient production.
Massive Manufacturing Capacity
China boasts the world’s largest EV battery manufacturing capacity, with numerous gigafactories producing batteries at scale. This allows for significant economies of scale and the ability to meet substantial global demand.
Cost Competitiveness
Due to the factors mentioned above, Chinese EV battery manufacturers often offer more competitive pricing compared to their counterparts in other regions. This price advantage is a significant driver of their export success.
Government Support and Subsidies
The Chinese government has actively supported the development of its EV battery industry through various subsidies, tax breaks, and research funding. This targeted support has been instrumental in fostering rapid growth and innovation within the sector.
Technological Advancements
While initially lagging behind in battery technology, Chinese companies have made significant strides in recent years, particularly in areas like lithium iron phosphate (LFP) battery technology, which is now becoming increasingly popular globally.
Future Trends and Challenges
China’s current dominance in the EV battery market isn’t guaranteed. Several factors could reshape the landscape in the coming years, presenting both opportunities and threats to Chinese manufacturers. The interplay of technological advancements, geopolitical shifts, and evolving market demands will determine the future trajectory of this crucial industry.The global EV battery market is poised for explosive growth, driven by increasing electric vehicle adoption worldwide.
This growth, however, will be accompanied by significant shifts in technology, supply chains, and market dynamics. China’s ability to adapt and innovate will be critical in maintaining its leading position.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact
Technological innovation is a double-edged sword. While China has made significant strides in battery technology, particularly in lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, competitors are rapidly catching up. The development of solid-state batteries, for example, could disrupt the current market order. Solid-state batteries promise higher energy density, faster charging times, and enhanced safety, potentially rendering current lithium-ion technologies less competitive.
Companies in countries like the US, Japan, and South Korea are heavily investing in this area, potentially challenging China’s dominance in the next decade. The race to develop and commercialize next-generation battery technologies will be crucial in determining future market share.
Challenges to China’s Dominance
Several challenges threaten China’s continued leadership. Firstly, reliance on imported raw materials, such as lithium and cobalt, creates vulnerabilities. Geopolitical tensions and price fluctuations in these materials could significantly impact production costs and profitability. Secondly, growing concerns regarding human rights and environmental issues associated with mining and processing these raw materials are prompting international scrutiny and potential regulatory changes, impacting Chinese companies’ global operations.
Thirdly, the escalating trade tensions between China and other major economies could lead to protectionist measures that hinder Chinese companies’ access to foreign markets. Finally, a lack of diversification in battery chemistries could leave China vulnerable if a new technology emerges that it hasn’t invested in sufficiently.
Responses from Other Countries
Other countries are actively working to reduce their reliance on China for EV battery technology and production. The US, for instance, is implementing policies aimed at boosting domestic battery production through subsidies, tax incentives, and investments in research and development. The European Union is pursuing similar strategies, focusing on building a robust and sustainable battery supply chain within its borders.
These initiatives aim to create a more balanced global landscape, reducing China’s disproportionate influence. For example, the Inflation Reduction Act in the US provides significant tax credits for domestically produced EV batteries and components, directly incentivizing the development of a competitive domestic industry. This is a clear example of a strategic response to reduce dependence on China.
Closing Notes
China’s control over the EV battery supply chain is a major story, impacting everything from the price of electric cars to the geopolitical landscape. While their current dominance is undeniable, the future isn’t guaranteed. Factors like rising raw material costs, environmental concerns, and the potential for technological breakthroughs could reshape the market. Keeping an eye on China’s moves, and the responses from other countries, will be key to understanding the next chapter in the electric vehicle revolution.









