Best EVs with vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology – Best EVs with vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology? Dude, that’s like, the future of driving, right? Imagine your electric car not just
-using* the grid, but
-giving back* to it. This isn’t some sci-fi fantasy; it’s happening now, with cars capable of feeding power back into the grid, potentially earning you some serious cash while helping stabilize the whole system.
We’re diving deep into the best EVs that offer this rad tech, looking at what makes them tick, the pros and cons, and what the future holds for V2G.
We’ll break down the current market, looking at manufacturers, models, and prices. Then, we’ll get into the nitty-gritty of the technology itself – how it works, its impact on your battery, and the safety features involved. We’ll also weigh the financial and environmental perks against any potential downsides, and explore the role of V2G in building a more sustainable energy future.
Think of it as your ultimate guide to owning a seriously cool, and possibly profitable, electric car.
Current Market Landscape of V2G EVs
The vehicle-to-grid (V2G) market for electric vehicles (EVs) is still emerging, but it’s showing promising signs of growth. While widespread adoption isn’t here yet, several manufacturers are actively developing and deploying V2G-capable vehicles, paving the way for a future where EVs can actively participate in the energy grid. The current landscape is characterized by a limited number of models, primarily focused on specific markets and applications, but with significant potential for expansion as technology matures and infrastructure develops.The availability of EVs with V2G technology varies considerably across the globe.
Currently, several key players are leading the charge, but the overall market remains relatively niche. Several factors are influencing the pace of adoption, including the cost of V2G technology, the need for supportive grid infrastructure, and consumer awareness. This section will delve into the specifics of the current market, focusing on key manufacturers, pricing, and available features.
Leading Manufacturers and Models
Several automakers are investing in V2G technology, though the number of commercially available V2G EVs remains limited. Nissan, with its Leaf, was an early pioneer, and continues to be a notable player. Other manufacturers are exploring and implementing V2G, but widespread adoption across mainstream models is still some time away. The development and deployment of V2G technology are influenced by factors such as government incentives, grid infrastructure limitations, and consumer demand.
This makes accurate prediction of market share difficult, as the playing field is still dynamic.
V2G EV Pricing and Specifications
Pricing and specifications for V2G EVs vary significantly depending on the manufacturer, model, and included features. The added V2G capability often increases the initial cost of the vehicle compared to standard EVs. Key features beyond the standard EV package typically include a bidirectional onboard charger and compatible software for communication with the grid. Below is a table summarizing some key examples, keeping in mind that the market is rapidly evolving and information may change quickly.
It’s crucial to check directly with manufacturers for the most up-to-date information.
| Manufacturer | Model | Price Range (USD) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nissan | Leaf (some models) | $27,400 – $36,000 (estimated, varies by region and options) | Bidirectional charging, V2G capability (availability varies by region and may require specific upgrades or partnerships) |
| (Add other manufacturers and models here as data becomes available. Information on pricing and availability for V2G-equipped vehicles from other manufacturers is currently limited and often varies by region and specific programs.) |
Technological Aspects of V2G in EVs
Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology represents a significant advancement in the electric vehicle (EV) landscape, transforming EVs from mere consumers of electricity into active participants in the power grid. This bidirectional charging capability opens up exciting possibilities for grid stability, renewable energy integration, and even revenue generation for EV owners. Understanding the underlying technology is crucial to grasping the potential and challenges of V2G.V2G technology fundamentally alters the relationship between EVs and the power grid.
Unlike unidirectional charging, where electricity flows only from the grid to the vehicle, V2G allows for a two-way flow of electricity. This means the EV’s battery can discharge power back into the grid when demand is high or renewable energy generation is abundant, effectively acting as a distributed energy storage resource.
V2G Technologies Employed in EVs
Several technologies enable bidirectional charging in EVs. The most common approaches involve sophisticated power electronics integrated into the onboard charger. These systems manage the complex process of switching between charging and discharging modes, ensuring efficient and safe power transfer. Some manufacturers utilize advanced inverter technology capable of handling both AC and DC power flows, while others employ dedicated V2G converters.
The specific technology used can influence factors like charging speed and overall system efficiency. For instance, some systems prioritize fast charging capabilities, while others focus on maximizing energy transfer efficiency during grid support operations.
Bidirectional Charging Process and Battery Life
The bidirectional charging process involves several steps. First, the EV’s battery management system (BMS) assesses the state of charge (SOC) and determines the available capacity for discharging. Then, communication protocols (like those based on standards like IEEE 1547) establish a connection with the grid operator. Once authorized, the EV’s onboard inverter converts DC battery power to AC power compatible with the grid.
The power is then fed back into the grid through a V2G charging station. This process is carefully managed to avoid over-discharging the battery and to ensure the grid remains stable. While concerns exist about the impact of frequent bidirectional charging on battery lifespan, research suggests that with proper management strategies and advanced BMS algorithms, the degradation is minimal and comparable to the effects of regular charging cycles.
