EV Tax Credits for Leased Vehicles 2025: So you’re thinking about leasing an electric car and snagging those sweet tax breaks? Awesome! But let’s be real, navigating the world of EV tax credits can feel like decoding a government conspiracy. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about the 2025 credits for leased EVs, from eligibility requirements to calculating your potential savings.
We’ll cover the nitty-gritty details so you can confidently drive off into the electric sunset (and save some serious cash).
We’ll explore the ins and outs of the Inflation Reduction Act’s impact, compare leasing to buying, and even throw in some state-level incentives to boost your savings even further. Think of this as your cheat sheet to maximizing your tax refund while going green. Get ready to electrify your wallet!
Eligibility Criteria for EV Tax Credits in 2025
Snagging a sweet EV tax credit in 2025? It’s not as simple as plugging in your car. There are a bunch of rules and regulations you need to know before you even think about filing. This section breaks down the key eligibility requirements, so you can figure out if you’re in the running.
Income Limitations for Leased EVs
The amount of your EV tax credit, or if you even qualify for one, hinges heavily on your Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI). Think of MAGI as your adjusted gross income (AGI) with a few extra tweaks. For 2025, the IRS will likely set specific MAGI thresholds. Exceeding these thresholds could mean a reduced credit or even disqualification.
For example, a single filer might see their credit reduced or eliminated if their MAGI surpasses a certain point, say $300,000. Similarly, married couples filing jointly might face restrictions if their combined MAGI exceeds a higher limit, perhaps $600,000. These numbers are estimates and the exact figures will be released by the IRS closer to tax season.
It’s crucial to check the official IRS guidelines to confirm the exact income limits.
Vehicle Requirements for EV Tax Credits
Beyond your income, the vehicle itself needs to meet certain criteria. First, there’s the Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price (MSRP). The credit might be capped for vehicles exceeding a certain MSRP, incentivizing the purchase of more affordable EVs. Let’s say that cap is set at $80,000 for SUVs and $55,000 for sedans. Anything above those prices might not qualify for the full credit.
Second, where the vehicle is assembled matters. The Inflation Reduction Act prioritizes vehicles assembled in North America to support domestic manufacturing. Importantly, the battery components must also meet certain sourcing requirements, focusing on materials sourced or processed in the US or countries with free trade agreements with the US. Failing to meet these assembly and battery sourcing requirements could disqualify the vehicle.
Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) Thresholds and Credit Amounts
The relationship between your MAGI and the credit amount is directly proportional. Generally, the higher your MAGI, the smaller your credit. Imagine three different taxpayers: Sarah, a single filer with a MAGI of $75,000; David, a single filer with a MAGI of $150,000; and Maria, a single filer with a MAGI of $250,000. Sarah might qualify for the full credit, while David receives a partially reduced credit, and Maria might not qualify at all, depending on the specific thresholds set by the IRS.
Again, these are examples; the actual credit amounts will depend on the official IRS guidelines for 2025.
Comparison: Leased vs. Purchased EVs
It’s important to understand that the eligibility criteria might differ slightly between leasing and purchasing an EV. While the income limits and vehicle requirements largely remain the same, the claim process and potential credit amount may vary.
| Criteria | Leased EV | Purchased EV |
|---|---|---|
| MAGI Limits | Same as purchased EVs; credit amount may be affected. | Same as leased EVs; credit amount may be affected. |
| Vehicle MSRP Limits | Same as purchased EVs. | Same as leased EVs. |
| Assembly Location | Must meet North American assembly requirements. | Must meet North American assembly requirements. |
| Claim Process | More complex; lessor may claim the credit and pass some or all of it to the lessee. | Relatively straightforward; claimed by the purchaser. |
Calculating the Tax Credit Amount for Leased EVs
Figuring out the exact amount of your EV tax credit when leasing can seem tricky, but it’s actually a pretty straightforward calculation once you understand the basics. The credit isn’t based on the total lease cost, but rather on the vehicle’s price and the portion of that price you’re effectively buying through your lease payments.The credit is calculated using a formula that considers the vehicle’s Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price (MSRP) and the lease terms.
The exact formula might change slightly from year to year depending on the specifics of the tax credit legislation, so it’s always a good idea to check the latest IRS guidelines. However, the core concept remains consistent.
