Average cost of car maintenance per year? Yeah, that’s a biggie. We’re talking everything from routine oil changes to those surprise “oh crap” repair bills. This isn’t just about throwing money at your car; it’s about understanding what factors influence those costs, how much you should realistically budget, and how to maybe, just maybe, save a few bucks along the way.
Think of this as your survival guide to keeping your ride running smoothly (and your wallet a little less stressed).
We’ll break down the typical costs, looking at things like the type of car you drive, how old it is, and even where you live. We’ll also explore the DIY vs. pro mechanic debate – are you handy enough to tackle some repairs yourself, or is it better to leave it to the experts? By the end, you’ll have a much clearer picture of what to expect and how to make smart decisions about your car’s upkeep.
Factors Influencing Yearly Car Maintenance Costs
Keeping your car in tip-top shape involves more than just filling the tank. Annual maintenance costs can vary wildly, depending on several key factors. Understanding these factors can help you budget effectively and avoid unexpected expenses. This section delves into the major influences on your yearly car maintenance bill.
Top Five Factors Impacting Annual Car Maintenance Expenses
Several key factors significantly impact the amount you’ll spend on car maintenance each year. These factors interact in complex ways, meaning that a change in one can significantly affect the others. For example, driving habits directly influence the frequency of needed repairs, and vehicle type affects the cost of parts and labor.
| Factor | Description | Cost Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Age | Older vehicles require more frequent and extensive repairs due to increased wear and tear. | High | A 10-year-old car might need a new transmission, costing thousands, while a newer car might only require routine fluid changes. |
| Driving Habits | Aggressive driving, frequent short trips, and neglecting routine maintenance contribute to faster wear and tear. | Medium | Someone who frequently accelerates and brakes harshly will likely need brake pad replacements sooner than someone with a gentler driving style. |
| Vehicle Type | SUVs and trucks generally have higher maintenance costs due to larger engines, more complex systems, and more expensive parts. | High | Replacing tires on a large truck will cost significantly more than replacing tires on a compact sedan. |
| Location | Labor costs and parts prices vary by region. Areas with higher costs of living tend to have higher maintenance costs. | Medium | A routine oil change in a major metropolitan area might cost more than in a rural town. |
| Maintenance Schedule Adherence | Regular maintenance, following the manufacturer’s recommended schedule, helps prevent major, costly repairs down the line. | Low | Regular oil changes can prevent engine damage, saving thousands in potential repair costs. |
Maintenance Costs for Different Car Types
The type of vehicle you own significantly influences your maintenance costs. Sedans, with their smaller engines and simpler designs, typically have lower maintenance costs compared to SUVs and trucks. SUVs, due to their larger size and often more powerful engines, require more frequent and expensive repairs. Trucks, especially heavy-duty models, have the highest maintenance costs due to their robust engines, larger components, and more frequent wear and tear on parts like tires and brakes.
For example, a simple brake job on a compact sedan might cost a few hundred dollars, while the same job on a heavy-duty pickup truck could easily exceed $1000.
Impact of Vehicle Age on Maintenance Costs
As vehicles age, maintenance costs inevitably increase. This is primarily due to increased wear and tear on various components. Older cars are more prone to needing major repairs, such as engine overhauls, transmission replacements, or suspension work, which can be very expensive. For instance, a relatively new car might only need routine maintenance like oil changes and tire rotations, costing a few hundred dollars annually.
However, a ten-year-old car might require significant repairs, potentially costing thousands of dollars per year. The cost of parts can also increase with age, as parts for older models might be harder to find and more expensive.
Breakdown of Typical Maintenance Costs
So, you’re trying to budget for car maintenance? It’s a tricky thing, but understanding the typical costs involved can help you plan ahead and avoid nasty surprises. This breakdown will give you a realistic picture of what to expect, factoring in routine upkeep, necessary repairs, and those unexpected emergencies. Remember, these are averages, and your actual costs will depend on your vehicle, driving habits, and a little bit of luck (or bad luck!).
Predicting exact car maintenance costs is tough because it varies so much based on factors like vehicle age, make and model, driving habits, and even where you live. However, we can break down the typical costs into three main categories to give you a better idea.