Optimized charging strategies, including limiting the depth of discharge and employing intelligent charging algorithms, can mitigate this impact. For example, studies have shown that carefully managed V2G cycling can extend battery life, particularly when paired with battery thermal management systems.
Safety Mechanisms in V2G Systems
Ensuring grid stability and preventing damage to the EV’s battery are paramount. Several safety mechanisms are incorporated into V2G systems. These include: overcurrent protection, voltage regulation, and sophisticated communication protocols to prevent overloading or instability. Furthermore, the BMS continuously monitors battery parameters (voltage, current, temperature) and shuts down the system if unsafe conditions are detected. These systems are designed to seamlessly integrate with existing grid protection mechanisms and to comply with relevant safety standards, minimizing the risks associated with bidirectional power flow.
The system’s response time to abnormal conditions is critical and needs to be extremely fast to prevent cascading failures. Real-time monitoring and control systems are essential for managing these events efficiently.
Components of a V2G System in an EV
A V2G-capable EV includes several key components: a high-power bidirectional onboard charger, a sophisticated battery management system (BMS), advanced power electronics (inverters), communication modules for grid interaction, and appropriate safety mechanisms (e.g., overcurrent protection, voltage regulation). The bidirectional charger is the heart of the system, capable of both charging and discharging the battery efficiently. The BMS plays a crucial role in monitoring the battery’s health and managing the charging and discharging processes.
The communication modules enable seamless interaction with the grid, allowing for real-time control and monitoring. These components work together to ensure safe and efficient bidirectional power flow. The specific design and configuration of these components vary depending on the vehicle manufacturer and the overall V2G system architecture.
Benefits and Drawbacks of V2G EV Ownership
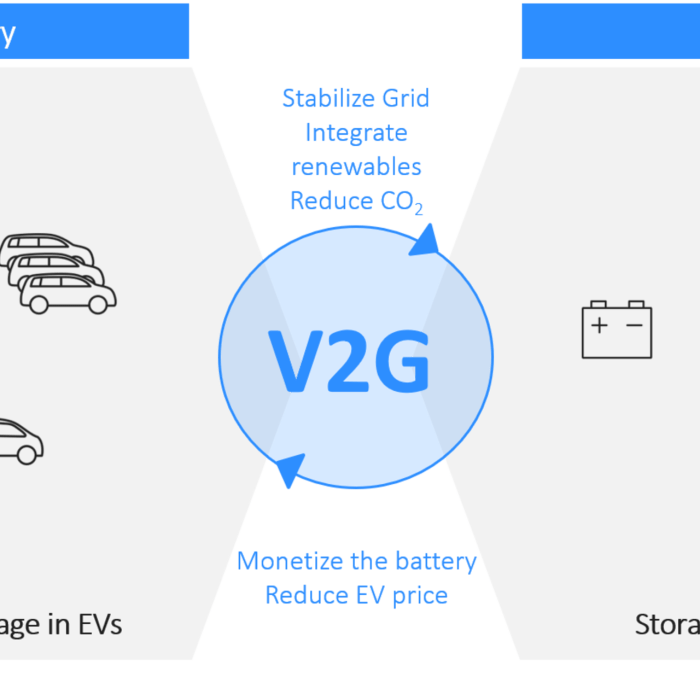
So, you’re thinking about buying an electric vehicle, but you’ve heard about this Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) thing. It sounds cool, but is it worth it? Let’s break down the pros and cons of owning a V2G-capable EV. There are some serious financial and environmental upsides, but also some potential downsides to consider.V2G technology offers a compelling blend of personal and societal benefits.
Essentially, it allows your EV’s battery to feed power back into the electricity grid, creating new revenue streams and enhancing grid stability. However, the technology also introduces some potential drawbacks, primarily related to battery wear and the added complexity of the system. Weighing these factors is crucial for any potential V2G EV owner.
Financial Benefits of V2G EV Ownership
V2G opens up a unique income stream for EV owners. By participating in demand response programs, you can essentially “rent out” your car’s battery capacity to the grid during peak demand periods. This means getting paid for the electricity your car provides, essentially turning your car into a small-scale power plant. The exact amount earned varies based on factors like electricity prices, grid needs, and the capacity of your battery, but several programs offer significant potential for supplementing your income.
For example, some utility companies offer payments based on kilowatt-hours (kWh) supplied, while others use a bidding system, allowing owners to maximize their earnings. Imagine earning extra money while your car is parked! This passive income generation could offset some of the initial higher cost of a V2G-capable vehicle.
So you’re looking at V2G EVs? That’s awesome, but before you dive in, check out the Cheapest states to own an EV in 2025 to see where your savings will really shine. Knowing where EVs are most affordable will help you maximize the return on your investment in a cool V2G-capable ride.