Credit Calculation Formula and Application
The tax credit is generally calculated as a percentage of the vehicle’s MSRP. This percentage depends on several factors, including the vehicle’s battery capacity and whether it meets other requirements (like being assembled in North America). The credit isn’t a direct reduction of your lease payments; instead, it reduces your overall tax liability. You claim the credit on your tax return, and it results in either a reduction of your tax owed or a refund if the credit exceeds your tax liability.
Think of it as getting a discount on your taxes rather than a discount on your lease.
Impact of Lease Terms on Credit Amount
Lease terms like length and mileage don’t directly affect the
So, 2025 EV tax credits for leased vehicles are looking pretty sweet, right? But, before you go nuts trying to snag one, remember that your driving record matters – check out this article on whether a speeding ticket increases insurance rates: Does a speeding ticket increase insurance rates?. High insurance could eat into those savings, so keep your foot off the gas! Getting that EV tax credit is definitely worth it, but smart driving is even better.
- calculation* of the tax credit amount. The calculation is based solely on the MSRP and the applicable percentage determined by the vehicle’s specifications. However, lease terms can indirectly influence the
- overall cost* and your potential savings. A longer lease term might lower your monthly payments, but it also means you’ll pay more overall for the vehicle’s use. Similarly, a higher mileage allowance will likely increase your monthly payments. These factors don’t change the tax credit itself, but they influence how much you ultimately benefit from it in relation to your total lease expense.
Step-by-Step Credit Calculation Example
Let’s say you lease a hypothetical EV with an MSRP of $40,000. The current tax credit offers a 30% credit for vehicles meeting specific requirements. This is a simplified example; the actual percentage and eligibility criteria will vary.
So, you’re thinking about snagging an EV and leasing it? Sweet! Remember to check out those 2025 EV tax credits. And, since you’ll be leasing, securing the right insurance is key – check out this helpful guide on Best insurance for leased cars 2025 to make sure you’re covered. Getting the best insurance will help you maximize those EV tax credit savings!
- Determine the MSRP: The MSRP of the vehicle is $40,000.
- Find the Applicable Credit Percentage: Let’s assume the vehicle qualifies for a 30% credit.
- Calculate the Credit Amount: Multiply the MSRP by the credit percentage: $40,000 – 0.30 = $12,000.
- Claim the Credit: You would claim this $12,000 credit on your federal income tax return using the appropriate IRS forms. This could result in a direct reduction of your taxes owed or a refund if the credit exceeds your tax liability.
Remember, this is a simplified illustration. Consult the IRS website or a tax professional for the most up-to-date information and to ensure you accurately calculate your tax credit based on your specific vehicle and lease agreement.
Comparison with Tax Credits for Purchased EVs: EV Tax Credits For Leased Vehicles 2025
So, you’re thinking about going electric, but the whole tax credit thing is a bit confusing, right? Especially when you’re trying to decide between leasing and buying. Let’s break down how the 2025 EV tax credits differ for leased versus purchased vehicles. Understanding these differences will help you make the most financially savvy decision for your next ride.The main difference boils down towho* claims the credit.
With a purchased EV, you, the buyer, claim the credit when you file your taxes. With a leased EV, the credit typically goes to the leasing company, who might then pass on some or all of the savings to you in the form of a lower monthly payment or other incentives. This isn’t always guaranteed, though, so it’s crucial to clarify the terms with your leasing company upfront.
The amount of the credit itself can also vary depending on the vehicle’s price, battery capacity, and where it was manufactured.
Eligibility Requirements for Leased vs. Purchased EVs
Eligibility for the EV tax credit, whether leasing or buying, hinges on several factors. These include the vehicle’s price, battery sourcing, and the buyer/lessee’s income. For purchased vehicles, the buyer must meet specific income limits to qualify. For leased vehicles, the requirements often mirror those for purchased vehicles, but the leasing company needs to meet the criteria to claim the credit on their tax return.
One key difference is that the modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) limits might be applied differently. For example, for a purchased EV, the MAGI limit applies to the individual or household filing the return, while for a leased vehicle, it might apply to the leasing company’s overall income. It’s important to note that the specific rules and income limits are subject to change, so it’s always best to consult the most up-to-date IRS guidelines.