Routine Maintenance Costs
Routine maintenance covers the regular tasks you should perform to keep your car running smoothly. These are preventative measures that ultimately save you money in the long run by preventing more costly repairs down the road. Neglecting these can lead to bigger, more expensive problems later.
So, you’re trying to budget for that average yearly car maintenance cost, right? It’s tough to predict, but unexpected repairs can really throw things off. For example, a failing alternator can be a huge headache, and if you’re seeing weird electrical issues, check out this article on Symptoms of a bad alternator diode before that small problem turns into a huge expense.
Getting a handle on potential problems like that helps keep your overall yearly maintenance costs more manageable.
- Oil Changes: $50 – $100 per change. Frequency depends on your vehicle and driving habits; usually every 3,000-7,500 miles. Synthetic oil is more expensive but can last longer.
- Tire Rotations & Balancing: $50 – $100. Ideally every 5,000-7,500 miles to ensure even tire wear.
- Fluid Top-offs (Coolant, Brake Fluid, Power Steering Fluid): $20 – $50. Check and top off fluids as needed, usually annually or every other year.
- Air Filter Replacement: $20 – $50. Every 12,000-15,000 miles or as needed.
- Other Inspections: $50 – $150. Annual inspections cover things like belts, hoses, and other components, often done in conjunction with an oil change.
Repair Costs
Repairs address problems that arise from wear and tear or previous damage. These are generally more expensive than routine maintenance and can vary greatly depending on the severity of the issue.
So, figuring out the average cost of car maintenance per year is kinda a crapshoot, right? It depends on a lot of factors, but a big one is brake pads. If you’re driving a 2025 Toyota Camry, you might want to check out this guide for Best brake pads for Toyota Camry 2025 to keep those replacement costs down.
Replacing them proactively can actually save you money in the long run and help keep your yearly maintenance budget more predictable.
- Brake Pad Replacement: $100 – $400. Frequency varies depending on driving habits, typically every 25,000-70,000 miles.
- Battery Replacement: $100 – $300. Every 3-5 years, depending on the battery and climate.
- Wiper Blade Replacement: $20 – $50 per set. As needed, usually annually or every other year.
- Suspension System Repairs: $300 – $1000+. This can vary significantly depending on the components needing repair and the vehicle.
Unexpected Issues
These are the curveballs – the unforeseen breakdowns or accidents that can significantly impact your annual maintenance budget. Setting aside a contingency fund is crucial to handle these situations.
- Flat Tire Repair/Replacement: $50 – $200+. This depends on the severity of the damage and if a tire needs to be replaced entirely.
- Major Mechanical Repairs (Engine, Transmission): $1000+. These are significant expenses, and often unpredictable.
- Accident-Related Repairs: Varies greatly depending on the extent of the damage. Insurance typically covers much of this, but deductibles apply.
Mileage’s Impact on Maintenance
Higher mileage generally means more frequent maintenance. For instance, someone driving 15,000 miles a year will need oil changes more often than someone driving 5,000 miles a year. Similarly, brake pads wear out faster with more frequent braking, and tires experience more wear and tear with higher mileage. Consider a scenario where one driver logs 10,000 miles annually and another driver logs 25,000.
The higher-mileage driver will likely need twice as many oil changes and potentially quicker tire and brake pad replacements.
Average Costs for Common Maintenance Procedures
The following table provides a general idea of average costs for some common maintenance procedures across different vehicle types. These are estimates, and actual costs may vary based on location, specific vehicle model, and the shop you choose.