Environmental Benefits of V2G
Beyond the financial perks, V2G contributes significantly to environmental sustainability. By providing power back to the grid during peak demand, V2G reduces the reliance on fossil fuel-powered power plants. This is especially beneficial when renewable energy sources like solar and wind are intermittent; V2G can help stabilize the grid by providing power when renewable sources are low. This improved grid stability leads to a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions and a smoother transition towards a cleaner energy future.
Moreover, V2G can assist in integrating more renewable energy into the grid by providing a buffer against fluctuations in renewable energy production.
Drawbacks and Challenges of V2G Technology
While the advantages are enticing, it’s important to acknowledge potential drawbacks. One major concern is the increased wear and tear on the EV’s battery. Constantly cycling the battery – charging and discharging – can reduce its lifespan compared to a vehicle used solely for transportation. This could lead to premature battery degradation and higher replacement costs in the long run.
Furthermore, the added complexity of V2G systems might increase the risk of technical issues and require more maintenance. Finally, the widespread adoption of V2G faces infrastructural challenges. The grid needs to be adapted to handle the bidirectional flow of electricity, requiring investment in smart grid technologies and compatible charging infrastructure.
Pros and Cons of Owning a V2G-Capable EV
It’s helpful to summarize the key points in a concise list.
The decision to own a V2G-capable EV involves carefully weighing these potential benefits against the associated challenges. Individual circumstances, such as driving habits and electricity prices, will influence the overall cost-benefit analysis.
- Pros:
- Potential for extra income from grid services.
- Contribution to a more sustainable energy system.
- Enhanced grid stability and renewable energy integration.
- Cons:
- Increased wear and tear on the EV battery, potentially shortening its lifespan.
- Higher initial cost of V2G-capable vehicles.
- Potential for increased maintenance and technical issues.
- Limited availability of V2G infrastructure and programs.
Infrastructure and Grid Integration

The widespread adoption of vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology hinges critically on the development of robust and intelligent infrastructure capable of handling the bidirectional flow of electricity between EVs and the power grid. This requires not only advancements in charging stations but also significant upgrades to the grid itself to accommodate the fluctuating power inputs and outputs from numerous V2G-enabled vehicles.Currently, V2G infrastructure development is in its nascent stages globally.
So you’re looking at the best EVs with vehicle-to-grid (V2G) tech? That’s awesome, but before you dive in, think about the long-term battery costs. Check out this article on EV battery leasing options 2025 to see if leasing might be a better fit for your budget. Knowing your battery costs helps you pick the right V2G-capable EV for your needs.
While several pilot projects and small-scale deployments exist in various countries, including the United States, Japan, and several European nations, a truly widespread network is still lacking. Many existing charging stations are unidirectional, only capable of supplying power to EVs, not receiving it. The development of bidirectional chargers is crucial, and these are still relatively expensive and not widely available.
Furthermore, the communication protocols and grid management systems needed to integrate V2G effectively are still under development and standardization.
Current State of V2G Infrastructure Development
The current state of V2G infrastructure is characterized by a patchwork of pilot projects and limited commercial deployments. Many research institutions and private companies are actively involved in developing and testing V2G technologies, but scaling up to a large-scale infrastructure requires significant investment and regulatory support. The limited availability of bidirectional chargers and the lack of standardized communication protocols represent significant barriers to wider adoption.
For example, the Nissan Leaf, one of the earliest EVs with V2G capability, saw limited deployment due to these infrastructure limitations. The focus now is on developing smarter charging stations that can seamlessly integrate with smart grids and handle the complexities of bidirectional power flow.
Role of Smart Grids in Facilitating V2G Adoption
Smart grids play a pivotal role in enabling the widespread adoption of V2G technology. Smart grids utilize advanced sensors, communication networks, and data analytics to optimize energy distribution and improve grid stability. The integration of V2G-capable EVs into a smart grid allows for a more dynamic and responsive system. Smart grid technologies can manage the aggregate power flow from numerous V2G EVs, preventing grid instability and ensuring efficient energy management.
This includes functionalities such as load balancing, peak demand reduction, and frequency regulation, all of which can be significantly enhanced by the flexible power provision of V2G EVs. Essentially, smart grids provide the necessary intelligence and control mechanisms to harness the full potential of V2G technology.
Regulatory and Policy Challenges Related to V2G Integration
The integration of V2G technology into electricity grids faces several regulatory and policy challenges. These include establishing clear standards and regulations for bidirectional chargers, ensuring grid safety and stability with V2G integration, and developing appropriate billing and compensation mechanisms for EV owners who provide grid services. Liability issues in case of grid failures involving V2G EVs also need to be addressed.