Calculation Methods for Leased vs. Purchased EVs
The calculation of the tax credit amount differs slightly depending on whether you’re leasing or buying. For purchased EVs, the credit is typically calculated based on the vehicle’s sale price, up to a certain limit. The calculation might also incorporate factors like battery capacity and domestic manufacturing. For leased vehicles, the credit calculation is more complex, and it’s often the leasing company that performs the calculation.
They might use a different formula, factoring in the lease term, residual value, and other variables. The credit amount might then be reflected in a reduced lease payment or as a separate rebate. The exact calculation method used by leasing companies can vary widely, highlighting the need for transparency in lease agreements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Leasing vs. Purchasing
Let’s summarize the key differences in a bullet point list:
- Purchased EVs:
- Advantage: You directly receive the full tax credit amount, potentially leading to significant savings.
- Advantage: You own the vehicle at the end of the loan term.
- Disadvantage: You are responsible for maintenance, repairs, and potential resale value depreciation.
- Disadvantage: Higher upfront costs compared to leasing.
- Leased EVs:
- Advantage: Lower monthly payments due to potential credit pass-through from the leasing company.
- Advantage: Less responsibility for maintenance and repairs (often covered by the lease).
- Disadvantage: You don’t own the vehicle at the end of the lease term.
- Disadvantage: The actual amount of the credit benefit might be less than for a purchased vehicle, depending on the leasing company’s practices.
Impact of the Inflation Reduction Act on Leased EV Credits
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) significantly revamped the landscape of EV tax credits, introducing changes that directly impact those leasing electric vehicles. Previously, leasing an EV often meant missing out on the full benefit of these credits. The IRA, however, introduced provisions designed to make the credits more accessible to leaseholders.The IRA’s key changes center around expanding eligibility requirements and clarifying the process for claiming credits on leased vehicles.
Before the IRA, many hurdles existed, limiting the accessibility of the credits for lessees. Now, the credit is more directly tied to the vehicle itself, rather than solely the purchaser. This shift has opened up the credit to a wider range of consumers.
IRA Provisions Affecting Leased EV Credits, EV tax credits for leased vehicles 2025
The IRA established a clean vehicle credit, replacing the previous system. This credit is available for both new and used clean vehicles, including EVs, with specific requirements for each. For leased vehicles, a crucial provision allows themanufacturer* to claim the credit, which is then passed on to the lessee in the form of a reduced monthly payment or other incentives.
This contrasts with the previous system where the credit was largely limited to the vehicle purchaser. This manufacturer claim process is a key differentiator and is designed to simplify access for lessees.
Eligibility Requirements Under the IRA
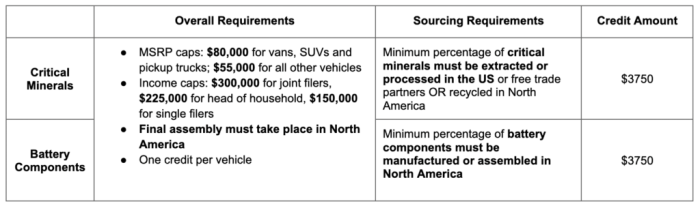
The IRA imposes several eligibility requirements for the clean vehicle credit, regardless of whether the vehicle is purchased or leased. These include limitations on vehicle MSRP, requirements for final assembly in North America, and income limitations for the buyer/lessee. For example, the MSRP cap affects the maximum credit amount. Furthermore, the vehicle must meet certain battery sourcing and critical mineral requirements to qualify.
The final assembly location requirement is another key factor, aiming to boost domestic manufacturing. These requirements, which were largely absent or less stringent in previous years, are crucial for determining eligibility under the IRA.
Credit Amount Calculation for Leased EVs
The credit amount calculation for leased EVs under the IRA is indirect. The manufacturer claims the credit based on the vehicle’s specifications and meets the aforementioned requirements. The manufacturer then incorporates this credit into the lease terms, resulting in a lower monthly payment for the lessee. The actual credit amount isn’t directly calculated by the lessee but is reflected in the reduced lease cost.
This indirect approach simplifies the process for the consumer while still achieving the goal of providing a financial incentive for clean vehicle adoption.