| Procedure | Small Sedan | Mid-Size SUV | Full-Size Truck |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil Change (Conventional) | $40-$60 | $60-$80 | $80-$100 |
| Oil Change (Synthetic) | $70-$100 | $90-$120 | $120-$150 |
| Tire Rotation & Balancing | $40-$60 | $50-$70 | $60-$80 |
| Brake Pad Replacement (Front) | $150-$300 | $200-$400 | $250-$500 |
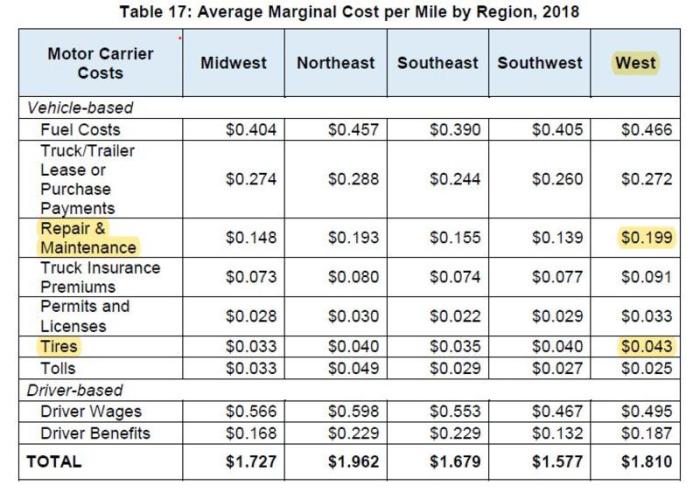
Regional Variations in Maintenance Costs
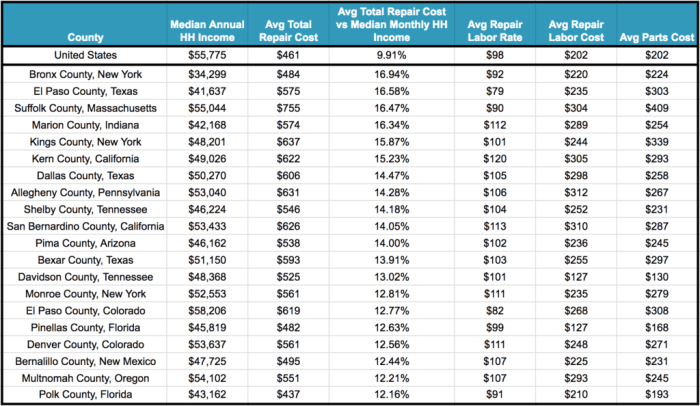
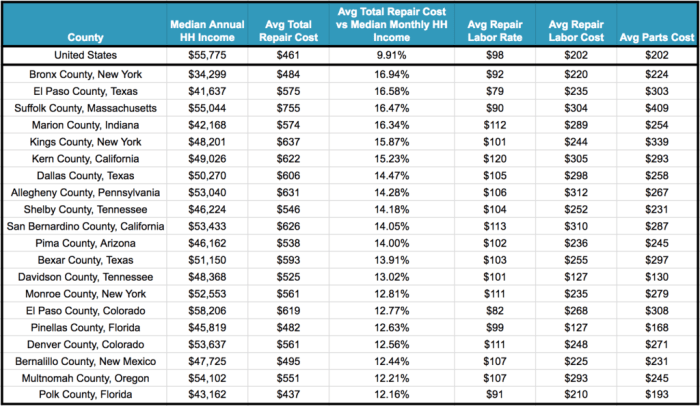
Geographical location significantly impacts the yearly cost of car maintenance. Factors like labor rates, the availability and cost of parts, and even the climate all play a role in determining how much you’ll spend keeping your car in top shape. These regional differences can be substantial, leading to considerable variations in overall maintenance expenses across the country.
Labor Costs and Parts Availability
Labor costs are a major driver of regional differences in car maintenance. Mechanic wages vary considerably across the country, influenced by factors such as local cost of living, unionization, and market demand for skilled automotive technicians. Areas with a high cost of living, like major metropolitan areas on the coasts, tend to have higher labor rates. For example, a simple oil change might cost $75 in a major city like New York City, while the same service might cost only $50 in a smaller town in the Midwest.
Furthermore, the availability of parts also contributes to regional variations. Parts are often more expensive in areas with limited competition or where shipping costs are high. Rural areas, for instance, might experience higher prices for parts due to longer shipping distances and fewer local suppliers.
Regional Comparison of Maintenance Costs
Let’s compare maintenance costs in three distinct regions: the Northeast, the South, and the West Coast. The Northeast, encompassing states like New York, Massachusetts, and Connecticut, generally features higher labor costs and a higher density of specialized repair shops, often leading to higher overall maintenance expenses. The South, including states like Texas, Georgia, and Florida, typically sees lower labor rates but might experience variations based on urban vs.
rural location. The West Coast, with states like California, Oregon, and Washington, presents a mixed bag. While major metropolitan areas like Los Angeles and San Francisco have high labor costs, more rural areas might have lower rates. However, the high cost of living in many West Coast areas often translates to higher overall expenses.