Furthermore, policies promoting the development and deployment of V2G infrastructure are crucial for driving innovation and fostering widespread adoption. For example, government incentives or subsidies for the installation of V2G chargers and the development of smart grid technologies could significantly accelerate the process. Lack of clear regulatory frameworks and inconsistent policies across different jurisdictions hinder investment and standardization.
Hypothetical Scenario Illustrating V2G Contribution to a Resilient and Sustainable Energy System
Imagine a scenario where a significant portion of vehicles in a city are V2G-enabled. During peak demand hours, the smart grid can draw power from these EVs, reducing the strain on traditional power plants and minimizing reliance on fossil fuel-based generation. During periods of excess renewable energy generation (e.g., solar power during sunny days), the surplus energy can be used to charge the EVs, storing energy for later use.
In the event of a power outage, these V2G EVs can act as distributed generation sources, providing backup power to critical infrastructure such as hospitals and emergency services, significantly enhancing grid resilience. This scenario highlights how V2G can contribute to a cleaner, more resilient, and sustainable energy future by optimizing energy use, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and improving grid stability.
Future Trends and Innovations in V2G Technology
The future of vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology looks bright, driven by increasing concerns about climate change, grid stability, and the rising adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). We can expect significant advancements in several key areas, leading to wider integration and greater benefits for both consumers and the power grid. The next few years will be pivotal in shaping the landscape of V2G, transforming it from a niche technology to a mainstream component of the energy infrastructure.
Predictions for V2G Growth and Adoption
Several factors point to significant growth in V2G adoption. Government incentives, like tax credits and subsidies for V2G-capable EVs and home charging infrastructure, are likely to play a major role. Furthermore, as battery technology improves and becomes more cost-effective, the barriers to entry for consumers will decrease. We can anticipate a scenario similar to the rapid adoption of solar panels, where initial high costs are followed by a period of decreasing prices and increased accessibility, spurred by economies of scale and technological breakthroughs.
For example, the success of Tesla’s Powerwall, a home battery system, demonstrates the growing consumer interest in energy storage and management, creating a favorable environment for V2G adoption.
Advancements in Battery Technology Enhancing V2G Capabilities
Advancements in battery chemistry, such as solid-state batteries and improved lithium-ion technologies, are crucial for enhancing V2G capabilities. Solid-state batteries, for example, offer the potential for increased energy density, faster charging times, and improved safety compared to current lithium-ion batteries. This translates directly into more frequent and efficient V2G cycles, making EVs more valuable assets for grid services. Furthermore, research into battery management systems (BMS) is focusing on extending battery lifespan and optimizing performance during V2G operations, mitigating concerns about reduced battery longevity.
Companies like Solid Power are already making strides in the development of solid-state battery technology, paving the way for a future where V2G is more practical and less detrimental to the vehicle’s battery health.
Emerging Technologies Improving V2G Efficiency and Safety, Best EVs with vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology
Several emerging technologies promise to enhance the efficiency and safety of V2G systems. Smart grid integration using advanced algorithms and machine learning can optimize energy flow and distribution, maximizing the benefits of V2G while minimizing strain on the grid. Improved communication protocols and cybersecurity measures are also vital to ensure seamless and secure V2G operations. Furthermore, the development of more robust and reliable power electronics, such as advanced inverters, will improve energy conversion efficiency and reduce energy losses during the charging and discharging process.
This is analogous to the improvements seen in solar panel inverters over the years, resulting in higher energy conversion rates.
A Future Scenario with Seamless V2G Integration
Imagine a city where thousands of V2G-enabled EVs are seamlessly integrated into a smart grid. During peak demand hours, these EVs automatically discharge stored energy back to the grid, preventing blackouts and stabilizing the power supply. During off-peak hours, they recharge using renewable energy sources like solar and wind, storing energy for later use. This dynamic energy exchange is managed by an intelligent grid system that optimizes energy flow, ensuring grid stability and minimizing reliance on fossil fuels.
The visual is one of a vibrant, interconnected network where EVs aren’t just vehicles but also active participants in a sustainable energy ecosystem. Residential areas are equipped with smart charging stations, capable of bidirectional energy flow, and the grid operator can tap into the collective energy storage capacity of these EVs to meet fluctuating demand. This scenario is not science fiction; it is a plausible and achievable future if we continue to invest in research and development in V2G technology.
Conclusion: Best EVs With Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) Technology
So, there you have it – the lowdown on the best EVs with V2G technology. From potentially earning extra cash to contributing to a greener planet, the benefits are pretty compelling. While there are still some hurdles to overcome, like infrastructure development and battery wear, the future of V2G looks bright. As more manufacturers jump on board and the tech gets even better, we’re likely to see a major shift in how we power our homes and our cars.
It’s not just about driving; it’s about being part of a smarter, more sustainable energy system – pretty awesome, right?