Changes Compared to Previous Years
Before the IRA, the tax credit landscape for leased EVs was considerably less favorable. The credits were often significantly limited or inaccessible for lessees. The IRA represents a major shift, offering a much clearer path for consumers leasing EVs to benefit from the tax incentives. The previous system often relied on complex calculations and interpretations, leading to uncertainty and limited access.
The IRA’s focus on the manufacturer claiming the credit and then incorporating it into the lease simplifies this process dramatically, leading to greater accessibility and transparency.
State-Level Incentives for Leased EVs
Securing an electric vehicle (EV) can be a significant financial undertaking, even with the federal tax credit. Fortunately, many states recognize the environmental and economic benefits of EV adoption and offer additional incentives to sweeten the deal, particularly for those leasing rather than purchasing. These state-level programs can significantly reduce the overall cost of leasing an EV, making them a more accessible option for a wider range of consumers.
The specifics of these incentives vary considerably, so it’s crucial to check your state’s regulations.State-level incentives for leased EVs are often less publicized than those for purchased vehicles, but they can be just as impactful. These incentives generally take the form of tax credits, rebates, or exemptions from sales tax. Some states might even offer combined incentives, layering state benefits on top of the federal tax credit.
Understanding these opportunities can be key to maximizing your savings when leasing an electric vehicle.
Examples of State Incentives for Leased EVs
Several states actively promote EV adoption through programs that benefit lessees. For example, some states offer direct rebates on the lease price of a qualifying EV. Others might provide a tax credit based on a percentage of the lease payments or the vehicle’s purchase price (even if leased). These incentives frequently have eligibility requirements, such as vehicle type, income limits, or residency stipulations.
It’s essential to review the specific rules of each program to ensure eligibility. For instance, California’s Clean Vehicle Rebate Project (CVRP) has previously offered rebates on leased EVs, though the specific details and availability change frequently. Similarly, New York offers various programs that might include benefits for leased EVs, although specific programs and eligibility requirements should be checked directly with the state.
Summary of State Incentives
The availability and details of state-level incentives are constantly evolving. The following table provides a snapshot of potential incentives; however, it’s imperative to check with the relevant state agency for the most current and accurate information before making any purchasing or leasing decisions. Remember, eligibility requirements and benefit amounts are subject to change.
| State | Incentive Type | Eligibility Criteria (Example) | Benefit Amount (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | Clean Vehicle Rebate Project (CVRP) | Vehicle must meet certain emission standards, income limits may apply, residency requirement. | Varies, check CVRP website for current amounts. |
| New York | Various State Programs (Check NYSDEC website) | Eligibility varies widely by program; income limits, vehicle type, and residency requirements often apply. | Varies significantly depending on the specific program. |
| Colorado | State Tax Credit (Check Colorado Department of Revenue) | Eligibility may depend on vehicle type, income level, and other factors. | Check the Colorado Department of Revenue website for current information. |
| Other States | Various Programs | Check your state’s Department of Motor Vehicles or equivalent agency for details. | Varies widely. |
Future Outlook of EV Tax Credits for Leased Vehicles
Predicting the future of EV tax credits for leased vehicles is tricky, given the rapidly evolving landscape of government policy and the EV market itself. However, based on current trends and the overarching goals of the Inflation Reduction Act, we can make some educated guesses about potential changes beyond 2025. The overarching aim seems to be a continued push towards domestic manufacturing and a gradual phasing out of subsidies as the EV market matures.The program’s evolution will likely hinge on several key factors.
The success of the current initiatives in boosting domestic EV production and sales will heavily influence future policy decisions. If the current incentives prove highly effective, we might see a gradual scaling back of the program, potentially with a shift in focus towards other aspects of the EV ecosystem, like charging infrastructure or battery technology. Conversely, if the market doesn’t respond as hoped, we might see extensions or even expansions of the current credit structure.
Projected Changes in Credit Structure
Several scenarios are plausible. One possibility is a gradual reduction in the credit amount over time, perhaps tied to increasing EV sales or achieving specific targets for domestic manufacturing. Another scenario could involve a shift in eligibility criteria, potentially focusing on vehicles with higher domestic content or specific battery chemistries deemed more sustainable. For example, we might see increased incentives for EVs using domestically sourced battery materials, mirroring similar trends in other sectors.