Illustrative Bar Graph of Yearly Maintenance Costs
Imagine a bar graph showing average yearly maintenance costs. The horizontal axis represents the three regions (Northeast, South, West Coast). The vertical axis represents the average yearly cost in US dollars. The bar representing the Northeast would be the tallest, reflecting the higher average cost. The bar for the South would be shorter than the Northeast’s, indicating a lower average cost.
The West Coast bar would fall somewhere in between, showcasing a moderate average cost due to the regional variations within the region. The exact heights of the bars would depend on specific data from reputable sources, but the general trend would consistently show the Northeast having the highest costs, followed by the West Coast, and then the South.
DIY vs. Professional Maintenance: Average Cost Of Car Maintenance Per Year
Deciding between tackling car maintenance yourself or entrusting it to professionals is a significant choice impacting both your wallet and your time. The best approach depends on your mechanical aptitude, available tools, and the specific task at hand. Weighing the pros and cons of each method carefully will lead to the most cost-effective and efficient solution for your individual circumstances.DIY car maintenance offers the potential for substantial cost savings, but it also requires time, skill, and the investment in tools.
Professional maintenance, while more expensive, provides peace of mind, expertise, and often a warranty on the performed work.
Cost Comparison: DIY vs. Professional Maintenance
The cost difference between DIY and professional maintenance can be dramatic, depending on the complexity of the task. Simple jobs like changing your oil might save you $50-$100 compared to a professional shop. However, more complex repairs, such as engine work or transmission issues, are best left to professionals due to the specialized tools and expertise required. Attempting complex repairs without the proper knowledge can lead to further damage and significantly higher costs in the long run.
For instance, a simple oil change might cost $30-$50 in parts at an auto parts store if you do it yourself, compared to $75-$150 at a professional shop. However, a major engine repair could cost thousands of dollars at a shop, while attempting it yourself could lead to irreversible damage and far exceed that cost.
Suitable DIY Maintenance Tasks
Many routine maintenance tasks are well-suited for DIY enthusiasts. These typically involve straightforward procedures with readily available instructions and tools. Examples include changing the oil and filter, replacing wiper blades, topping off fluids (like coolant, brake fluid, and power steering fluid), rotating tires, and replacing air filters. These tasks generally require minimal specialized tools and knowledge, making them accessible to most car owners.
The key is to have the right tools, follow clear instructions, and take your time. Rushing can lead to mistakes.
Maintenance Tasks Best Left to Professionals
More complex repairs and maintenance tasks should be left to qualified mechanics. These include brake repairs (especially involving ABS systems), timing belt replacement, major engine repairs, transmission work, electrical system repairs, and suspension work. These tasks often require specialized tools, diagnostic equipment, and extensive knowledge of automotive systems. Improperly performing these tasks can lead to significant safety hazards and costly repairs.
For example, attempting a timing belt replacement without the proper knowledge and tools could result in serious engine damage.
Potential Cost Savings of DIY Maintenance
The potential cost savings of DIY maintenance are substantial, especially when considering the cumulative cost of regular maintenance over the lifespan of a vehicle. However, it’s crucial to factor in the initial investment in tools. A basic set of tools, including a socket wrench set, screwdrivers, and a jack, can cost several hundred dollars. Additionally, you need to account for the cost of parts and materials.
Despite the upfront costs, the long-term savings can be considerable. For example, consistently changing your own oil can save you hundreds of dollars annually, easily offsetting the initial tool investment.
Step-by-Step Guide: Changing Your Oil, Average cost of car maintenance per year
Changing your oil is a fundamental DIY maintenance task. Before you begin, consult your owner’s manual for specific recommendations on oil type and quantity. Here’s a basic guide:
- Gather your supplies: new oil (check your owner’s manual for the correct type and amount), new oil filter, oil filter wrench, wrench for your drain plug, drain pan, funnel, jack, jack stands (crucial for safety!), rags or paper towels.
- Warm up your engine for a few minutes to thin the oil.