Think of the current push for American-made solar panels – a similar logic could be applied to EV batteries. The credit might also become more targeted towards lower-income consumers or those in specific geographic areas to address equity concerns. A final possibility is the complete phasing out of the program once the EV market reaches a certain level of maturity and market penetration.
This would parallel the historical trajectory of other government incentive programs designed to stimulate nascent industries.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and vehicle design will inevitably shape the future of EV tax credits. For example, the development of solid-state batteries could significantly alter the eligibility criteria, potentially leading to higher credits for vehicles using this technology due to their improved performance and safety characteristics. Similarly, advancements in fast-charging technology could influence the design of future incentive programs, perhaps by rewarding vehicles with faster charging capabilities.
This is analogous to how fuel efficiency standards have historically influenced vehicle design and the subsequent availability of tax credits. The development of more sustainable and ethically sourced battery materials will also likely play a role, potentially leading to bonus credits for vehicles using these materials.
Influence of Market Dynamics
The overall health and competitiveness of the EV market will play a crucial role. If the EV market experiences rapid growth and becomes increasingly price-competitive, the need for significant government subsidies might diminish, leading to a reduction or elimination of the tax credit program. Conversely, if the market faces challenges, such as supply chain disruptions or a lack of consumer demand, the government might extend or expand the credit program to stimulate growth.
Consider the impact of the semiconductor shortage on the auto industry – similar supply chain issues could necessitate continued or expanded government support for the EV sector.
Illustrative Examples of Lease Agreements and Credit Calculations
Let’s walk through a hypothetical lease agreement and demonstrate how the 2025 EV tax credit calculation works for leased vehicles. Understanding this process is crucial for both lessees and leasing companies. This example uses simplified figures for clarity; real-world calculations may involve more nuanced factors.
The following example illustrates a lease agreement and the subsequent tax credit calculation. Remember that actual credit amounts will depend on the specifics of your lease and vehicle.
Sample Lease Agreement Details
This example uses a fictional lease agreement for a 2025 eligible electric vehicle.
Vehicle: “EcoMotion X” Electric SUV
Lease Term: 36 months
Monthly Payment: $700
MSRP (Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price): $50,000
Residual Value (Value of the vehicle at the end of the lease): $25,000
Lease Acquisition Fee: $500
Total Lease Payments (excluding acquisition fee): $25,200 ($700/month
– 36 months)
Total Lease Cost (including acquisition fee): $25,700
Step-by-Step Tax Credit Calculation
The calculation is based on the modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) and other requirements set by the Inflation Reduction Act. For this example, we’ll assume the lessee meets all eligibility requirements. The key factor is the total lease cost, which is used to determine the credit amount.
Step 1: Determine the eligible lease cost. This typically involves the total lease payments (excluding any fees not directly related to the lease itself) plus the acquisition fee. In this case, the eligible lease cost is $25,700.
Step 2: Apply the applicable percentage. The percentage applied to the eligible lease cost to determine the credit amount varies depending on the vehicle’s MSRP and other factors. Let’s assume for this example that the applicable percentage is 30% (this is a hypothetical percentage and may vary).
Step 3: Calculate the tax credit amount. Multiply the eligible lease cost by the applicable percentage. In this case: $25,700
– 0.30 = $7710.
Visual Representation of Tax Credit Calculation
Here’s a text-based representation of the calculation:
Eligible Lease Cost: $25,700
Applicable Percentage: 30%
----------------------------------
Tax Credit Amount: $7,710
It’s important to note that this is a simplified example. The actual calculation might involve adjustments for factors such as the vehicle’s battery capacity, final sale price, and other lease terms.
Always consult the official IRS guidelines and your tax professional for the most accurate calculation for your specific situation.
Conclusion

Leasing an EV in 2025 could mean some hefty tax savings, but the rules are complex. Remember, eligibility hinges on factors like your income, the car’s price and origin, and the specifics of your lease agreement. This guide has equipped you with the knowledge to navigate the process, but remember to double-check the details with a tax professional or the IRS to ensure you’re maximizing your benefits.
Happy driving (and happy saving!).