- Securely jack up your vehicle and place it on jack stands. Never work under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
- Locate the oil drain plug underneath the engine. Position your drain pan underneath.
- Carefully loosen and remove the drain plug, allowing the old oil to drain completely. This may take 15-20 minutes.
- Once drained, replace the drain plug, tightening it securely but not over-tightening.
- Locate the oil filter. Use the oil filter wrench to remove the old filter.
- Lightly lubricate the rubber gasket on the new oil filter with fresh oil.
- Install the new oil filter by hand, tightening it according to the manufacturer’s instructions (usually about ¾ to 1 full turn after the gasket contacts the engine).
- Locate the oil fill cap (usually marked with an oil can symbol). Remove the cap.
- Using a funnel, carefully pour the correct amount of new oil into the engine.
- Replace the oil fill cap.
- Lower your vehicle and check the oil level using the dipstick. Add more oil if necessary to reach the “full” mark.
- Start the engine and let it run for a few minutes. Check for any leaks.
- Dispose of the old oil and filter properly at a designated recycling center.
Strategies for Reducing Car Maintenance Costs
Keeping your car in tip-top shape doesn’t have to break the bank. By implementing smart strategies and prioritizing preventative maintenance, you can significantly reduce your annual car maintenance expenses and extend the life of your vehicle. This section Artikels practical steps you can take to achieve substantial savings.
Regular maintenance is key to preventing costly repairs down the line. Ignoring small issues can quickly escalate into major problems, resulting in significantly higher repair bills. Proactive maintenance not only saves money but also enhances your vehicle’s safety and performance.
Regular Maintenance Schedules and Their Impact on Preventing Costly Repairs
Sticking to a regular maintenance schedule, as Artikeld in your owner’s manual, is the single most effective way to reduce long-term maintenance costs. This typically involves routine checks like oil changes, tire rotations, fluid top-offs, and filter replacements. By addressing these items proactively, you prevent minor issues from becoming major headaches (and expenses). For example, neglecting an oil change can lead to engine damage costing thousands of dollars, whereas a timely oil change costs a fraction of that.
Similarly, ignoring worn brake pads can lead to rotor damage, a much more expensive repair.
Benefits of Purchasing an Extended Warranty and Mitigation of Unexpected Repair Expenses
An extended warranty, while an upfront cost, can offer significant protection against unexpected major repairs. Consider the cost-benefit analysis. A relatively small annual payment for an extended warranty can potentially save you thousands of dollars on repairs that fall outside of your standard warranty. For example, if your transmission fails after your standard warranty expires, the repair cost could easily exceed the cost of the extended warranty.
However, it’s crucial to carefully review the terms and conditions of any extended warranty before purchasing to understand exactly what’s covered and what’s excluded.
Five Practical Strategies for Reducing Annual Car Maintenance Costs
Here are five practical strategies you can implement to significantly reduce your annual car maintenance costs:
- Perform basic maintenance yourself: Simple tasks like checking fluids, changing air filters, and washing your car can easily be done at home, saving you labor costs. This requires minimal tools and a bit of time, but the savings can add up quickly.
- Shop around for parts and services: Don’t automatically go to the dealership for repairs. Independent mechanics often offer competitive pricing and quality service. Compare prices from multiple sources before committing to a repair.
- Use high-quality parts: While cheaper parts might seem appealing, investing in higher-quality parts can lead to longer lifespan and fewer replacements down the road. This upfront investment often translates into long-term savings.
- Drive carefully: Aggressive driving habits, such as hard braking and rapid acceleration, put extra stress on your vehicle’s components, leading to increased wear and tear and more frequent repairs. Smooth driving extends the life of your car and reduces maintenance needs.
- Keep detailed records: Maintaining a log of all maintenance performed, including dates, services, and costs, helps you track expenses, identify potential problems early, and avoid unnecessary repairs.
Final Conclusion
So, there you have it – a pretty comprehensive look at the average yearly cost of keeping your car in tip-top shape. From understanding the major cost drivers to exploring DIY options and money-saving strategies, we’ve covered a lot of ground. Remember, regular maintenance is key to preventing costly repairs down the line. Knowing what to expect and planning ahead will help keep your car running smoothly and your bank account a little happier.
Now go forth and conquer those car maintenance challenges!